Coated paper features a smooth, glossy surface achieved through a layer of compounds that enhance print quality and color vibrancy, making it ideal for high-resolution images and professional presentations. Uncoated paper lacks this coating, resulting in a matte finish that absorbs ink quickly, providing a natural texture suitable for writing and everyday printing. Choosing between coated and uncoated paper depends on the desired visual impact and functional application of the printed material.
Table of Comparison
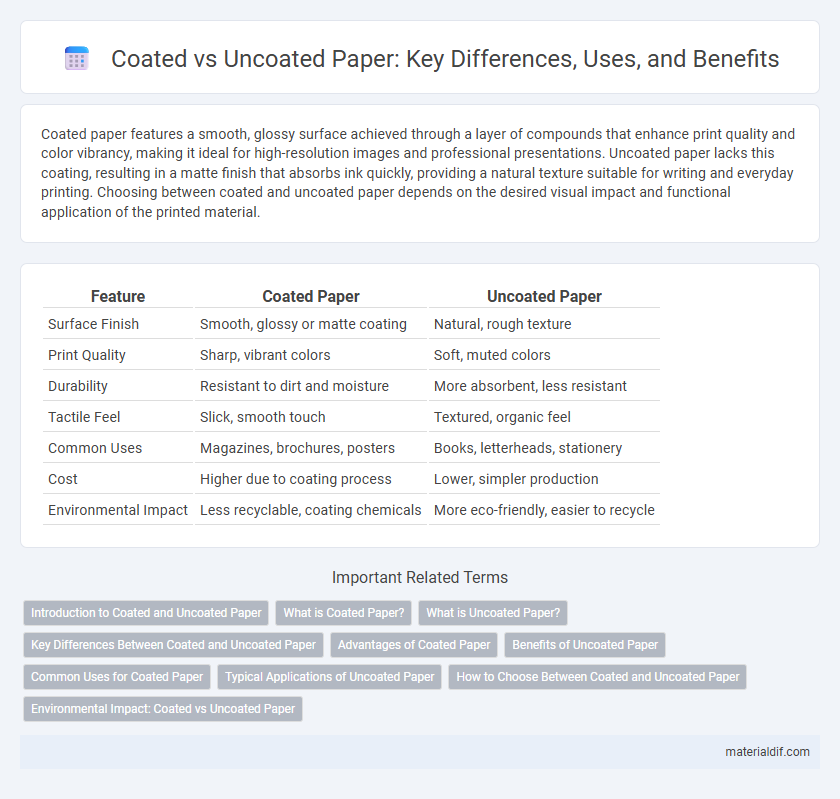
| Feature | Coated Paper | Uncoated Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Finish | Smooth, glossy or matte coating | Natural, rough texture |
| Print Quality | Sharp, vibrant colors | Soft, muted colors |
| Durability | Resistant to dirt and moisture | More absorbent, less resistant |
| Tactile Feel | Slick, smooth touch | Textured, organic feel |
| Common Uses | Magazines, brochures, posters | Books, letterheads, stationery |
| Cost | Higher due to coating process | Lower, simpler production |
| Environmental Impact | Less recyclable, coating chemicals | More eco-friendly, easier to recycle |
Introduction to Coated and Uncoated Paper
Coated paper features a surface layer of materials like clay or latex, enhancing smoothness, brightness, and ink holdout for high-quality printing results. Uncoated paper lacks this surface finish, resulting in a more porous texture that absorbs ink differently, producing a softer appearance ideal for writing and everyday printing. The choice between coated and uncoated paper impacts print clarity, durability, and tactile feel depending on the intended use.
What is Coated Paper?
Coated paper is a type of paper treated with a surface coating composed of materials such as clay, latex, or calcium carbonate to enhance its smoothness, brightness, and printability. This coating improves ink absorption, resulting in sharper and more vibrant images, making coated paper ideal for high-quality printing tasks like magazines, brochures, and photographic prints. Compared to uncoated paper, coated paper offers better resistance to smudging and provides a glossy, matte, or satin finish that enhances visual appeal.
What is Uncoated Paper?
Uncoated paper is a type of paper that lacks a surface coating, making it more porous and absorbent compared to coated paper. This paper is commonly used for writing, printing, and packaging due to its natural texture and ability to hold ink well without smudging. It is favored for brochures, books, and office stationery where a matte finish and tactile quality are preferred.
Key Differences Between Coated and Uncoated Paper
Coated paper features a smooth, glossy finish achieved through a layer of substances like clay or latex, enhancing color vibrancy and sharpness, which makes it ideal for high-quality printing and photography. In contrast, uncoated paper has a porous surface without any finishing layer, resulting in a more natural texture that absorbs ink quickly but often produces less vivid images, commonly used for letterheads and writing paper. The key differences between coated and uncoated paper involve print quality, texture, ink absorption, and typical applications, with coated paper prioritizing image clarity and uncoated paper emphasizing tactile feel and bleed resistance.
Advantages of Coated Paper
Coated paper offers superior surface smoothness and enhanced print quality due to its clay or polymer coating, resulting in sharper images and vibrant colors. It provides increased durability and resistance to dirt, moisture, and fingerprints, making it ideal for high-end marketing materials and photo prints. The coating also prevents ink absorption, reducing ink consumption and drying time.
Benefits of Uncoated Paper
Uncoated paper offers superior printability for detailed text and fine line art due to its porous surface, which absorbs ink evenly and reduces smudging. It is environmentally friendly, often made from recycled fibers and is more easily recyclable compared to coated paper. Uncoated paper also provides a natural texture and matte finish, enhancing readability and tactile appeal for books, stationery, and business materials.
Common Uses for Coated Paper
Coated paper is commonly used for high-quality printing projects such as magazines, brochures, and flyers due to its smooth surface and enhanced ink retention, which produces vibrant colors and sharp images. It is also preferred for packaging, labels, and photographic prints where durability and visual appeal are critical. These applications benefit from coated paper's glossy or matte finish, which helps resist smudging and improves overall print clarity.
Typical Applications of Uncoated Paper
Uncoated paper is widely used in applications such as letterheads, stationery, books, and envelopes due to its natural texture and absorbency. It offers superior printability for writing instruments like pens and pencils, making it ideal for notebooks and forms that require handwriting. This paper type is preferred in everyday office printing and publishing where a non-glossy, matte finish enhances readability and tactile experience.
How to Choose Between Coated and Uncoated Paper
Choosing between coated and uncoated paper depends on the intended use and desired finish; coated paper offers a smooth surface ideal for vibrant, high-resolution images, while uncoated paper provides a natural texture suitable for writing and readability. Consider the printing method and durability requirements, as coated paper resists ink absorption and enhances color contrast, whereas uncoated paper absorbs ink more readily, reducing smudging but producing softer visuals. Budget and environmental factors also influence the choice, with uncoated paper often being more cost-effective and eco-friendly due to fewer chemical treatments.
Environmental Impact: Coated vs Uncoated Paper
Coated paper typically requires more chemicals and energy during production, resulting in a higher environmental footprint compared to uncoated paper, which is often made using fewer additives and less water. Uncoated paper tends to be more biodegradable and easier to recycle, reducing its impact on landfills and lowering carbon emissions. Sustainable sourcing and certification, such as FSC or PEFC, play a crucial role in mitigating the environmental effects of both coated and uncoated paper products.
Coated Paper vs Uncoated Paper Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com