Hemp bioplastic offers a sustainable alternative to petroleum plastic by being biodegradable and derived from renewable resources, reducing environmental pollution and carbon footprint. Unlike petroleum-based plastics, hemp bioplastics decompose naturally without releasing harmful toxins, supporting a circular economy. The cultivation of hemp requires fewer pesticides and less water, making hemp bioplastic a more eco-friendly option for reducing plastic waste globally.
Table of Comparison
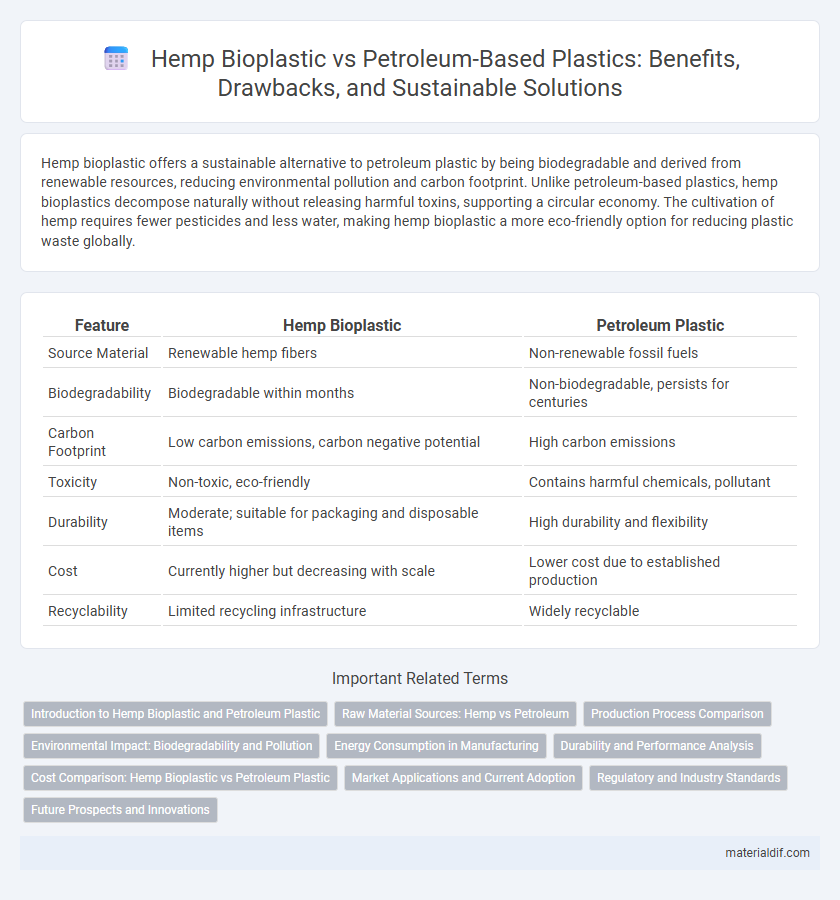
| Feature | Hemp Bioplastic | Petroleum Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Source Material | Renewable hemp fibers | Non-renewable fossil fuels |
| Biodegradability | Biodegradable within months | Non-biodegradable, persists for centuries |
| Carbon Footprint | Low carbon emissions, carbon negative potential | High carbon emissions |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic, eco-friendly | Contains harmful chemicals, pollutant |
| Durability | Moderate; suitable for packaging and disposable items | High durability and flexibility |
| Cost | Currently higher but decreasing with scale | Lower cost due to established production |
| Recyclability | Limited recycling infrastructure | Widely recyclable |
Introduction to Hemp Bioplastic and Petroleum Plastic
Hemp bioplastic is derived from renewable hemp fibers and cellulose, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics made from fossil fuels. Hemp bioplastics exhibit biodegradability, lower carbon emissions, and reduced environmental impact compared to petroleum plastics, which contribute significantly to pollution and non-biodegradable waste. The growing demand for eco-friendly materials highlights the potential of hemp bioplastics in reducing reliance on finite petroleum resources while supporting circular economy initiatives.
