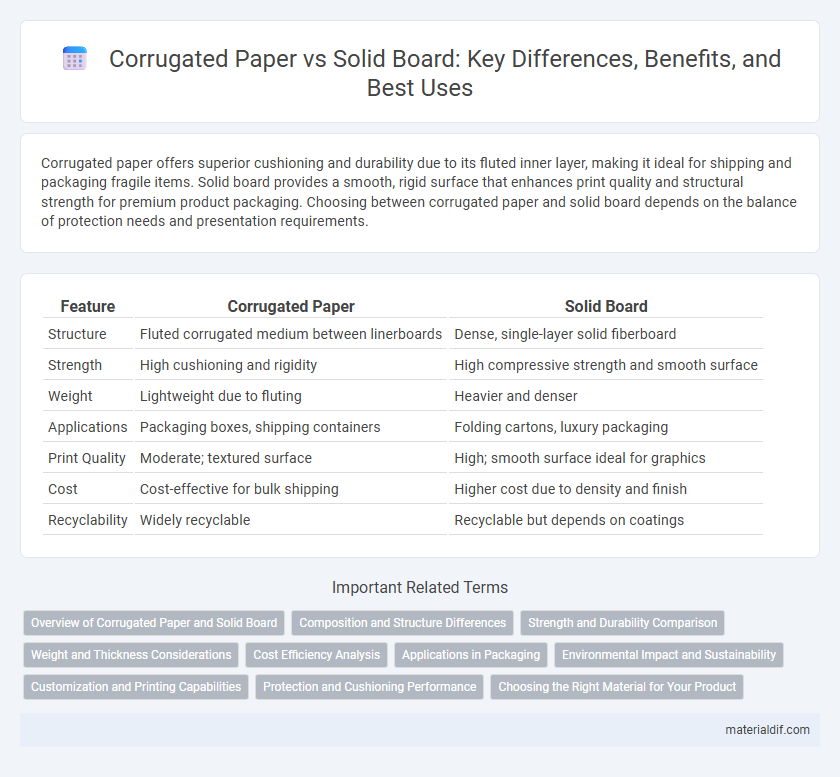
Corrugated paper offers superior cushioning and durability due to its fluted inner layer, making it ideal for shipping and packaging fragile items. Solid board provides a smooth, rigid surface that enhances print quality and structural strength for premium product packaging. Choosing between corrugated paper and solid board depends on the balance of protection needs and presentation requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Corrugated Paper | Solid Board |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Fluted corrugated medium between linerboards | Dense, single-layer solid fiberboard |
| Strength | High cushioning and rigidity | High compressive strength and smooth surface |
| Weight | Lightweight due to fluting | Heavier and denser |
| Applications | Packaging boxes, shipping containers | Folding cartons, luxury packaging |
| Print Quality | Moderate; textured surface | High; smooth surface ideal for graphics |
| Cost | Cost-effective for bulk shipping | Higher cost due to density and finish |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable | Recyclable but depends on coatings |
Overview of Corrugated Paper and Solid Board
Corrugated paper features a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two liners, providing exceptional strength, cushioning, and lightweight protection ideal for packaging and shipping. Solid board, composed of multiple layers of compacted pulp fiber, offers a smooth surface with high rigidity and durability, suitable for premium packaging and printing applications. Both materials balance strength and weight differently, with corrugated paper excelling in impact resistance and solid board excelling in aesthetic quality and structural stability.
Composition and Structure Differences
Corrugated paper consists of a fluted corrugated sheet sandwiched between two linerboards, providing lightweight strength and cushioning ideal for packaging. Solid board, also known as chipboard or pulpboard, is made from compressed layers of pulp or recycled fibers, offering a dense and rigid structure suitable for printing and high-quality packaging. The fluted core in corrugated paper creates air pockets for shock absorption, contrasting with the uniform, compact composition of solid board that delivers superior surface smoothness and rigidity.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Corrugated paper features a layered fluted structure that provides high impact resistance and cushioning, making it ideal for packaging fragile items. Solid board, composed of compressed fiberboard, offers superior rigidity and moisture resistance, resulting in enhanced durability for heavy-duty applications. When comparing strength, corrugated paper excels in shock absorption, while solid board outperforms in structural stability and long-term resilience.
Weight and Thickness Considerations
Corrugated paper typically offers a lightweight solution with thickness ranging from 1/8 inch to over 1/2 inch, providing cushioning and structural support. Solid board, often denser and heavier, ranges from 0.04 to 0.12 inches in thickness, offering superior rigidity and smoother surfaces for printing. Weight considerations depend on application needs, where corrugated paper excels in impact resistance and lightweight shipping, while solid board provides durability for premium packaging.
Cost Efficiency Analysis
Corrugated paper offers significant cost efficiency due to its lower material and production expenses compared to solid board, making it ideal for bulk packaging applications. The lightweight nature of corrugated paper reduces shipping costs and improves handling efficiency, contributing to overall savings in supply chain logistics. Conversely, solid board provides superior strength and durability but at a higher cost, making it less economical for high-volume, short-term use.
Applications in Packaging
Corrugated paper is widely used in packaging due to its lightweight and cushioning properties, making it ideal for shipping boxes and protective packaging. Solid board offers superior rigidity and smooth surfaces, suitable for high-end retail packaging and folding cartons. Both materials serve distinct roles in packaging, with corrugated paper favored for durability in transport, while solid board excels in presentation and product protection.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Corrugated paper demonstrates superior environmental benefits compared to solid board, as it requires less raw material and consumes less energy during production, leading to a lower carbon footprint. Its higher recyclability rate and biodegradability contribute significantly to reducing landfill waste and encouraging circular economy practices. Sustainable sourcing of cellulose fibers for corrugated paper further enhances its eco-friendly profile, distinguishing it as a preferred choice for environmentally conscious packaging solutions.
Customization and Printing Capabilities
Corrugated paper offers versatile customization options with various flute sizes and thicknesses, allowing for tailored strength and cushioning, while solid board provides a smooth, rigid surface ideal for high-quality printing and detailed graphics. Solid board excels in vibrant color reproduction and fine print resolution, making it suitable for premium packaging, whereas corrugated paper supports durable, large-scale printing for branding on shipping boxes. Brands often choose corrugated paper for functional customization and solid board for visually striking, customizable print finishes.
Protection and Cushioning Performance
Corrugated paper offers superior cushioning due to its fluted inner layer, which absorbs shocks and impacts effectively, making it ideal for fragile items. Solid board, while denser and more rigid, provides excellent structural support but less shock absorption compared to corrugated paper. The combination of corrugated paper's impact resistance and solid board's firmness determines optimal protection for packaging applications.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Product
Selecting the right packaging material between corrugated paper and solid board depends on product weight, fragility, and shipping conditions. Corrugated paper offers superior cushioning and shock absorption, ideal for heavy or fragile items requiring extra protection during transit. Solid board provides a smooth, rigid surface best suited for lightweight products and retail displays needing a sleek, high-quality appearance.
Corrugated paper vs Solid board Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com