Paper lamination involves applying a thin plastic film to the paper surface, enhancing durability, water resistance, and overall protection. Paper varnishing, on the other hand, adds a glossy or matte coating that improves visual appeal and surface texture without significantly increasing thickness or rigidity. Choosing between lamination and varnishing depends on the desired finish, durability requirements, and cost considerations for printed materials.
Table of Comparison
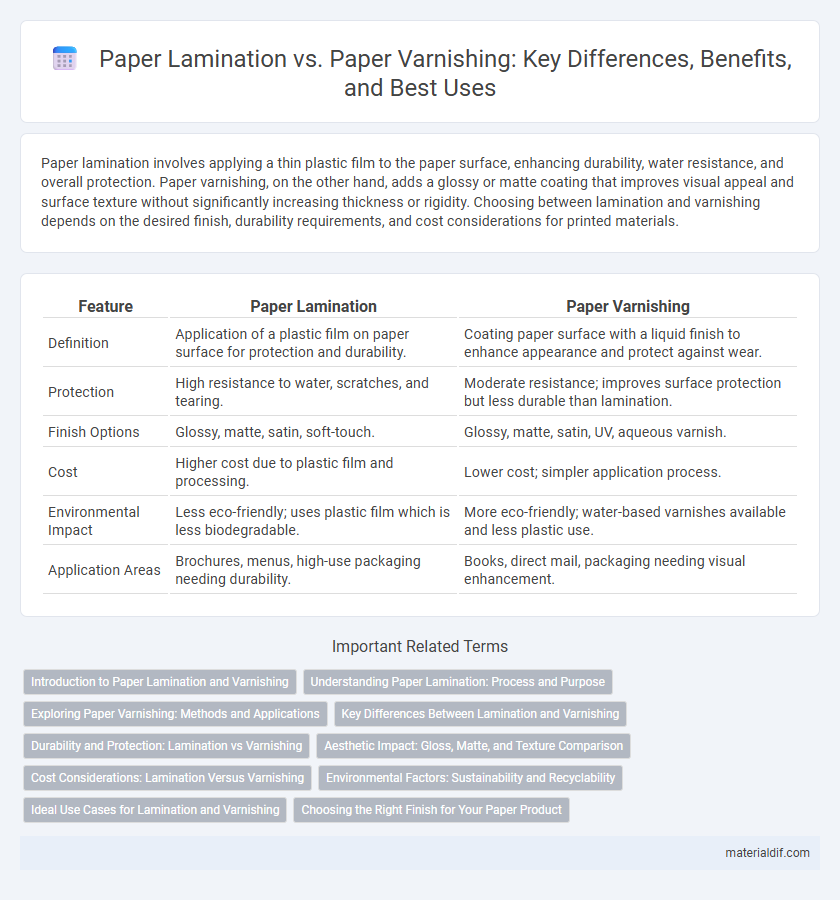
| Feature | Paper Lamination | Paper Varnishing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Application of a plastic film on paper surface for protection and durability. | Coating paper surface with a liquid finish to enhance appearance and protect against wear. |
| Protection | High resistance to water, scratches, and tearing. | Moderate resistance; improves surface protection but less durable than lamination. |
| Finish Options | Glossy, matte, satin, soft-touch. | Glossy, matte, satin, UV, aqueous varnish. |
| Cost | Higher cost due to plastic film and processing. | Lower cost; simpler application process. |
| Environmental Impact | Less eco-friendly; uses plastic film which is less biodegradable. | More eco-friendly; water-based varnishes available and less plastic use. |
| Application Areas | Brochures, menus, high-use packaging needing durability. | Books, direct mail, packaging needing visual enhancement. |
Introduction to Paper Lamination and Varnishing
Paper lamination involves applying a thin plastic film to paper surfaces, enhancing durability, moisture resistance, and visual appeal. Paper varnishing uses a liquid coating that adds gloss, matte, or satin finishes while protecting against scratches and wear. Both techniques improve paper longevity and aesthetics, with lamination offering stronger protection and varnishing providing varied surface textures.