Raw Material Sources: Hemp vs Petroleum
Hemp bioplastic derives from the cellulose and fibers of the hemp plant, offering a renewable and biodegradable raw material source that reduces reliance on fossil fuels. Petroleum plastic is synthesized from hydrocarbons extracted from non-renewable crude oil, contributing to long-term environmental degradation and carbon emissions. The sustainable cultivation of hemp requires less land, water, and pesticides compared to petroleum extraction, making hemp bioplastic a more eco-friendly alternative in raw material sourcing.
Production Process Comparison
Hemp bioplastic production involves extracting cellulose fibers from hemp stalks, which are then processed into biodegradable polymers through environmentally friendly methods that reduce carbon emissions. In contrast, petroleum plastic manufacturing relies on refining crude oil through energy-intensive processes that emit significant greenhouse gases and generate non-renewable waste. The renewable nature and lower environmental impact of hemp bioplastics make their production process more sustainable compared to the fossil fuel-based petroleum plastics.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradability and Pollution
Hemp bioplastic significantly reduces environmental impact due to its biodegradability, decomposing naturally within months, unlike petroleum plastic which can persist for centuries and contribute to long-term pollution. The cultivation of hemp requires fewer pesticides and less water, minimizing soil and water contamination associated with petroleum plastic production. Hemp bioplastics also lower carbon emissions throughout their lifecycle, presenting a sustainable alternative to conventional plastics derived from fossil fuels.
Energy Consumption in Manufacturing
Hemp bioplastic requires significantly less energy during manufacturing compared to petroleum-based plastic, reducing overall carbon emissions and environmental impact. The cultivation of hemp is energy-efficient, as it absorbs CO2 and grows quickly with minimal agricultural inputs, lowering the embodied energy of the final bioplastic product. In contrast, petroleum plastic relies on energy-intensive extraction and refining processes, increasing its manufacturing energy consumption dramatically.
Durability and Performance Analysis
Hemp bioplastic exhibits superior biodegradability and resistance to UV degradation compared to petroleum plastic, enhancing environmental sustainability without compromising durability. Performance analysis reveals hemp-based plastics maintain structural integrity under heat and mechanical stress, rivaling conventional petroleum plastics in tensile strength and flexibility. These properties make hemp bioplastics a viable alternative for applications demanding long-term performance and reduced ecological impact.
Cost Comparison: Hemp Bioplastic vs Petroleum Plastic
Hemp bioplastic offers a competitive advantage over petroleum plastic with lower raw material costs due to the rapid growth cycle and carbon sequestration benefits of hemp crops. Production expenses for hemp bioplastic remain higher currently due to limited processing infrastructure but are expected to decrease as technology scales. Petroleum plastic production benefits from established, large-scale supply chains, resulting in lower immediate manufacturing costs but higher environmental externalities and fluctuating oil prices impact long-term cost stability.
Market Applications and Current Adoption
Hemp bioplastic is gaining traction in industries such as packaging, automotive, and consumer goods due to its biodegradability and renewable nature, contrasting with petroleum plastic's dominance in mass production and durability. Market adoption of hemp bioplastic is expanding as companies seek sustainable alternatives to reduce plastic pollution and carbon footprint, though petroleum plastic remains prevalent due to its established supply chains and cost-effectiveness. Innovations in hemp fiber processing and increasing regulations against single-use plastics are driving growth in hemp bioplastic applications across commercial sectors.
Regulatory and Industry Standards
Hemp bioplastic offers significant environmental benefits over petroleum plastic, prompting regulatory bodies such as the European Union and the U.S. EPA to introduce specific standards encouraging its adoption. Industry standards like ASTM D7611 and ISO 22642 are evolving to address the biodegradability and compostability of hemp bioplastics, ensuring compliance with safety and environmental guidelines. The growing emphasis on sustainable materials is driving policy shifts that favor hemp bioplastics in packaging and automotive sectors due to their lower carbon footprint and renewable nature.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Hemp bioplastic offers significant environmental advantages over petroleum-based plastics, including biodegradability and lower carbon emissions during production. Innovations in hemp fiber extraction and processing technologies are enhancing the material's strength and flexibility, making it a viable alternative for packaging and automotive industries. Future prospects indicate growing investment in hemp bioplastics research, driven by increasing regulatory pressures to reduce plastic pollution and a shift toward sustainable materials in global markets.
Hemp bioplastic vs Petroleum plastic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com