Sulfite paper is produced using the sulfite pulping process, which results in a smoother surface and higher purity ideal for printing and writing applications. Sulfate paper, on the other hand, is made through the kraft process, providing greater strength and durability suitable for packaging and industrial uses. Comparing sulfite and sulfate papers allows selection based on desired texture, strength, and application needs.
Table of Comparison
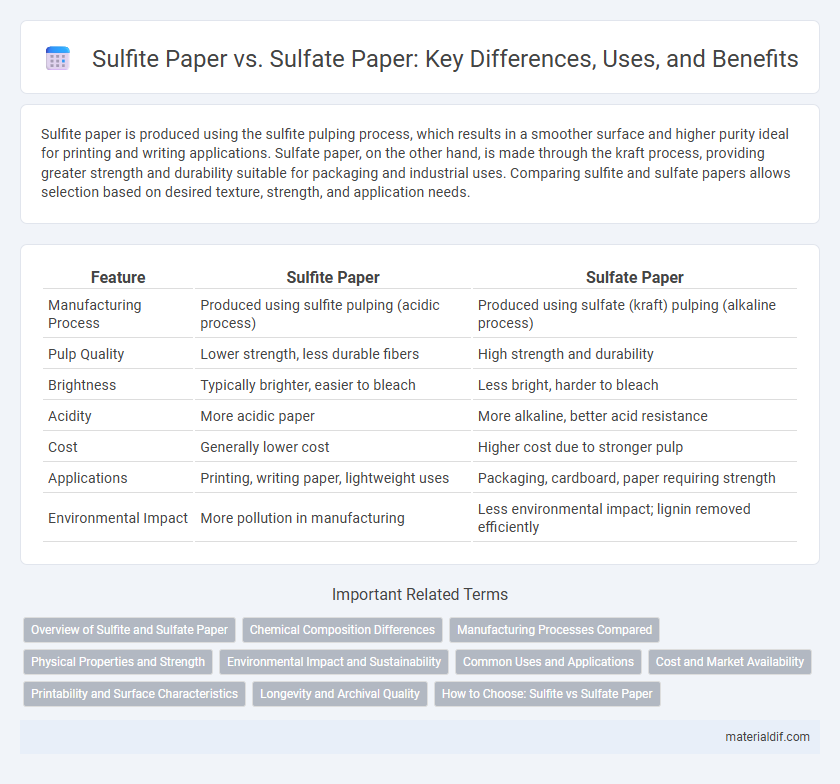
| Feature | Sulfite Paper | Sulfate Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Produced using sulfite pulping (acidic process) | Produced using sulfate (kraft) pulping (alkaline process) |
| Pulp Quality | Lower strength, less durable fibers | High strength and durability |
| Brightness | Typically brighter, easier to bleach | Less bright, harder to bleach |
| Acidity | More acidic paper | More alkaline, better acid resistance |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to stronger pulp |
| Applications | Printing, writing paper, lightweight uses | Packaging, cardboard, paper requiring strength |
| Environmental Impact | More pollution in manufacturing | Less environmental impact; lignin removed efficiently |
Overview of Sulfite and Sulfate Paper
Sulfite paper is produced using the sulfite process, which involves treating wood chips with sulfurous acid to remove lignin, resulting in a high-quality, smooth, and bright pulp primarily used for fine printing and writing papers. Sulfate paper, also known as kraft paper, is made through the sulfate process that uses sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide, yielding stronger and more durable fibers suitable for packaging and industrial applications. The fundamental difference lies in their chemical pulping methods, impacting their strength, brightness, and typical use cases in the paper industry.
Chemical Composition Differences
Sulfite paper primarily uses wood pulp treated with sulfurous acid, resulting in cellulose fibers with fewer lignin residues and a smoother texture, whereas sulfate paper, also known as kraft paper, is produced by the kraft process involving sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide, yielding stronger, more durable fibers. The sulfite process removes more lignin but produces weaker pulp, making sulfite paper suitable for fine printing and smooth finishes, while the sulfate process retains more lignin, resulting in coarse, resistant paper ideal for packaging and industrial use. Differences in chemical additives and pH levels during processing significantly influence the paper's brightness, strength, and biodegradability.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Sulfite paper is produced using the sulfite pulping process, which employs sulfurous acid and bisulfite ions to break down lignin, resulting in a pulp with higher brightness and smoother texture. Sulfate paper, made through the kraft process, uses a mixture of sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide to remove lignin, yielding stronger fibers and increased durability. The kraft process allows for higher yield and better chemical recovery, making sulfate paper more suitable for applications requiring strength and longevity.
Physical Properties and Strength
Sulfite paper typically exhibits a finer texture and higher brightness due to the chemical pulping process that removes lignin more effectively, resulting in smoother and more printable surfaces. Sulfate paper, produced through the kraft process, generally offers superior strength and durability because of longer and stronger cellulose fibers. Physically, sulfate paper resists tearing and moisture better, making it preferable for packaging and heavy-duty applications, while sulfite paper is often favored for high-quality printing and writing materials.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sulfite paper production generates higher amounts of sulfur dioxide emissions, contributing significantly to air pollution and acid rain, whereas sulfate paper mills often implement more efficient recovery systems that reduce environmental pollutants and energy consumption. The sulfate process promotes sustainability by enabling chemical recovery and reuse, minimizing waste, and lowering water usage compared to the more chemically intensive sulfite method. Overall, sulfate paper offers a greener alternative through improved energy efficiency, reduced toxic emissions, and better potential for renewable fiber sourcing.
Common Uses and Applications
Sulfite paper is primarily used for high-quality printing, fine art, and archival documents due to its smooth texture and durability. Sulfate paper, also known as kraft paper, is commonly utilized in packaging, industrial wrapping, and construction because of its superior strength and resistance to tearing. Both types serve distinct roles across industries, with sulfite paper favored for aesthetic applications and sulfate paper preferred for functional, heavy-duty purposes.
Cost and Market Availability
Sulfite paper generally costs more due to its higher-quality fibers and smoother texture, making it preferred for premium printing and fine art applications. Sulfate paper offers a more affordable option with greater market availability, favored in packaging and mass-market uses due to its stronger, coarser fibers. The broader supply chain for sulfate paper ensures easier procurement and lower prices, significantly impacting cost-sensitive industries.
Printability and Surface Characteristics
Sulfite paper offers a smoother surface with finer fiber bonding, enhancing printability by delivering sharper images and better ink absorption. Sulfate paper, known for its higher strength and durability, provides a rougher surface that can affect ink adhesion and print clarity. Choosing between sulfite and sulfate paper depends on the desired balance between print quality and mechanical performance in the final product.
Longevity and Archival Quality
Sulfite paper typically exhibits higher longevity and superior archival quality due to its acidic-free processing, which reduces yellowing and brittleness over time. Sulfate paper, while often more durable and stronger from its chemical composition, is prone to acid-related degradation that compromises long-term preservation. Archival-quality documents predominantly utilize sulfite paper to ensure resistance to environmental factors and maintain integrity for centuries.
How to Choose: Sulfite vs Sulfate Paper
Choosing between sulfite and sulfate paper depends on application needs and durability requirements. Sulfite paper offers smoother surface quality ideal for printing and writing, while sulfate paper provides higher strength and superior resistance to water and chemicals, making it suitable for packaging and industrial use. Evaluating the balance between surface finish and mechanical performance guides the selection for specific purposes.
Sulfite paper vs Sulfate paper Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com