Tinted glass reduces glare and heat by absorbing solar radiation, making it ideal for energy-efficient buildings. Reflective glass, coated with a thin metallic layer, reflects a significant portion of sunlight, enhancing privacy and reducing cooling costs. Both types of glass improve comfort and energy performance but vary in appearance and light transmission.
Table of Comparison
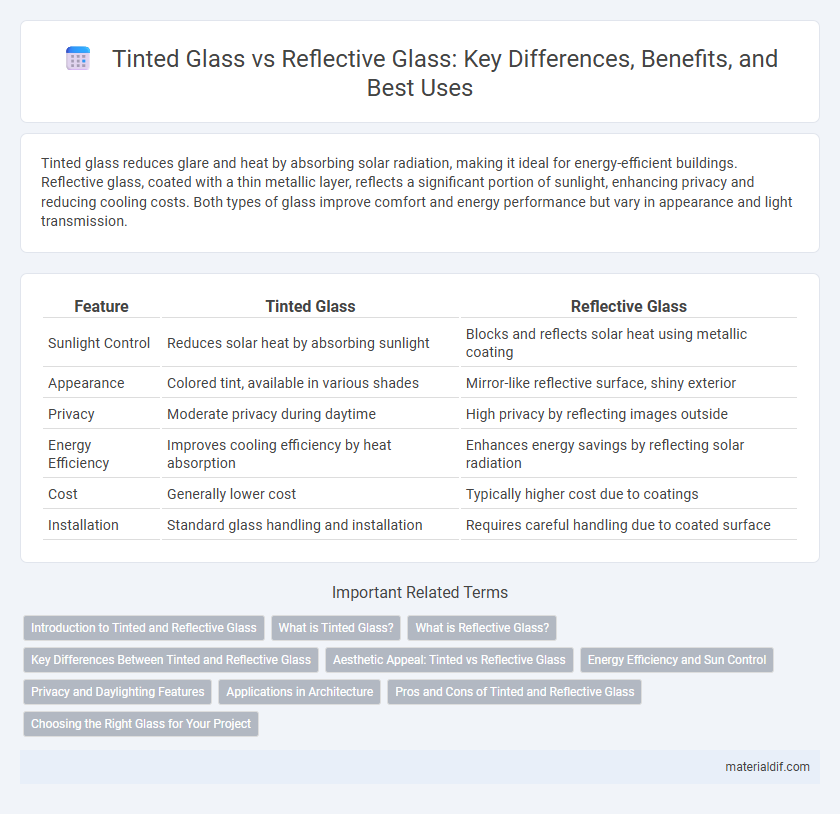
| Feature | Tinted Glass | Reflective Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Sunlight Control | Reduces solar heat by absorbing sunlight | Blocks and reflects solar heat using metallic coating |
| Appearance | Colored tint, available in various shades | Mirror-like reflective surface, shiny exterior |
| Privacy | Moderate privacy during daytime | High privacy by reflecting images outside |
| Energy Efficiency | Improves cooling efficiency by heat absorption | Enhances energy savings by reflecting solar radiation |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Typically higher cost due to coatings |
| Installation | Standard glass handling and installation | Requires careful handling due to coated surface |
Introduction to Tinted and Reflective Glass
Tinted glass reduces solar heat gain and glare by incorporating color pigments, enhancing energy efficiency and comfort in buildings. Reflective glass features a thin metallic coating that reflects a significant portion of sunlight, providing superior privacy and reducing interior heat. Both types improve energy performance while offering aesthetic and functional benefits tailored to specific architectural needs.
What is Tinted Glass?
Tinted glass is specially manufactured by adding metal oxides or other chemicals during production to absorb and reduce solar heat and glare. This type of glass minimizes UV radiation penetration while maintaining transparency and is commonly used in automotive and architectural applications for energy efficiency. Its color variations help in controlling light transmission and enhancing privacy without compromising visibility.
What is Reflective Glass?
Reflective glass is a type of coated glass designed to reduce glare and solar heat gain by reflecting a significant portion of sunlight away from the building. It typically features a metallic or film coating that enhances privacy by limiting visibility from the outside while maintaining clear views from the interior. This makes reflective glass ideal for energy-efficient commercial facades and residential windows where heat control and privacy are prioritized.
Key Differences Between Tinted and Reflective Glass
Tinted glass reduces solar heat by absorbing sunlight and lowering glare, providing privacy without significantly altering exterior appearance. Reflective glass, coated with a thin metallic layer, reflects a higher percentage of solar energy, enhancing energy efficiency and offering mirror-like privacy during daylight. Both types improve building performance but differ in optical characteristics and thermal control effectiveness.
Aesthetic Appeal: Tinted vs Reflective Glass
Tinted glass offers a subtler, uniform color that enhances a building's aesthetic by reducing glare while preserving natural light. Reflective glass provides a mirror-like finish that creates a striking visual contrast and a modern, sleek appearance by reflecting the surrounding environment. Both types of glass contribute distinct stylistic effects, with tinted glass favoring muted elegance and reflective glass emphasizing bold sophistication.
Energy Efficiency and Sun Control
Tinted glass reduces solar heat gain by absorbing a portion of sunlight, improving energy efficiency by lowering cooling costs in buildings. Reflective glass, coated with a thin metallic layer, effectively reflects infrared and visible light, offering superior sun control and reducing glare. Both types enhance comfort and energy savings, but reflective glass generally provides higher performance in blocking solar radiation while maintaining natural daylight.
Privacy and Daylighting Features
Tinted glass reduces glare and solar heat gain by absorbing light, offering moderate privacy while maintaining natural daylighting. Reflective glass features a metallic coating that reflects a significant amount of light, enhancing privacy by limiting visibility from the outside and also controlling daylight penetration. Both types improve energy efficiency, with reflective glass providing superior privacy and more controlled daylight compared to tinted glass.
Applications in Architecture
Tinted glass reduces solar heat gain and glare, making it ideal for residential buildings and office windows where energy efficiency and occupant comfort are priorities. Reflective glass, with its mirrored surface, is commonly used in commercial skyscrapers and facades to enhance privacy while controlling light transmission and minimizing glare. Both types improve building aesthetics and energy performance but cater to different architectural needs based on light control and appearance preferences.
Pros and Cons of Tinted and Reflective Glass
Tinted glass reduces glare and heat by absorbing solar energy, enhancing privacy while preserving visibility but can slightly distort natural colors and reduce daylight. Reflective glass offers superior heat and glare control due to its mirrored surface, improving energy efficiency and privacy, yet it limits outward visibility and may alter the building's exterior appearance. Both types improve comfort and energy savings, with tinted glass favored for subtle aesthetics and reflective glass preferred for high-performance solar control.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Project
Tinted glass absorbs a portion of solar heat and reduces glare by adding color, making it ideal for enhancing privacy and controlling interior temperatures in residential and commercial buildings. Reflective glass features a metallic coating that reflects solar radiation, offering superior heat rejection and privacy while maintaining natural daylight, often preferred for high-rise office facades. Selecting between tinted and reflective glass depends on project requirements such as thermal performance, aesthetic preferences, and light transmission needs to optimize energy efficiency and occupant comfort.
Tinted glass vs Reflective glass Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com