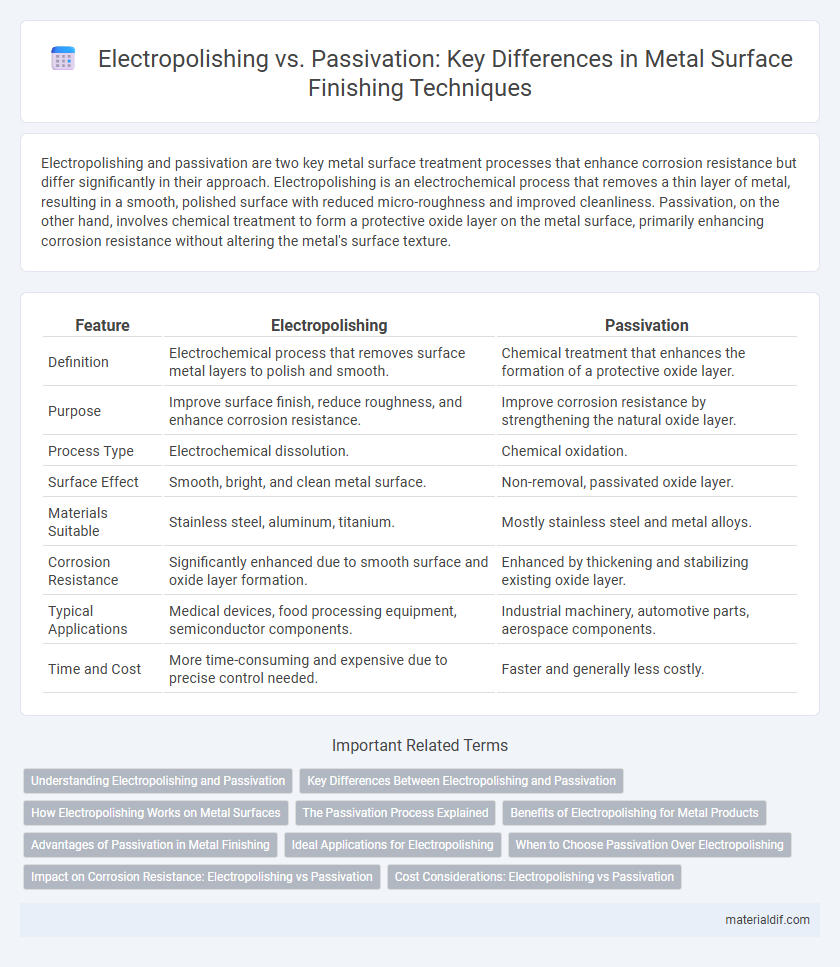
Electropolishing and passivation are two key metal surface treatment processes that enhance corrosion resistance but differ significantly in their approach. Electropolishing is an electrochemical process that removes a thin layer of metal, resulting in a smooth, polished surface with reduced micro-roughness and improved cleanliness. Passivation, on the other hand, involves chemical treatment to form a protective oxide layer on the metal surface, primarily enhancing corrosion resistance without altering the metal's surface texture.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Electropolishing | Passivation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Electrochemical process that removes surface metal layers to polish and smooth. | Chemical treatment that enhances the formation of a protective oxide layer. |
| Purpose | Improve surface finish, reduce roughness, and enhance corrosion resistance. | Improve corrosion resistance by strengthening the natural oxide layer. |
| Process Type | Electrochemical dissolution. | Chemical oxidation. |
| Surface Effect | Smooth, bright, and clean metal surface. | Non-removal, passivated oxide layer. |
| Materials Suitable | Stainless steel, aluminum, titanium. | Mostly stainless steel and metal alloys. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Significantly enhanced due to smooth surface and oxide layer formation. | Enhanced by thickening and stabilizing existing oxide layer. |
| Typical Applications | Medical devices, food processing equipment, semiconductor components. | Industrial machinery, automotive parts, aerospace components. |
| Time and Cost | More time-consuming and expensive due to precise control needed. | Faster and generally less costly. |
Understanding Electropolishing and Passivation
Electropolishing is an electrochemical process that removes a thin layer of metal from the surface, resulting in a smooth, corrosion-resistant finish by reducing surface roughness and contaminants. Passivation involves treating stainless steel with acid solutions to form a thin, protective oxide layer that enhances corrosion resistance without altering the surface texture. Both processes improve metal durability, but electropolishing enhances cleanliness and smoothness, while passivation specifically strengthens the oxide barrier against environmental damage.
