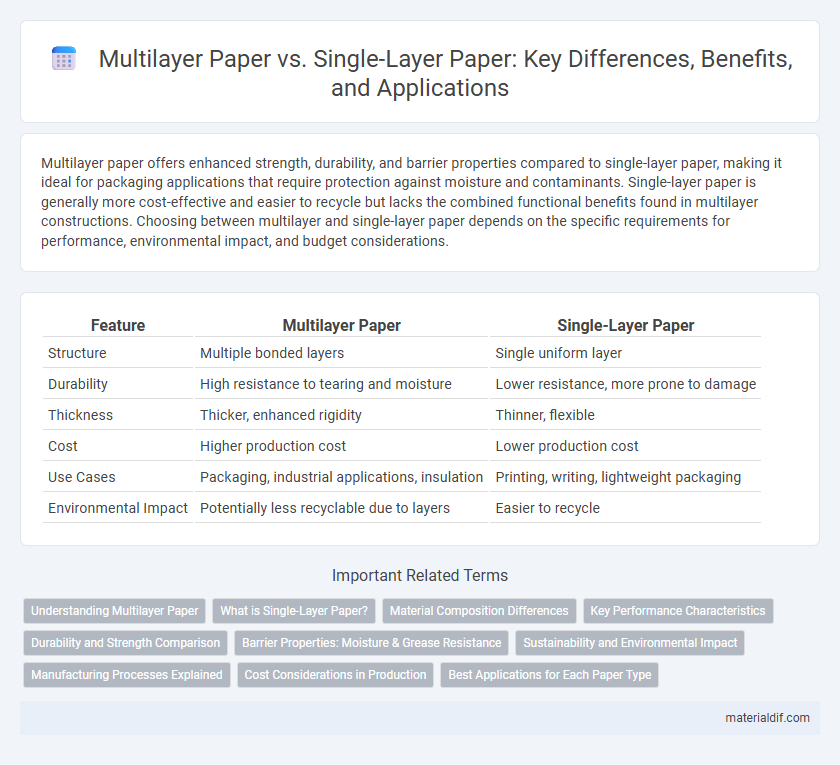
Multilayer paper offers enhanced strength, durability, and barrier properties compared to single-layer paper, making it ideal for packaging applications that require protection against moisture and contaminants. Single-layer paper is generally more cost-effective and easier to recycle but lacks the combined functional benefits found in multilayer constructions. Choosing between multilayer and single-layer paper depends on the specific requirements for performance, environmental impact, and budget considerations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Multilayer Paper | Single-Layer Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Multiple bonded layers | Single uniform layer |
| Durability | High resistance to tearing and moisture | Lower resistance, more prone to damage |
| Thickness | Thicker, enhanced rigidity | Thinner, flexible |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower production cost |
| Use Cases | Packaging, industrial applications, insulation | Printing, writing, lightweight packaging |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially less recyclable due to layers | Easier to recycle |
Understanding Multilayer Paper
Multilayer paper consists of two or more layers bonded together to enhance strength, durability, and specialized functionality compared to single-layer paper. Each layer in multilayer paper can be engineered with specific materials, such as recycled fibers or coated surfaces, to optimize properties like tear resistance, printability, and moisture barrier performance. This layered construction enables applications in packaging, printing, and industrial uses where enhanced mechanical and protective qualities are essential.
What is Single-Layer Paper?
Single-layer paper consists of a single uniform sheet made from pulp fibers compressed together, offering simplicity in production and cost-effectiveness. This type of paper provides basic strength and printability but lacks the enhanced durability and specialized properties found in multilayer paper. Single-layer paper is commonly used for standard writing, printing, and packaging applications where minimal barrier or cushioning performance is required.
Material Composition Differences
Multilayer paper consists of multiple bonded layers, each optimized for specific properties such as strength, barrier resistance, and printability, while single-layer paper is made from a homogeneous pulp mixture. The inner layers in multilayer paper often incorporate recycled fibers or specialized additives to enhance durability and moisture resistance, whereas single-layer paper typically relies on uniform fiber composition. These material composition differences allow multilayer paper to outperform single-layer variants in applications requiring superior mechanical performance and functional versatility.
Key Performance Characteristics
Multilayer paper offers enhanced durability and strength due to its multiple bonded layers, improving tear resistance and load-bearing capacity compared to single-layer paper. It provides superior moisture resistance and barrier properties, making it suitable for packaging applications requiring protection against external elements. Single-layer paper, while more cost-effective and lightweight, typically lacks the enhanced structural integrity and protective qualities found in multilayer alternatives.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Multilayer paper exhibits superior durability and strength compared to single-layer paper due to its composite structure, which enhances resistance to tearing and improves load-bearing capacity. The laminated layers in multilayer paper distribute stress more evenly, reducing the risk of damage under mechanical pressure. Single-layer paper, while lighter and more flexible, lacks the reinforced integrity necessary for high-strength packaging applications.
Barrier Properties: Moisture & Grease Resistance
Multilayer paper provides superior barrier properties compared to single-layer paper due to its multiple protective coatings, enhancing moisture and grease resistance significantly. The additional layers act as effective barriers against water vapor and oil penetration, making multilayer paper ideal for packaging perishable goods and greasy foods. Single-layer paper lacks these multi-barrier attributes, resulting in lower durability and weaker resistance to moisture and grease.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Multilayer paper offers enhanced durability and barrier properties, reducing the need for additional packaging materials and lowering overall waste generation compared to single-layer paper. The use of multilayer structures can optimize resource efficiency by combining recycled fibers and reducing energy consumption during production. However, multilayer paper recycling is more complex, potentially limiting circularity and requiring advanced sorting technologies to maintain sustainability benefits.
Manufacturing Processes Explained
Multilayer paper is manufactured through a lamination process that bonds multiple layers of pulp sheets together, enhancing strength, durability, and barrier properties compared to single-layer paper, which is produced by depositing a uniform pulp slurry onto a flat wire mesh. The multilayer approach allows for precise control over each layer's composition, thickness, and moisture content, optimizing performance attributes such as tear resistance and printability. In contrast, single-layer paper's simpler manufacturing process limits its ability to customize mechanical and functional properties, making it less suitable for demanding packaging or industrial applications.
Cost Considerations in Production
Multilayer paper production typically incurs higher costs due to the complexity of layering processes and the need for specialized machinery, increasing capital investment and maintenance expenses. Single-layer paper manufacturing is more cost-effective with simpler production lines, resulting in lower energy consumption and material waste. However, multilayer paper offers enhanced durability and functionality which can justify the higher initial costs in applications requiring superior performance.
Best Applications for Each Paper Type
Multilayer paper offers enhanced durability and moisture resistance, making it ideal for packaging fragile items and food products requiring preservation. Single-layer paper provides lightweight flexibility and cost-effectiveness, suited for printing, printing labels, and everyday office use. Selecting the appropriate paper type optimizes performance based on specific application requirements such as strength, barrier properties, and budget constraints.
Multilayer paper vs Single-layer paper Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com