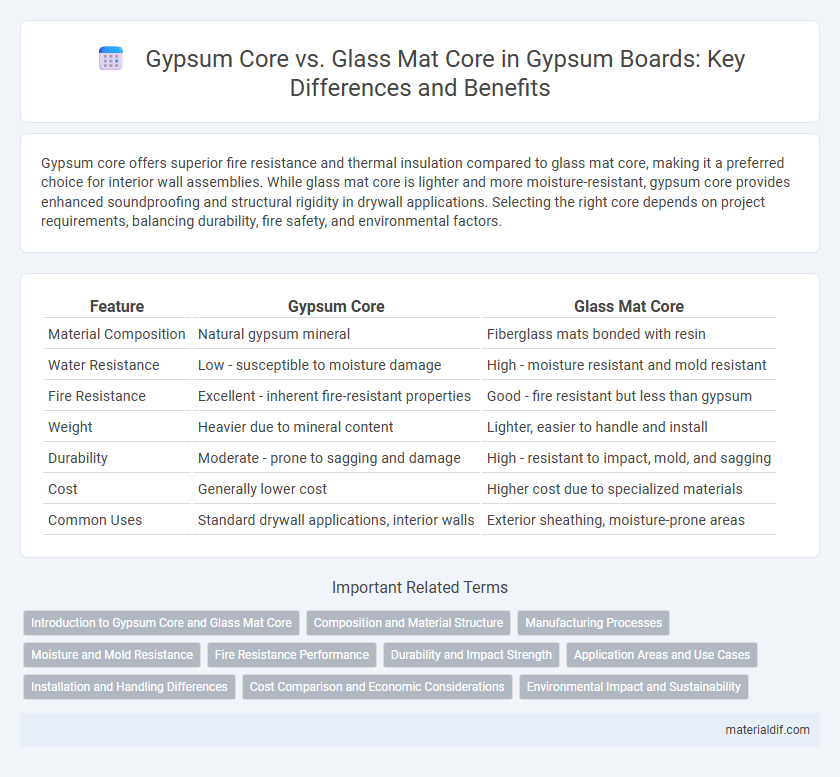
Gypsum core offers superior fire resistance and thermal insulation compared to glass mat core, making it a preferred choice for interior wall assemblies. While glass mat core is lighter and more moisture-resistant, gypsum core provides enhanced soundproofing and structural rigidity in drywall applications. Selecting the right core depends on project requirements, balancing durability, fire safety, and environmental factors.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gypsum Core | Glass Mat Core |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural gypsum mineral | Fiberglass mats bonded with resin |
| Water Resistance | Low - susceptible to moisture damage | High - moisture resistant and mold resistant |
| Fire Resistance | Excellent - inherent fire-resistant properties | Good - fire resistant but less than gypsum |
| Weight | Heavier due to mineral content | Lighter, easier to handle and install |
| Durability | Moderate - prone to sagging and damage | High - resistant to impact, mold, and sagging |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to specialized materials |
| Common Uses | Standard drywall applications, interior walls | Exterior sheathing, moisture-prone areas |
Introduction to Gypsum Core and Glass Mat Core
Gypsum core consists of a dense, calcined gypsum material encased between layers of paper or fiberglass mats, offering excellent fire resistance and sound insulation in building panels. Glass mat core features a fiberglass mat saturated with resin or other binders, providing enhanced moisture resistance and durability in exterior applications. Both cores are integral to wallboard and ceiling panel manufacturing, with gypsum core favored for indoor environments and glass mat core suitable for moisture-prone areas.
Composition and Material Structure
Gypsum core consists primarily of calcium sulfate dihydrate crystals formed into a rigid, dense matrix that offers excellent fire resistance and soundproofing. Glass mat core is composed of fiberglass mats impregnated with resin, creating a lightweight, moisture-resistant structure that enhances durability in humid environments. The material structure of gypsum promotes thermal insulation and rigidity, whereas glass mat cores provide flexibility and reduced susceptibility to mold and mildew.
Manufacturing Processes
Gypsum core boards are manufactured by hydrating and mixing gypsum with additives, then sandwiching the slurry between facing sheets and curing it to form a rigid core. Glass mat core boards use fibrous glass mats impregnated with resins, pressed under heat to create a moisture-resistant, lightweight core. The gypsum process emphasizes chemical setting and drying, while the glass mat process relies on thermal curing and composite bonding techniques.
Moisture and Mold Resistance
Gypsum core offers good fire resistance but is highly susceptible to moisture damage and mold growth, compromising structural integrity in damp environments. Glass mat core, composed of fiberglass mats, provides superior moisture and mold resistance, making it ideal for high-humidity areas such as bathrooms and kitchens. Selecting glass mat core drywall significantly reduces the risk of mold infestation and prolongs wall durability in moisture-prone conditions.
Fire Resistance Performance
Gypsum core boards demonstrate superior fire resistance due to their inherent ability to release water vapor when exposed to high temperatures, effectively slowing heat transfer and preventing fire spread. Glass mat core panels, while providing enhanced moisture resistance, often lack the same level of fire retardancy as gypsum, making gypsum core a preferred choice in fire-rated wall assemblies. Fire tests such as ASTM E119 highlight gypsum's performance in maintaining structural integrity under fire conditions compared to glass mat core alternatives.
Durability and Impact Strength
Gypsum core offers excellent rigidity and fire resistance but is more susceptible to water damage and impact-related cracking compared to glass mat core. Glass mat core provides superior durability and significantly higher impact strength due to its fiberglass reinforcement, which enhances moisture resistance and structural integrity. Choosing glass mat core panels ensures longer-lasting performance in high-moisture and high-traffic environments, reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
Application Areas and Use Cases
Gypsum core is predominantly used in interior wall panels and ceilings due to its fire resistance, soundproofing, and ease of installation, making it ideal for residential and commercial construction. Glass mat core offers enhanced moisture and mold resistance, making it suitable for exterior sheathing, roofing underlayment, and environments exposed to high humidity. Both cores provide structural support, but gypsum excels in fire-rated applications while glass mat is preferred for durability in wet or exterior conditions.
Installation and Handling Differences
Gypsum core panels offer lighter weight and easier cutting, resulting in faster installation compared to glass mat core panels, which are denser and require more effort during handling. Gypsum cores provide superior nail-holding strength, reducing the risk of damage or faulty fastening during setup, whereas glass mat cores resist moisture and mold better but necessitate specialized tools for precise cutting. The ease of handling gypsum core drywall makes it a preferred choice for standard indoor applications, while glass mat core is favored in high-moisture environments despite a more challenging installation process.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Gypsum core drywall typically costs less than glass mat core drywall due to the lower material and manufacturing expenses, making it a preferred choice for budget-sensitive projects. Glass mat cores offer enhanced moisture and mold resistance but come with higher price points, impacting the overall project budget and lifecycle cost. Economic considerations must balance initial cost savings of gypsum core with potential long-term benefits and durability of glass mat core in humid or wet environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gypsum core panels offer a more sustainable option compared to glass mat cores due to their natural composition and recyclability, reducing landfill waste and environmental pollution. The production of gypsum cores typically involves lower energy consumption and emits fewer greenhouse gases than glass mat cores, which rely on synthetic materials and energy-intensive manufacturing processes. Using gypsum cores supports circular economy principles by enabling easier recycling and repurposing in construction, enhancing overall environmental impact reduction.
Gypsum core vs Glass mat core Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com