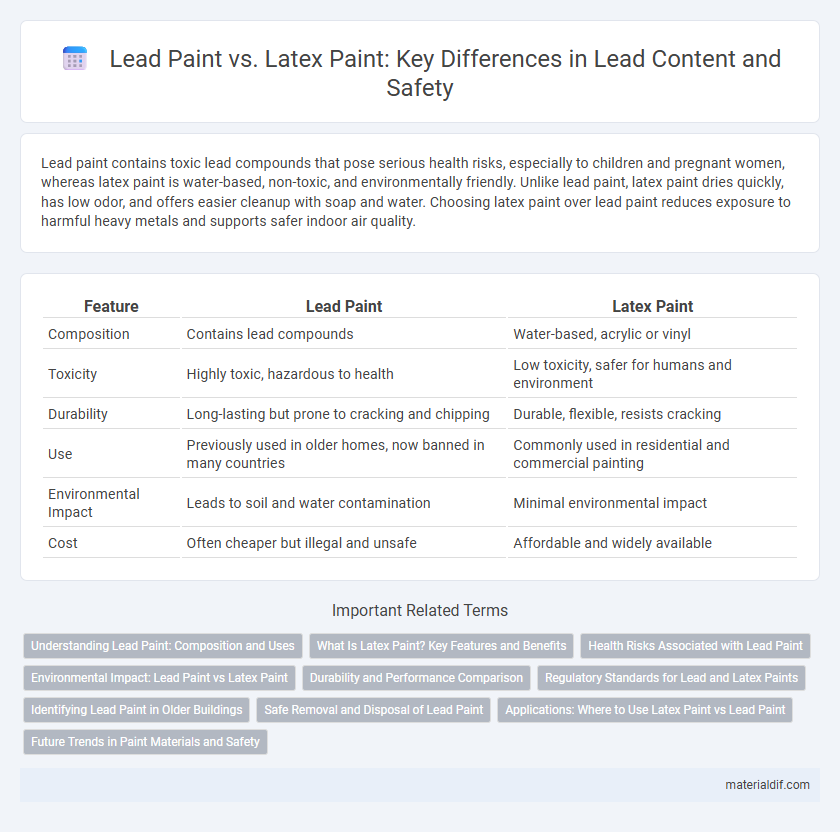
Lead paint contains toxic lead compounds that pose serious health risks, especially to children and pregnant women, whereas latex paint is water-based, non-toxic, and environmentally friendly. Unlike lead paint, latex paint dries quickly, has low odor, and offers easier cleanup with soap and water. Choosing latex paint over lead paint reduces exposure to harmful heavy metals and supports safer indoor air quality.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lead Paint | Latex Paint |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Contains lead compounds | Water-based, acrylic or vinyl |
| Toxicity | Highly toxic, hazardous to health | Low toxicity, safer for humans and environment |
| Durability | Long-lasting but prone to cracking and chipping | Durable, flexible, resists cracking |
| Use | Previously used in older homes, now banned in many countries | Commonly used in residential and commercial painting |
| Environmental Impact | Leads to soil and water contamination | Minimal environmental impact |
| Cost | Often cheaper but illegal and unsafe | Affordable and widely available |
Understanding Lead Paint: Composition and Uses
Lead paint contains lead compounds such as lead carbonate or lead chromate, which provided durability and vibrant colors used extensively in homes and industrial applications before its ban in residential use in the late 1970s. The chemical composition contributed to its resistance against moisture and corrosion, making it ideal for metal surfaces, wooden structures, and exterior walls. Understanding lead paint's toxic properties and its persistence in old buildings is crucial for proper identification and safe removal during renovation or remodeling projects.
What Is Latex Paint? Key Features and Benefits
Latex paint is a water-based paint composed primarily of acrylic resins, offering quick drying times and easy cleanup with soap and water. It provides excellent flexibility, resistance to cracking, and low levels of harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs), making it a safer alternative to lead-based paint. Ideal for interior and exterior surfaces, latex paint delivers vibrant color retention and durability, enhancing both aesthetics and indoor air quality.
Health Risks Associated with Lead Paint
Lead paint contains toxic lead compounds that pose significant health risks, especially to children and pregnant women. Exposure to lead paint can cause neurological damage, developmental delays, and respiratory issues. Unlike latex paint, which is water-based and non-toxic, lead paint deteriorates over time, releasing harmful dust and chips that increase the risk of lead poisoning.
Environmental Impact: Lead Paint vs Latex Paint
Lead paint releases toxic lead particles into the environment, contaminating soil and water, posing severe health risks to humans and wildlife. Latex paint, made primarily from water-based polymers, has a significantly lower environmental footprint due to its reduced emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and non-toxic composition. Choosing latex paint over lead-based alternatives helps minimize hazardous waste and supports safer ecosystem balances.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Lead paint offers superior durability and excellent adhesion on various surfaces, making it resistant to chipping and wear over time. Latex paint, while less durable than lead-based options, provides better flexibility, resists cracking, and dries faster with lower toxicity. For long-term performance, lead paint excels in harsh environments but poses significant health risks, whereas latex paint balances reasonable durability with enhanced safety and ease of maintenance.
Regulatory Standards for Lead and Latex Paints
Regulatory standards for lead paint strictly limit lead content to minimize health risks, with the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission enforcing a maximum of 90 parts per million lead in residential paints. Latex paints are subject to VOC (volatile organic compounds) regulations, governed by the EPA and state authorities, ensuring lower emissions and improved indoor air quality. Compliance with these regulations is critical for manufacturers and consumers to prevent lead poisoning and reduce environmental impact.
Identifying Lead Paint in Older Buildings
Lead paint in older buildings is typically characterized by its age, often applied before 1978 when lead-based paints were banned for residential use in the United States. Identification involves using a lead paint test kit or hiring certified professionals who utilize X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analyzers for accurate detection. Recognizing deteriorating, chipping, or peeling paint in homes built before the late 20th century is critical for addressing potential lead exposure risks.
Safe Removal and Disposal of Lead Paint
Safe removal and disposal of lead paint require specialized techniques to prevent toxic lead dust and chips from contaminating the environment. Professional abatement involves using HEPA vacuums, wet sanding, and chemical strippers, while sealed containment and proper disposal at hazardous waste facilities ensure compliance with EPA regulations. Latex paint, being non-toxic and water-based, poses no such risks and can be removed and disposed of with standard safety precautions.
Applications: Where to Use Latex Paint vs Lead Paint
Latex paint is ideal for interior walls, ceilings, and trim due to its low toxicity, quick drying time, and easy cleanup with water, making it suitable for homes, schools, and offices. Lead paint, once widely used for its durability and moisture resistance, is now restricted because of its toxicity, but it may still be found in older buildings and used in certain industrial applications requiring high corrosion resistance. For safety reasons, modern construction and renovation projects prioritize latex paint to reduce health risks associated with lead exposure.
Future Trends in Paint Materials and Safety
Future trends in paint materials emphasize the shift from lead-based paints to advanced latex formulations with enhanced durability and non-toxic properties. Innovations in bio-based and low-VOC latex paints offer safer alternatives, reducing environmental and health risks associated with lead exposure. Regulatory policies continue to favor eco-friendly latex paints, driving research towards sustainable, high-performance coatings for residential and industrial use.
Lead Paint vs Latex Paint Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com