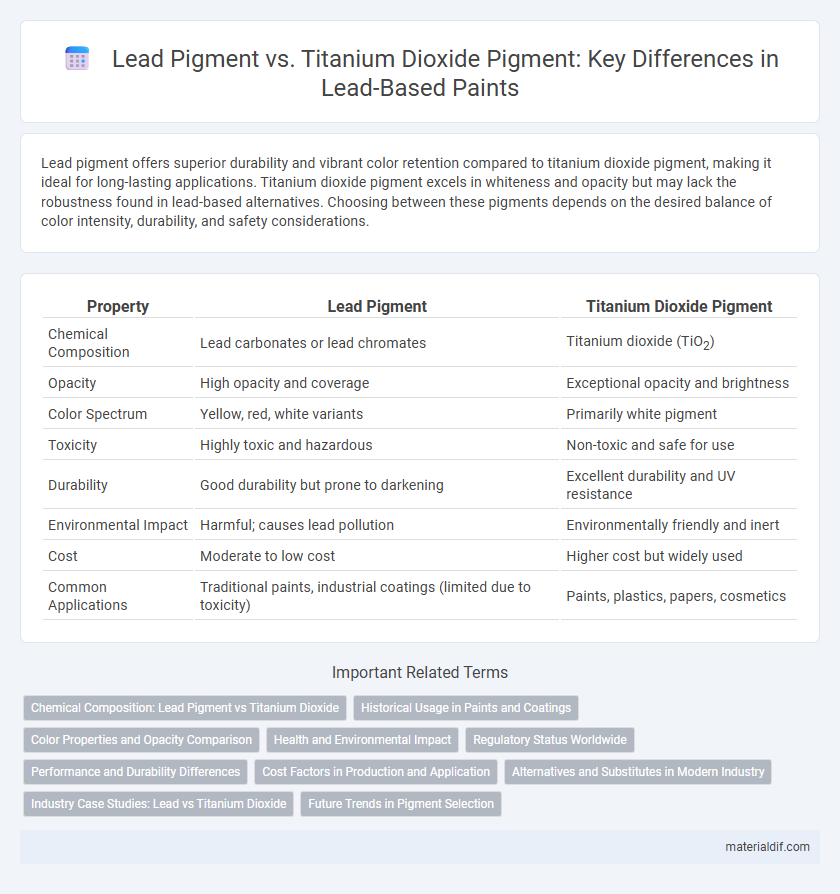
Lead pigment offers superior durability and vibrant color retention compared to titanium dioxide pigment, making it ideal for long-lasting applications. Titanium dioxide pigment excels in whiteness and opacity but may lack the robustness found in lead-based alternatives. Choosing between these pigments depends on the desired balance of color intensity, durability, and safety considerations.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lead Pigment | Titanium Dioxide Pigment |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Lead carbonates or lead chromates | Titanium dioxide (TiO2) |
| Opacity | High opacity and coverage | Exceptional opacity and brightness |
| Color Spectrum | Yellow, red, white variants | Primarily white pigment |
| Toxicity | Highly toxic and hazardous | Non-toxic and safe for use |
| Durability | Good durability but prone to darkening | Excellent durability and UV resistance |
| Environmental Impact | Harmful; causes lead pollution | Environmentally friendly and inert |
| Cost | Moderate to low cost | Higher cost but widely used |
| Common Applications | Traditional paints, industrial coatings (limited due to toxicity) | Paints, plastics, papers, cosmetics |
Chemical Composition: Lead Pigment vs Titanium Dioxide
Lead pigment primarily consists of lead carbonate (PbCO3) or lead chromate (PbCrO4), known for its bright yellow to orange hues and high opacity. Titanium dioxide pigment is composed of titanium dioxide (TiO2) in either rutile or anatase crystalline forms, offering superior whiteness, brightness, and UV resistance. The chemical stability and non-toxicity of titanium dioxide make it a preferred choice over lead pigments, which pose significant toxicity and environmental hazards.
