Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) features a branched molecular structure that gives it flexibility, making it ideal for packaging films and containers. High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) has a linear structure with minimal branching, resulting in higher strength and rigidity, commonly used in pipes, bottles, and toys. Both plastics are recyclable and resistant to moisture, but HDPE offers better chemical resistance and durability.
Table of Comparison
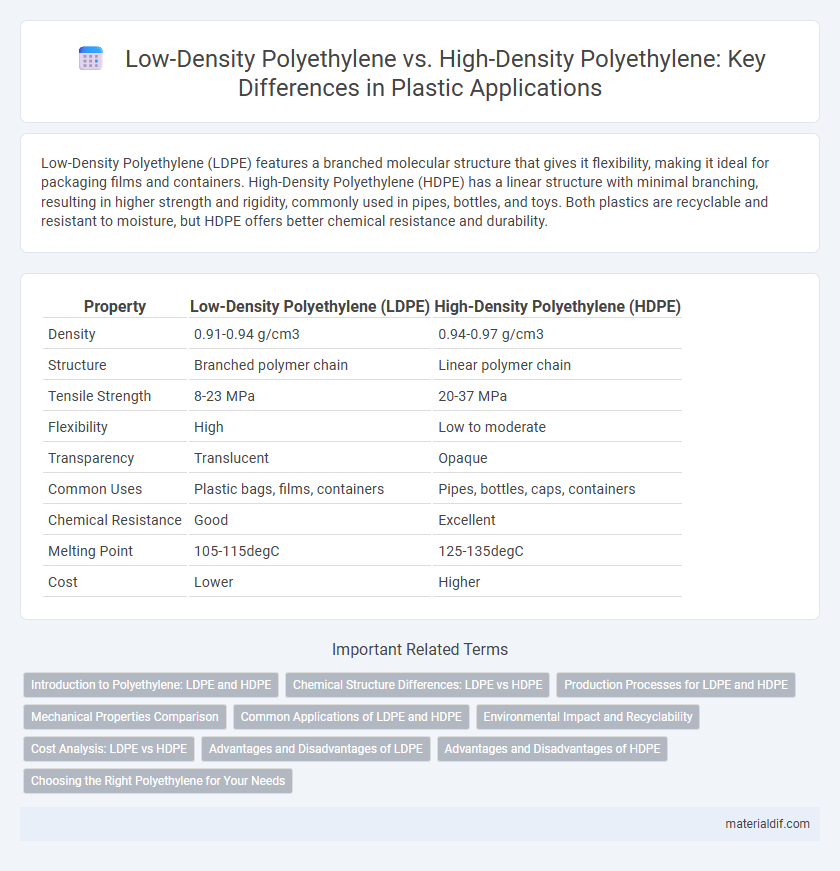
| Property | Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) | High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 0.91-0.94 g/cm3 | 0.94-0.97 g/cm3 |
| Structure | Branched polymer chain | Linear polymer chain |
| Tensile Strength | 8-23 MPa | 20-37 MPa |
| Flexibility | High | Low to moderate |
| Transparency | Translucent | Opaque |
| Common Uses | Plastic bags, films, containers | Pipes, bottles, caps, containers |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Melting Point | 105-115degC | 125-135degC |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Polyethylene: LDPE and HDPE
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) features a branched polymer structure resulting in lower density, flexibility, and impact resistance, commonly used in packaging films and containers. High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) has a linear structure with minimal branching, providing higher tensile strength, chemical resistance, and rigidity, ideal for piping, bottles, and automotive parts. Both LDPE and HDPE are thermoplastics derived from ethylene polymerization, widely utilized in diverse industrial and consumer applications due to their versatile mechanical properties.
Chemical Structure Differences: LDPE vs HDPE
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) features a highly branched polymer structure, resulting in weaker intermolecular forces and lower density. In contrast, High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) has a linear polymer chain with minimal branching, enabling tighter packing and higher crystallinity. These chemical structure differences lead to distinct physical properties, with HDPE offering greater tensile strength and chemical resistance than LDPE.
Production Processes for LDPE and HDPE
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is produced through a high-pressure polymerization process using free radical initiators, resulting in branched polymer chains that impart its characteristic flexibility. High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is manufactured via catalytic polymerization at low pressure using Ziegler-Natta or metallocene catalysts, producing linear polymer chains with minimal branching, contributing to its higher density and strength. These distinct production methods dictate the molecular structure and physical properties, making LDPE suitable for applications like plastic bags, while HDPE is preferred for containers and piping.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) exhibits lower tensile strength and rigidity compared to High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE), making it more flexible and impact-resistant. HDPE's crystalline structure provides superior tensile strength, stiffness, and resistance to environmental stress cracking. These mechanical properties make HDPE ideal for applications requiring durability, while LDPE suits flexible packaging and films.
Common Applications of LDPE and HDPE
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is commonly used in flexible packaging such as plastic bags, films, and containers due to its softness and flexibility. High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is preferred for rigid applications like bottles, piping, and plastic lumber because of its high strength and durability. The specific molecular structure of LDPE allows for elasticity, while HDPE's linear polymer chains result in superior tensile strength and chemical resistance.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) exhibits lower environmental impact due to its flexibility and lower energy requirements in production, but its recyclability is limited by contamination and degradation during reuse. High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) offers superior recyclability with higher purity and structural integrity, making it a preferred material in circular economy practices and reducing plastic waste. Both polymers contribute to plastic pollution if improperly managed, but HDPE is more widely accepted in recycling streams, enhancing environmental sustainability.
Cost Analysis: LDPE vs HDPE
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) generally costs more per kilogram than High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) due to its more complex polymer branching and production process. HDPE offers better cost efficiency in large-scale manufacturing and applications requiring high tensile strength, making it preferred for packaging and piping. LDPE's higher price reflects its flexibility and clarity advantages, suitable for specialty films and coatings, though budget constraints often steer bulk buyers toward HDPE.
Advantages and Disadvantages of LDPE
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) offers superior flexibility and impact resistance compared to High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE), making it ideal for applications like plastic bags and film wraps. However, LDPE has lower tensile strength and chemical resistance, limiting its use in heavy-duty containers and industrial piping where HDPE excels due to its higher density and durability. The choice between LDPE and HDPE depends on balancing flexibility needs with mechanical strength and environmental exposure requirements.
Advantages and Disadvantages of HDPE
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) offers superior strength, durability, and chemical resistance compared to Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE), making it ideal for heavy-duty containers and industrial applications. HDPE's high tensile strength and resistance to impact reduce the risk of cracking or deformation under stress, extending product lifespan. However, HDPE is less flexible and more prone to brittleness at low temperatures, which can limit its use in applications requiring material pliability or exposure to cold environments.
Choosing the Right Polyethylene for Your Needs
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) offers flexibility, transparency, and resistance to impact, making it ideal for packaging films, bags, and containers requiring soft texture. High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) provides superior strength, rigidity, and chemical resistance, suited for heavy-duty applications like piping, containers, and structural components. Selecting between LDPE and HDPE depends on factors such as required durability, flexibility, and environmental exposure for optimal performance.
Low-Density Polyethylene vs High-Density Polyethylene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com