Lead sheeting offers superior radiation shielding and durability compared to polyethylene sheeting, making it the preferred choice in medical and industrial environments. Polyethylene sheeting is lightweight, cost-effective, and flexible but lacks the dense protective properties of lead, limiting its use in high-radiation applications. Choosing between lead and polyethylene sheeting depends on specific safety requirements, budget constraints, and the desired balance between protection and ease of installation.
Table of Comparison
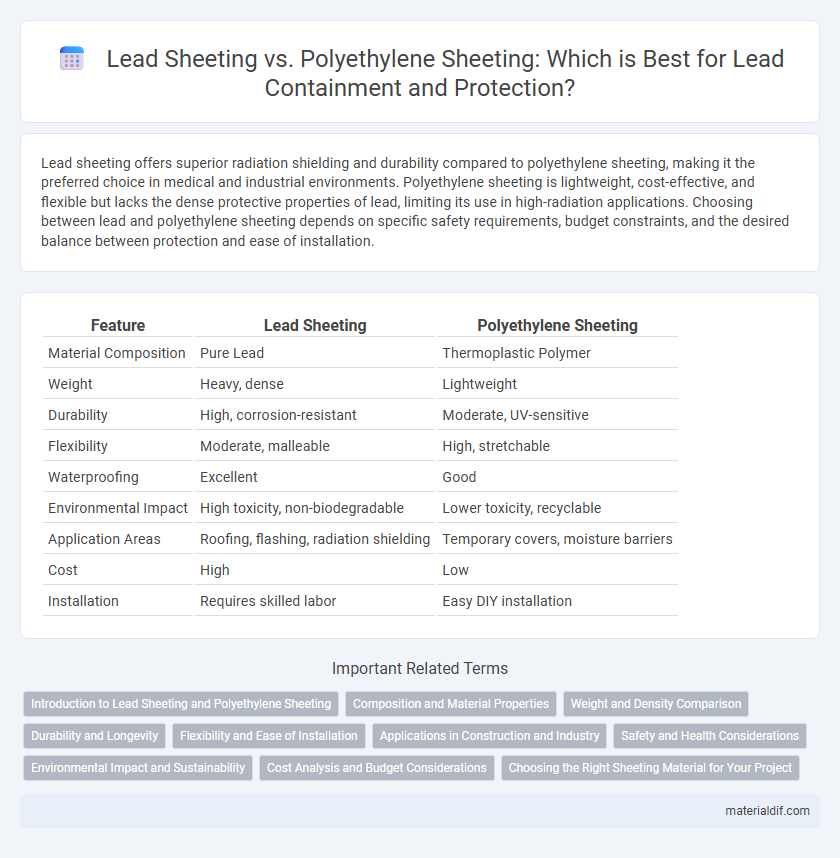
| Feature | Lead Sheeting | Polyethylene Sheeting |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Pure Lead | Thermoplastic Polymer |
| Weight | Heavy, dense | Lightweight |
| Durability | High, corrosion-resistant | Moderate, UV-sensitive |
| Flexibility | Moderate, malleable | High, stretchable |
| Waterproofing | Excellent | Good |
| Environmental Impact | High toxicity, non-biodegradable | Lower toxicity, recyclable |
| Application Areas | Roofing, flashing, radiation shielding | Temporary covers, moisture barriers |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Installation | Requires skilled labor | Easy DIY installation |
Introduction to Lead Sheeting and Polyethylene Sheeting
Lead sheeting offers exceptional durability, malleability, and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for roofing, flashing, and underwater applications. Polyethylene sheeting, a lightweight and flexible plastic material, provides excellent moisture barriers and UV resistance, commonly used in construction, agriculture, and packaging. Understanding the distinct properties of lead and polyethylene sheeting helps in selecting the appropriate material for specific insulation, protection, and waterproofing needs.