Historical Usage in Paints and Coatings
Lead pigment, notably lead white, dominated paint formulations for centuries due to its excellent opacity and durability, playing a critical role in artistic and architectural applications from the Renaissance through the early 20th century. Titanium dioxide pigment emerged in the early 1900s as a safer, non-toxic alternative, rapidly gaining popularity because of its superior whiteness, brightness, and UV resistance. Despite its historical prominence, lead pigment usage declined sharply after regulatory restrictions highlighted health risks, making titanium dioxide the industry standard in modern paints and coatings.
Color Properties and Opacity Comparison
Lead pigments exhibit superior opacity and vibrant color intensity compared to titanium dioxide pigments, making them highly effective for applications requiring rich hues and strong coverage. Titanium dioxide pigments offer excellent whiteness and brightness but generally provide lower opacity than lead-based pigments, often necessitating higher application thicknesses. The superior hiding power of lead pigments contributes to their historical preference in artist paints and industrial coatings despite modern environmental concerns.
Health and Environmental Impact
Lead pigment poses significant health risks due to its toxicity, causing neurological damage and developmental issues, while titanium dioxide pigment is generally considered safer for human health. Environmentally, lead pigments contribute to soil and water contamination with persistent heavy metals, whereas titanium dioxide, although less toxic, can impact aquatic ecosystems through nanoparticle runoff. Regulatory bodies increasingly restrict lead pigment use to minimize its hazardous effects on both health and the environment.
Regulatory Status Worldwide
Lead pigment faces widespread regulatory restrictions due to its high toxicity and environmental hazards, with many countries banning or severely limiting its use in consumer products, especially paints. Titanium dioxide pigment is globally recognized as a safer alternative, approved by major regulatory agencies such as the U.S. EPA, EU REACH, and WHO for widespread use in coatings, plastics, and cosmetics. Regulatory frameworks consistently classify lead pigments as hazardous substances, enforcing strict controls, while titanium dioxide enjoys broad regulatory acceptance due to its non-toxic profile.
Performance and Durability Differences
Lead pigment offers superior opacity and excellent adhesion, resulting in durable coatings resistant to moisture and UV degradation. Titanium dioxide pigment provides higher brightness and better weather resistance but may require additional additives to match lead's corrosion protection and longevity in harsh environments. Comparative studies indicate lead pigments excel in performance for industrial metal coatings, while titanium dioxide is preferred for eco-friendly applications due to lower toxicity.
Cost Factors in Production and Application
Lead pigment often incurs higher production costs due to stricter environmental regulations and hazardous material handling requirements, impacting overall manufacturing expenses. Titanium dioxide pigment benefits from large-scale availability and efficient production methods, resulting in lower unit costs and widespread use in coatings and plastics. Application costs favor titanium dioxide as it offers superior coverage with less pigment needed, reducing material costs despite a generally higher raw material price compared to lead-based pigments.
Alternatives and Substitutes in Modern Industry
Lead pigment, historically valued for its opacity and durability, is increasingly replaced by titanium dioxide pigment in modern industry due to health and environmental concerns. Titanium dioxide offers superior whiteness, non-toxicity, and excellent UV resistance, making it the preferred alternative in paints, coatings, and plastics. Emerging substitutes like zinc oxide and organic pigments also provide viable options, especially in applications demanding enhanced safety and sustainability.
Industry Case Studies: Lead vs Titanium Dioxide
Industry case studies reveal that lead pigments, historically valued for their durability and opacity, have largely been supplanted by titanium dioxide pigments due to toxicity concerns and stringent environmental regulations. Titanium dioxide offers superior brightness, whiteness, and non-toxic properties, making it the preferred choice in coatings, plastics, and paper industries. Research highlights that titanium dioxide's chemical stability and UV resistance enhance product longevity, driving its dominance over lead-based pigments in modern industrial applications.
Future Trends in Pigment Selection
Future trends in pigment selection emphasize the shift from lead-based pigments to titanium dioxide due to regulatory restrictions and environmental concerns. Titanium dioxide offers superior opacity, whiteness, and non-toxicity, making it the preferred choice in coatings, plastics, and paints. Advances in nano-engineered titanium dioxide pigments are expected to enhance durability and UV resistance, driving its dominance in sustainable pigment markets.
Lead pigment vs Titanium dioxide pigment Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com