Key Differences Between Electropolishing and Passivation
Electropolishing is an electrochemical process that removes a thin layer of metal, enhancing surface smoothness, while passivation involves treating the metal with acid to form a protective oxide layer that prevents corrosion. Electropolishing improves metal brightness and reduces surface roughness, making it ideal for aesthetic and sanitary applications, whereas passivation primarily enhances corrosion resistance without altering surface texture. Key differences include electropolishing's material removal and surface refinement versus passivation's chemical treatment focused solely on oxide layer formation.
How Electropolishing Works on Metal Surfaces
Electropolishing removes a thin layer of metal from the surface through an electrochemical process that smooths and brightens by selectively dissolving microscopic peaks. This process improves corrosion resistance and cleanliness by creating a uniform, passive oxide layer while reducing surface roughness. Electropolishing is particularly effective on stainless steel, aluminum, and other alloys used in industries requiring high standards of hygiene and finish.
The Passivation Process Explained
The passivation process involves treating metal surfaces, typically stainless steel, with an acid solution to remove free iron and enhance the formation of a thin, protective oxide layer that improves corrosion resistance. This chemical treatment results in a uniform, inert surface that prevents rust and extends the metal's durability in harsh environments. Passivation is often preferred over electropolishing when the goal is to optimize corrosion resistance without significantly altering the metal's surface roughness or appearance.
Benefits of Electropolishing for Metal Products
Electropolishing enhances metal products by creating a smooth, clean surface that reduces surface roughness and removes contaminants at the microscopic level. This process significantly improves corrosion resistance and reduces the risk of bacterial contamination, making it ideal for medical, food, and pharmaceutical applications. Compared to passivation, electropolishing offers superior surface finish and durability, extending the lifespan and performance of stainless steel and other metal components.
Advantages of Passivation in Metal Finishing
Passivation enhances corrosion resistance by creating a stable, inert oxide layer on stainless steel and other metals, significantly reducing surface reactivity. This metal finishing process improves durability and maintains the metal's aesthetic appearance without altering dimensions, making it ideal for precision components. Passivation also requires minimal environmental impact compared to electropolishing, as it uses less aggressive chemicals and generates fewer hazardous wastes.
Ideal Applications for Electropolishing
Electropolishing is ideal for stainless steel components requiring enhanced corrosion resistance, smooth surface finish, and reduced microbial adhesion, commonly used in medical devices, food processing, and aerospace industries. This electrochemical process removes microscopic peaks and contaminants, improving surface uniformity and cleanliness beyond what passivation alone achieves. Applications demanding hygienic, polished surfaces and improved fatigue resistance benefit significantly from electropolishing over standard chemical passivation.
When to Choose Passivation Over Electropolishing
Passivation is preferred over electropolishing when the primary goal is to enhance corrosion resistance by forming a stable, thin oxide layer on stainless steel surfaces without altering surface texture. It is ideal for maintaining tight dimensional tolerances in precision components where material removal could be detrimental. Passivation is also favored in applications requiring improved chemical resistance and cleanliness, such as medical devices and food processing equipment.
Impact on Corrosion Resistance: Electropolishing vs Passivation
Electropolishing significantly enhances corrosion resistance by removing surface impurities and creating a smooth, passive oxide layer that inhibits metal degradation. Passivation increases corrosion resistance by chemically treating the metal to form a protective oxide film, primarily on stainless steel and similar alloys. Compared to passivation, electropolishing provides a more uniform surface finish and superior long-term protection against corrosion in aggressive environments.
Cost Considerations: Electropolishing vs Passivation
Electropolishing typically incurs higher initial equipment and operational costs due to its complex electrical process and need for specialized acid solutions, while passivation generally requires lower expenses with simpler chemical treatments. However, electropolishing offers long-term cost savings by producing a smoother, more corrosion-resistant surface that reduces maintenance and extends metal lifespan compared to passivation. Cost-effectiveness between the two methods largely depends on the metal type, desired finish quality, and specific application requirements in industries such as aerospace or medical devices.
Electropolishing vs Passivation Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com