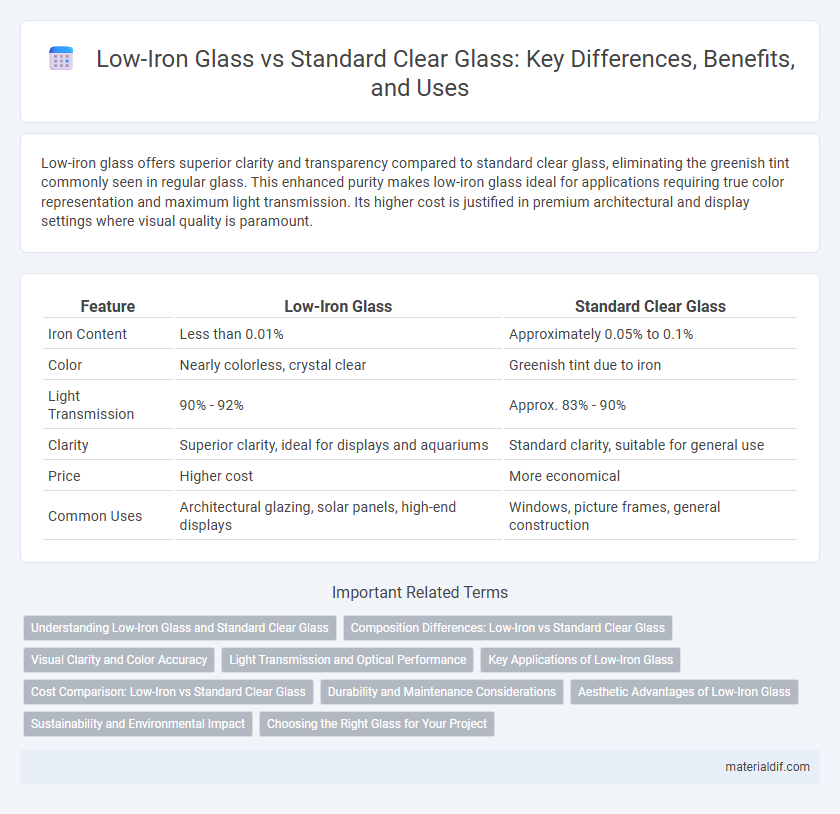
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and transparency compared to standard clear glass, eliminating the greenish tint commonly seen in regular glass. This enhanced purity makes low-iron glass ideal for applications requiring true color representation and maximum light transmission. Its higher cost is justified in premium architectural and display settings where visual quality is paramount.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Low-Iron Glass | Standard Clear Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Iron Content | Less than 0.01% | Approximately 0.05% to 0.1% |
| Color | Nearly colorless, crystal clear | Greenish tint due to iron |
| Light Transmission | 90% - 92% | Approx. 83% - 90% |
| Clarity | Superior clarity, ideal for displays and aquariums | Standard clarity, suitable for general use |
| Price | Higher cost | More economical |
| Common Uses | Architectural glazing, solar panels, high-end displays | Windows, picture frames, general construction |
Understanding Low-Iron Glass and Standard Clear Glass
Low-iron glass contains significantly reduced iron content, typically less than 0.01%, resulting in higher clarity and minimal greenish tint compared to standard clear glass, which usually has about 0.1% iron. This enhanced transparency in low-iron glass improves color accuracy and allows more natural light transmission, making it ideal for applications requiring true color representation and heightened brightness. Standard clear glass's moderate iron level causes a greenish hue, which can distort color perception and slightly reduce light passage.
Composition Differences: Low-Iron vs Standard Clear Glass
Low-iron glass contains significantly reduced iron content compared to standard clear glass, typically less than 0.03% Fe2O3, which minimizes the greenish tint common in conventional clear glass containing about 0.1% to 0.3% iron oxide. This difference in iron oxide concentration enhances light transmittance and color neutrality in low-iron glass, making it ideal for applications requiring high clarity and true color representation. Standard clear glass's higher iron content absorbs more light in the blue-green spectrum, resulting in lower visible light transmission and a subtle green hue.
Visual Clarity and Color Accuracy
Low-iron glass offers superior visual clarity and enhanced color accuracy compared to standard clear glass, due to its reduced iron content that minimizes the greenish tint typical in regular glass. This results in brighter, more true-to-life colors, making it ideal for applications requiring precise color rendering such as art framing and high-end retail displays. Standard clear glass, with higher iron impurities, often distorts colors and reduces transparency, impacting overall visual quality.
Light Transmission and Optical Performance
Low-iron glass offers superior light transmission, typically around 91%, compared to standard clear glass which transmits approximately 83-84%. This enhanced optical performance results from reduced iron content, minimizing the greenish tint found in standard clear glass and providing a clearer, more natural view. The higher clarity and brightness of low-iron glass make it ideal for applications requiring maximum transparency and color accuracy.
Key Applications of Low-Iron Glass
Low-iron glass is preferred in architectural applications requiring maximum light transmission and true color clarity, such as in display cases, solar panels, and museum glazing. Its reduced iron content minimizes the green tint found in standard clear glass, making it ideal for skylights, storefronts, and aquariums where visual accuracy and brightness are critical. This glass type is also favored in high-end furniture and glass facades that demand enhanced transparency and aesthetic appeal.
Cost Comparison: Low-Iron vs Standard Clear Glass
Low-iron glass typically costs 20-50% more than standard clear glass due to its higher purity and enhanced clarity, which reduces the green tint found in standard glass. The price difference varies based on thickness, size, and supplier but is justified in applications requiring superior light transmission and color accuracy, such as display cases and high-end architectural projects. Standard clear glass remains the more cost-effective option for general use where slight green hues are acceptable.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Low-iron glass exhibits higher durability due to its enhanced purity and resistance to discoloration compared to standard clear glass, which is more prone to yellowing over time. Maintenance of low-iron glass requires less frequent cleaning to preserve clarity, while standard clear glass may accumulate visible impurities faster, necessitating regular upkeep. Both types offer strong structural integrity, but the lower iron content in low-iron glass contributes to longer-lasting aesthetic appeal and easier maintenance.
Aesthetic Advantages of Low-Iron Glass
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and brilliance compared to standard clear glass by significantly reducing the greenish tint caused by iron content. Its enhanced transparency allows for more accurate color representation and improved light transmission, making architectural and display applications more visually appealing. The aesthetic advantage of low-iron glass is particularly evident in high-end storefronts, art galleries, and luxury interiors, where clarity and color fidelity are critical.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Low-iron glass offers enhanced solar heat control and natural light transmission, significantly reducing energy consumption in buildings compared to standard clear glass. Its higher clarity allows for better daylight utilization, minimizing reliance on artificial lighting and lowering carbon emissions. Produced with less iron oxide, low-iron glass improves recyclability and supports sustainable construction practices.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Project
Low-iron glass offers higher clarity and transparency compared to standard clear glass, making it ideal for projects requiring true color representation and minimal green tint. Standard clear glass contains higher iron content, resulting in a subtle greenish hue that can affect aesthetics in design-sensitive applications. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing factors such as budget, visual performance, and the specific lighting conditions of the project environment.
Low-iron glass vs Standard clear glass Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com