Hemp plastic offers a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based plastic by being biodegradable and derived from renewable resources, reducing environmental pollution and reliance on fossil fuels. Unlike conventional plastics, hemp plastic decomposes more rapidly, minimizing landfill waste and greenhouse gas emissions. Its production also consumes less energy and water, making it an eco-friendly choice in various industries.
Table of Comparison
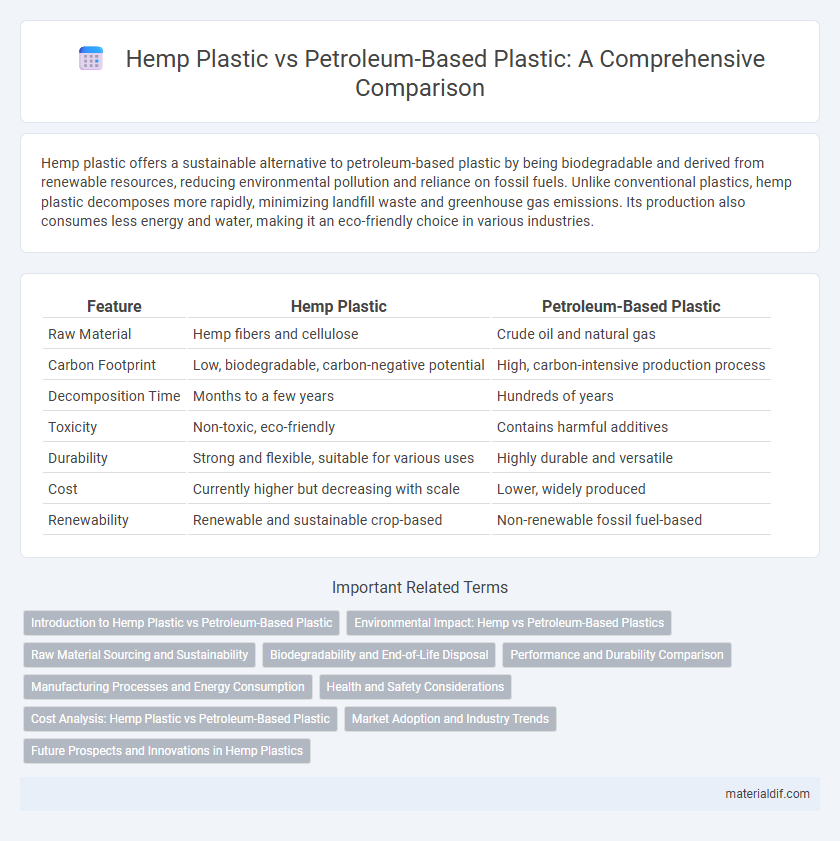
| Feature | Hemp Plastic | Petroleum-Based Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Hemp fibers and cellulose | Crude oil and natural gas |
| Carbon Footprint | Low, biodegradable, carbon-negative potential | High, carbon-intensive production process |
| Decomposition Time | Months to a few years | Hundreds of years |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic, eco-friendly | Contains harmful additives |
| Durability | Strong and flexible, suitable for various uses | Highly durable and versatile |
| Cost | Currently higher but decreasing with scale | Lower, widely produced |
| Renewability | Renewable and sustainable crop-based | Non-renewable fossil fuel-based |
Introduction to Hemp Plastic vs Petroleum-Based Plastic
Hemp plastic is a biodegradable, eco-friendly alternative derived from hemp fibers and cellulose, offering reduced carbon emissions and less reliance on fossil fuels compared to petroleum-based plastic. Petroleum-based plastics, made from non-renewable crude oil, contribute significantly to environmental pollution and greenhouse gas emissions due to their slow degradation rates. The rising demand for sustainable materials positions hemp plastic as a promising solution to mitigate plastic waste and fossil fuel dependency.
