Archival paper is specifically designed for long-term preservation, featuring acid-free materials that prevent yellowing and deterioration over time. Standard paper, in contrast, often contains acidic components that cause it to degrade faster, making it less suitable for important documents or artwork meant to last. Choosing archival paper ensures durability and longevity, essential for preserving valuable papers and maintaining their quality across decades.
Table of Comparison
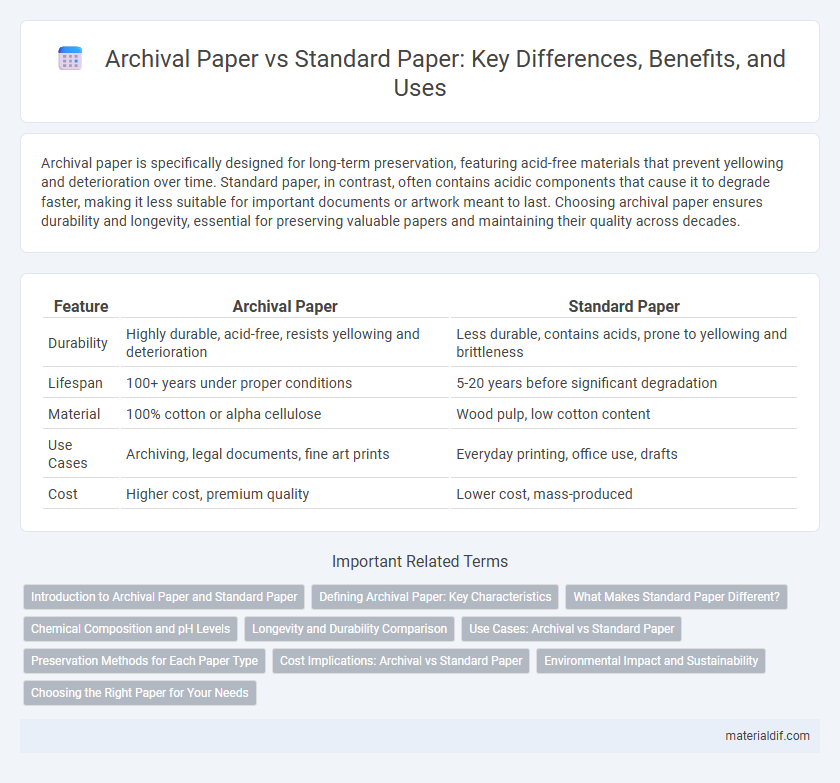
| Feature | Archival Paper | Standard Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Highly durable, acid-free, resists yellowing and deterioration | Less durable, contains acids, prone to yellowing and brittleness |
| Lifespan | 100+ years under proper conditions | 5-20 years before significant degradation |
| Material | 100% cotton or alpha cellulose | Wood pulp, low cotton content |
| Use Cases | Archiving, legal documents, fine art prints | Everyday printing, office use, drafts |
| Cost | Higher cost, premium quality | Lower cost, mass-produced |
Introduction to Archival Paper and Standard Paper
Archival paper is specifically designed for long-term durability, featuring high-quality fibers, acid-neutral or alkaline pH levels, and lignin-free content to prevent yellowing and deterioration over time. Standard paper typically contains acidic components and lower-quality fibers, making it prone to aging, brittleness, and discoloration. The choice between archival and standard paper significantly affects the longevity and preservation of important documents, artworks, or records.
Defining Archival Paper: Key Characteristics
Archival paper is specifically designed for long-term preservation, featuring acid-free and lignin-free composition to prevent yellowing and deterioration over time. It typically has a neutral or slightly alkaline pH, enhancing its durability against environmental factors such as humidity and light exposure. High-quality fibers, often cotton or alpha cellulose, contribute to its strength and resistance to aging, making it ideal for documents, artworks, and records requiring permanent retention.
What Makes Standard Paper Different?
Standard paper typically contains higher levels of lignin and acidic compounds, which cause it to yellow and deteriorate faster than archival paper. Archival paper is acid-free and often made from cotton or other durable fibers that ensure longevity and resistance to aging. The chemical stability and fiber quality distinctly separate standard paper from the long-lasting archival counterparts.
Chemical Composition and pH Levels
Archival paper is specifically designed with a high pH alkaline or neutral composition, often incorporating calcium carbonate as a buffering agent to prevent acid deterioration over time. Standard paper typically contains acidic components and lignin, which contribute to faster yellowing, brittleness, and degradation. The enhanced chemical stability and neutral pH of archival paper ensure long-term preservation and resistance to environmental damage.
Longevity and Durability Comparison
Archival paper is specifically manufactured using acid-free materials and lignin-free fibers, ensuring a lifespan of over 100 years without significant deterioration, making it ideal for documents that require long-term preservation. Standard paper, often produced with acidic pulps, tends to yellow and become brittle within decades due to chemical breakdown, significantly compromising durability and readability. The superior pH balance and fiber composition of archival paper provide enhanced resistance to environmental factors such as humidity, light, and temperature fluctuations compared to standard paper.
Use Cases: Archival vs Standard Paper
Archival paper is specifically designed for long-term preservation, making it ideal for important documents, legal records, and historical archives that require durability and acid-free composition to prevent deterioration over decades. Standard paper suits everyday printing needs such as office memos, drafts, or casual notes where longevity is not critical. Choosing archival paper ensures protection against yellowing, brittleness, and fading, whereas standard paper offers cost-effective functionality for non-permanent use.
Preservation Methods for Each Paper Type
Archival paper, composed of acid-free materials and lignin-free fibers, utilizes preservation methods such as controlled temperature and humidity to prevent deterioration and yellowing over time. Standard paper, often containing acidic components, requires deacidification treatments and protective coatings to extend longevity, though it remains more susceptible to brittleness and fading. Proper storage in acid-free folders and protection from light exposure are critical for maintaining the integrity of both paper types.
Cost Implications: Archival vs Standard Paper
Archival paper, designed for long-term preservation, typically costs 50% to 200% more than standard paper due to its acid-free, lignin-free composition ensuring durability and resistance to yellowing. While standard paper is less expensive upfront, frequent replacements and degradation over time can lead to higher cumulative expenses in projects requiring longevity. For businesses prioritizing document preservation, investing in archival paper reduces costs associated with damage, restoration, and reprints in the long run.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Archival paper is designed with acid-free materials and lignin-free content, ensuring longevity and reducing environmental degradation over time compared to standard paper that often contains harmful chemicals causing faster deterioration and pollution. The manufacturing processes of archival paper typically use fewer bleaches and toxic substances, resulting in lower emissions and a smaller carbon footprint. Choosing archival paper supports sustainability by minimizing waste due to degradation, promoting conservation of resources, and aligning with eco-friendly document preservation practices.
Choosing the Right Paper for Your Needs
Archival paper offers superior longevity and acid-free properties, making it ideal for preserving important documents, artwork, and photographs without yellowing or deterioration over time. Standard paper is more affordable and suitable for everyday printing tasks, but it lacks the durability and archival quality needed for long-term preservation. Selecting archival paper ensures your documents remain intact for decades, while standard paper meets basic printing needs cost-effectively.
Archival Paper vs Standard Paper Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com