Lead sheeting offers superior radiation shielding and durability, making it ideal for medical and industrial applications requiring heavy-duty protection. Rubber sheeting provides flexibility and resistance to chemicals, suitable for general-purpose sealing and insulation tasks. Choosing between lead and rubber sheeting depends on the specific needs for weight, protection level, and environmental resistance.
Table of Comparison
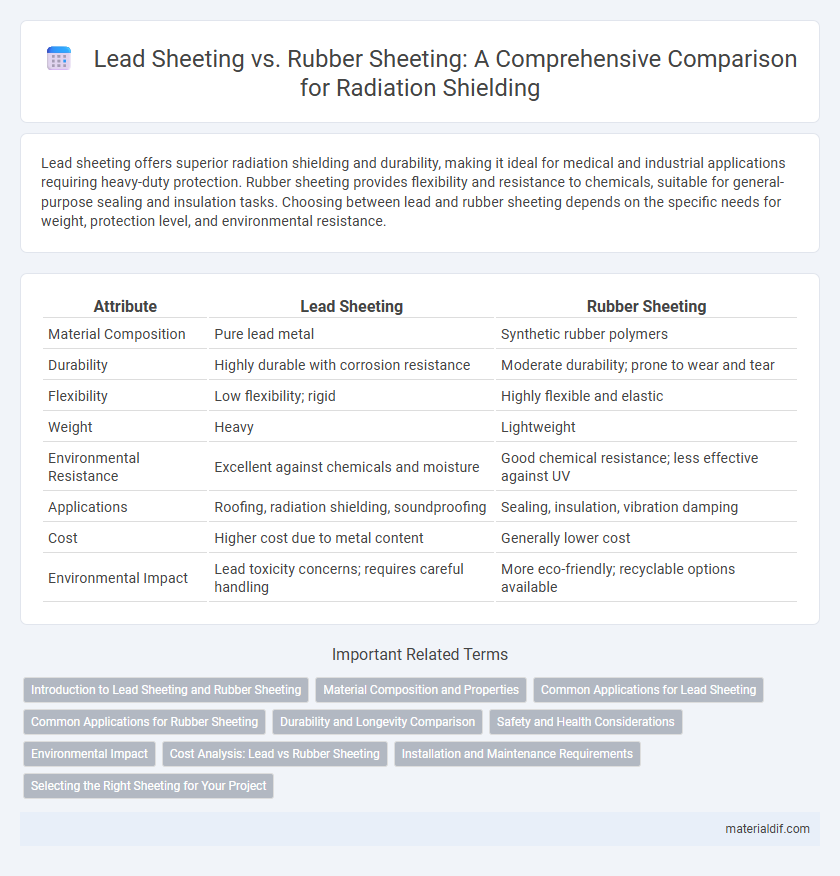
| Attribute | Lead Sheeting | Rubber Sheeting |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Pure lead metal | Synthetic rubber polymers |
| Durability | Highly durable with corrosion resistance | Moderate durability; prone to wear and tear |
| Flexibility | Low flexibility; rigid | Highly flexible and elastic |
| Weight | Heavy | Lightweight |
| Environmental Resistance | Excellent against chemicals and moisture | Good chemical resistance; less effective against UV |
| Applications | Roofing, radiation shielding, soundproofing | Sealing, insulation, vibration damping |
| Cost | Higher cost due to metal content | Generally lower cost |
| Environmental Impact | Lead toxicity concerns; requires careful handling | More eco-friendly; recyclable options available |
Introduction to Lead Sheeting and Rubber Sheeting
Lead sheeting offers exceptional durability and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for roofing, flashing, and waterproofing applications in construction. Rubber sheeting provides flexibility and elasticity, often used for sealing, vibration dampening, and protective linings in industrial environments. Both materials serve distinct roles based on their physical properties and environmental suitability.