Environmental Impact: Hemp vs Petroleum-Based Plastics
Hemp plastic significantly reduces environmental impact by being biodegradable and requiring less energy for production compared to petroleum-based plastics, which contribute to pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Hemp cultivation absorbs CO2, promoting carbon sequestration, while petroleum extraction and plastic manufacturing release substantial carbon dioxide, exacerbating climate change. The biodegradability of hemp plastic prevents long-term landfill accumulation and marine pollution, unlike petroleum plastics that persist for hundreds of years.
Raw Material Sourcing and Sustainability
Hemp plastic is derived from renewable hemp fibers and cellulose, offering a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based plastic, which relies heavily on finite fossil fuels. The cultivation of hemp requires fewer pesticides, less water, and enriches soil health, making its raw material sourcing environmentally friendly. In contrast, petroleum-based plastics contribute significantly to carbon emissions and environmental pollution throughout their lifecycle.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Disposal
Hemp plastic offers superior biodegradability compared to petroleum-based plastic, breaking down naturally within months under composting conditions, which significantly reduces environmental pollution. In contrast, petroleum-based plastics can take hundreds of years to decompose, contributing to persistent landfill waste and microplastic contamination. End-of-life disposal of hemp plastic is more sustainable, as it can be composted or recycled biologically, whereas petroleum-based plastics often require complex and energy-intensive recycling processes.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Hemp plastic demonstrates superior biodegradability and resistance to UV degradation compared to petroleum-based plastic, making it a more sustainable option for long-term use. Its tensile strength can rival or exceed that of conventional plastics, enhancing its durability in various applications such as automotive parts and packaging. Furthermore, hemp plastic exhibits better thermal stability, reducing deformation under high temperatures and extending product lifespan.
Manufacturing Processes and Energy Consumption
Hemp plastic manufacturing involves the extraction of cellulose fibers from hemp plants, which are then processed into biodegradable composites using lower energy inputs compared to petroleum-based plastic production that relies heavily on fossil fuel extraction and refining. The energy consumption for producing hemp plastic is significantly reduced due to the renewable nature of hemp and fewer synthesis steps required in polymer formation. In contrast, petroleum-based plastics demand high temperatures and intensive chemical processes that increase carbon emissions and overall environmental impact.
Health and Safety Considerations
Hemp plastic offers significant health and safety advantages over petroleum-based plastic due to its biodegradability and non-toxic composition, reducing harmful chemical exposure and environmental pollution. Petroleum-based plastics often contain additives like phthalates and BPA, which are linked to endocrine disruption and other health risks during production and disposal. Utilizing hemp plastic minimizes the release of carcinogenic substances and microplastics, enhancing overall public health and workplace safety.
Cost Analysis: Hemp Plastic vs Petroleum-Based Plastic
Hemp plastic generally incurs higher initial production costs due to limited agricultural scale and processing technology compared to petroleum-based plastic, which benefits from established large-scale refining infrastructure and raw material availability. Long-term cost advantages of hemp plastic emerge through renewable resource usage, potential biodegradability, and reduced environmental remediation expenses associated with petroleum-based polymer waste. Economic feasibility improves as industrial hemp cultivation expands, driving down material costs and enhancing hemp plastic's competitiveness in the sustainable materials market.
Market Adoption and Industry Trends
Hemp plastic is gaining momentum as sustainable packaging and automotive industries seek eco-friendly alternatives to petroleum-based plastics, driven by increasing consumer demand for biodegradable materials. Market adoption of hemp plastic is bolstered by its lower carbon footprint, renewability, and regulatory incentives promoting green products. Industry trends indicate a growing investment in hemp cultivation and bioplastic R&D, positioning hemp plastic as a competitive player in the global plastics market.
Future Prospects and Innovations in Hemp Plastics
Hemp plastics offer promising future prospects due to their biodegradability, lower carbon footprint, and sustainable sourcing compared to petroleum-based plastics derived from fossil fuels. Innovations in hemp biocomposites are enhancing material strength, flexibility, and cost-efficiency, positioning hemp as a viable alternative in automotive, packaging, and consumer goods industries. Ongoing research in polymer blending and cellulose fiber optimization continues to improve the performance and scalability of hemp plastic production.
Hemp plastic vs Petroleum-based plastic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com