Understanding Paper Lamination: Process and Purpose
Paper lamination involves applying a protective plastic film to paper surfaces, enhancing durability and resistance to moisture and wear. This process uses heat and pressure to bond the laminate, resulting in a smooth, glossy, or matte finish that prolongs the life of printed materials. Unlike paper varnishing, which applies a thin coating for aesthetic shine or texture, lamination provides a robust barrier essential for heavy-use documents and outdoor applications.
Exploring Paper Varnishing: Methods and Applications
Paper varnishing enhances durability and aesthetics by applying a transparent protective coating using methods such as spray, curtain, and UV varnishing. This process adds resistance to moisture, scratches, and fading while allowing customization with matte, gloss, or satin finishes. Common applications include book covers, packaging, and promotional materials where high-quality visual appeal and protection are essential.
Key Differences Between Lamination and Varnishing
Paper lamination involves applying a thin plastic film to paper surfaces, enhancing durability, moisture resistance, and rigidity, whereas paper varnishing uses a liquid coating to add gloss, matte, or satin finishes that improve visual appeal and protect against scratches. Lamination provides superior protection against water and physical wear, making it ideal for items requiring long-lasting use, while varnishing primarily enhances aesthetics and offers moderate protection. The choice between lamination and varnishing depends on the desired balance of durability and finish quality for printed materials.
Durability and Protection: Lamination vs Varnishing
Paper lamination offers superior durability and protection by encasing the paper in a plastic film that resists moisture, tearing, and stains, making it ideal for frequently handled documents. Paper varnishing provides a protective coating that enhances surface smoothness and adds a glossy or matte finish but offers less resistance to physical damage and environmental factors. Lamination outperforms varnishing in long-term preservation by maintaining rigidity and preventing ink smudging under harsh conditions.
Aesthetic Impact: Gloss, Matte, and Texture Comparison
Paper lamination offers a durable glossy or matte finish that enhances color vibrancy and provides a smooth, tactile surface, making it ideal for high-impact visual appeal. Paper varnishing selectively adds gloss or matte coating in specific areas, creating subtle texture contrasts that enrich design details without altering the paper's base feel. Comparing both, lamination results in an all-over uniform finish emphasizing protection and sheen, while varnishing excels in aesthetic dimensionality and strategic highlights.
Cost Considerations: Lamination Versus Varnishing
Paper lamination generally incurs higher upfront costs due to materials like plastic films and specialized equipment, but it offers enhanced durability and water resistance that can reduce long-term expenses. Varnishing, often cheaper initially, provides a cost-effective way to improve paper appearance and protect against minor wear without the added thickness or feel of lamination. When balancing budget constraints and usage requirements, lamination is preferable for heavy-duty protection while varnishing suits projects emphasizing aesthetic enhancement with lower investment.
Environmental Factors: Sustainability and Recyclability
Paper lamination involves coating paper with a plastic film, significantly reducing its recyclability and increasing environmental impact due to plastic waste. Paper varnishing uses a liquid coating that enhances durability while maintaining better recyclability and a smaller environmental footprint. Choosing paper varnishing supports sustainability goals by enabling easier recycling and reducing reliance on non-biodegradable materials.
Ideal Use Cases for Lamination and Varnishing
Paper lamination is ideal for projects requiring enhanced durability, water resistance, and protection from physical damage, such as menus, ID cards, and outdoor signage. Paper varnishing is best suited for improving visual appeal and adding a tactile finish to printed materials like business cards, brochures, and book covers without significantly increasing thickness or rigidity. Selecting lamination or varnishing depends on the desired balance between protection, aesthetic enhancement, and cost-effectiveness.
Choosing the Right Finish for Your Paper Product
Paper lamination offers durable protection and enhanced visual appeal by applying a plastic film, making it ideal for products exposed to frequent handling or moisture. Paper varnishing provides a glossy or matte finish by coating with a liquid varnish, enhancing color vibrancy while maintaining the natural texture of the paper. Selecting the right finish depends on factors such as intended use, desired durability, budget, and aesthetic preferences to ensure optimal performance and appearance.
Paper lamination vs Paper varnishing Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com