Material Composition and Properties
Lead sheeting consists primarily of pure lead, a dense metal known for its excellent corrosion resistance, malleability, and radiation shielding properties, making it ideal for construction and industrial applications. Rubber sheeting is composed of natural or synthetic elastomers, offering flexibility, durability, and resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and weathering, which suits it for sealing, gasketing, and cushioning purposes. The contrasting compositions result in lead sheeting excelling in heavy-duty, protective roles, while rubber sheeting provides elastic and insulating functions.
Common Applications for Lead Sheeting
Lead sheeting is widely used in construction for roofing, flashing, and weatherproofing due to its durability, malleability, and corrosion resistance. It is commonly applied in radiation shielding in medical and nuclear facilities, providing effective protection against X-rays and gamma rays. Additionally, lead sheeting serves in soundproofing and damp-proofing applications, enhancing building performance and longevity.
Common Applications for Rubber Sheeting
Rubber sheeting is commonly used in industrial gaskets, vibration dampening, and weatherproofing due to its excellent elasticity and resistance to oils and chemicals. It is preferred for sealing applications in automotive, manufacturing, and construction industries where flexibility and durability are essential. Unlike lead sheeting, rubber sheeting offers superior impact absorption and non-toxic properties, making it suitable for food processing and medical environments.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Lead sheeting offers superior durability and longevity compared to rubber sheeting, resisting weathering, corrosion, and UV damage for decades without significant degradation. Rubber sheeting tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to sunlight and temperature fluctuations, resulting in cracks and loss of elasticity within 5-10 years. For applications requiring long-term protection and minimal maintenance, lead sheeting remains the more reliable option.
Safety and Health Considerations
Lead sheeting poses significant health risks due to lead's toxicity, requiring strict handling protocols, protective equipment, and proper ventilation to prevent lead poisoning and respiratory issues. Rubber sheeting offers a safer alternative as it is non-toxic and less likely to cause harmful exposure, making it preferable in environments prioritizing worker safety. Both materials require awareness of their properties, but rubber sheeting significantly minimizes health hazards compared to lead sheeting.
Environmental Impact
Lead sheeting poses significant environmental risks due to its toxicity and potential to contaminate soil and water systems, leading to long-term ecological damage. Rubber sheeting offers a more sustainable alternative, as it is often made from recyclable materials and has a lower environmental footprint during production and disposal. Choosing rubber sheeting minimizes hazardous waste and reduces the impact on ecosystems compared to lead sheeting.
Cost Analysis: Lead vs Rubber Sheeting
Lead sheeting typically incurs higher initial costs due to the raw material's weight and density compared to rubber sheeting, which is generally more affordable and easier to handle. While lead offers superior durability and long-term performance in applications requiring weather resistance and impact protection, rubber sheeting provides cost-effective flexibility and insulation but may require more frequent replacement. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals that lead sheeting's upfront investment can be justified by its longevity, whereas rubber sheeting suits budgets prioritizing lower immediate expenses and ease of installation.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Lead sheeting requires precise handling during installation due to its weight and malleability, often necessitating skilled labor for proper fitting on roofs or structures to ensure durability. Maintenance involves periodic inspections for corrosion and potential damage from environmental exposure, with repairs typically requiring specialized welding or patching techniques. Rubber sheeting, conversely, offers easier installation with flexible, lightweight materials that can be quickly adhered or mechanically fastened, demanding less specialized labor and fewer tools, and requires less frequent maintenance mainly focused on checking for tears or punctures.
Selecting the Right Sheeting for Your Project
Lead sheeting offers superior durability and excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for long-term roofing and waterproofing projects, especially in historic building restoration. Rubber sheeting provides exceptional flexibility and tensile strength, suitable for applications requiring waterproof membranes and expansion joints in modern construction. Selecting the right sheeting depends on environmental exposure, structural requirements, and project longevity, balancing lead's weight and cost against rubber's adaptability and ease of installation.
Lead Sheeting vs Rubber Sheeting Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com