Composition and Material Properties
Lead sheeting consists primarily of pure lead, known for its high density, malleability, and excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for radiation shielding and waterproofing applications. Polyethylene sheeting is composed of long chains of ethylene polymers, offering flexibility, chemical resistance, and lightweight durability, suitable for moisture barriers and packaging. The distinct material properties--lead's heavy metal density versus polyethylene's polymeric resilience--determine their different use cases in construction and industrial settings.
Weight and Density Comparison
Lead sheeting has a significantly higher density of approximately 11.34 g/cm3 compared to polyethylene sheeting, which typically ranges from 0.91 to 0.96 g/cm3, resulting in much greater weight per unit volume. This density difference makes lead sheeting substantially heavier and more effective for applications requiring mass and radiation shielding. In contrast, polyethylene sheeting's light weight and lower density offer easier handling and flexibility but less protective mass than lead sheeting.
Durability and Longevity
Lead sheeting offers superior durability and longevity compared to polyethylene sheeting due to its resistance to UV degradation, corrosion, and extreme weather conditions, often lasting over 100 years in roofing applications. Polyethylene sheeting, while lightweight and cost-effective, typically degrades within 5 to 10 years when exposed to sunlight and harsh environmental elements, requiring frequent replacement. The dense, malleable nature of lead enhances its performance in waterproofing and structural protection, making it a preferred choice for long-term construction projects.
Flexibility and Ease of Installation
Lead sheeting offers superior flexibility, conforming easily to complex shapes and contours, making it ideal for roofing, flashing, and waterproofing applications that require precise fitting. Polyethylene sheeting, while lightweight and cost-effective, tends to be less flexible and can be more challenging to mold around irregular surfaces, often requiring additional fastening methods during installation. The ease of installation with lead sheeting is enhanced by its pliability and malleability, reducing labor time compared to the rigid nature of polyethylene sheets.
Applications in Construction and Industry
Lead sheeting offers superior durability and excellent radiation shielding, making it ideal for applications in medical facilities, roofing, and waterproofing in construction. Polyethylene sheeting is prized for its lightweight, flexibility, and chemical resistance, commonly used for vapor barriers, temporary covers, and insulation in industrial settings. Choosing between lead and polyethylene sheeting depends on specific project requirements such as weight constraints, environmental exposure, and protective properties.
Safety and Health Considerations
Lead sheeting poses significant health risks due to lead exposure, which can cause neurological damage and respiratory problems, making strict handling and disposal protocols essential. Polyethylene sheeting, being non-toxic and chemically inert, offers a safer alternative with minimal health hazards during installation and removal. Proper ventilation and personal protective equipment are critical when working with lead sheeting to minimize the risk of lead dust inhalation and contamination.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Lead sheeting poses significant environmental concerns due to its toxicity and potential for soil and water contamination during production and disposal. Polyethylene sheeting, while derived from fossil fuels, offers higher recyclability and lower ecological footprint when managed properly. Sustainable construction increasingly favors polyethylene sheeting for its reduced environmental impact and improved lifecycle performance.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Lead sheeting offers superior durability and corrosion resistance but comes with a higher initial cost compared to polyethylene sheeting, which is more affordable and lightweight. Budget considerations must account for long-term performance, as lead's extended lifespan can reduce replacement expenses, while polyethylene's lower upfront price suits short-term projects or limited budgets. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including maintenance and environmental impact, ensures an informed decision between these two sheeting materials.
Choosing the Right Sheeting Material for Your Project
Lead sheeting provides exceptional durability, radiation shielding, and weather resistance, making it ideal for roofing, flashing, and soundproofing applications in construction projects requiring longevity. Polyethylene sheeting offers a lightweight, flexible, and cost-effective solution, commonly used for moisture barriers, temporary weather protection, and agricultural covers. Selecting the right sheeting material depends on project requirements such as durability, environmental exposure, safety standards, and budget constraints.
Lead Sheeting vs Polyethylene Sheeting Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com