E-glass and S-glass are two common types of glass fibers used in composite materials, with E-glass primarily valued for its excellent electrical insulation and cost-effectiveness. S-glass offers superior tensile strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for aerospace and high-performance applications. Selecting between E-glass and S-glass depends on the balance needed between durability, strength, and budget considerations in engineering projects.
Table of Comparison
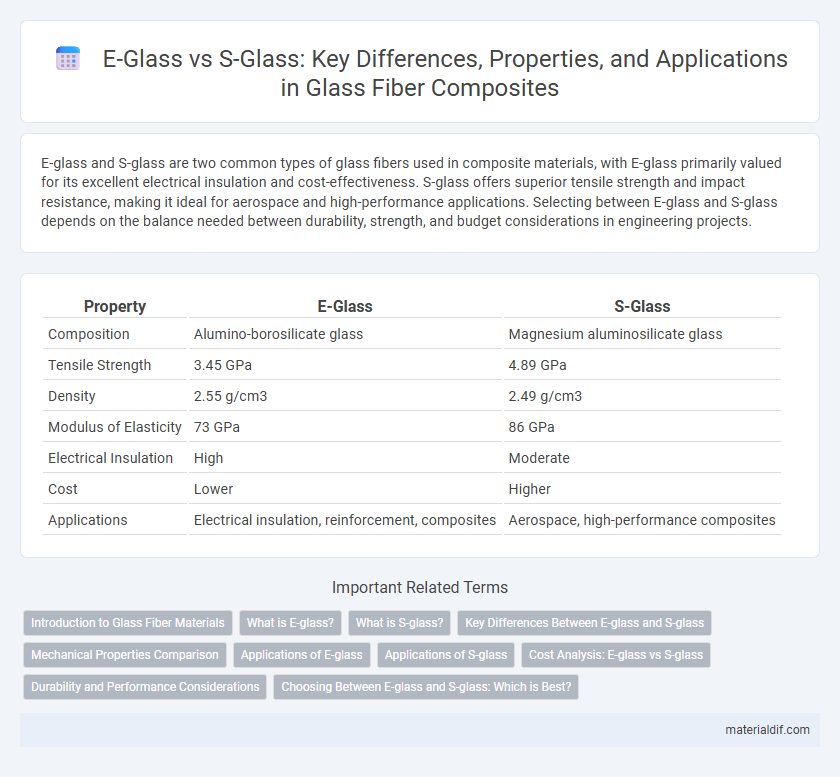
| Property | E-Glass | S-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Alumino-borosilicate glass | Magnesium aluminosilicate glass |
| Tensile Strength | 3.45 GPa | 4.89 GPa |
| Density | 2.55 g/cm3 | 2.49 g/cm3 |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 73 GPa | 86 GPa |
| Electrical Insulation | High | Moderate |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Applications | Electrical insulation, reinforcement, composites | Aerospace, high-performance composites |
Introduction to Glass Fiber Materials
E-glass and S-glass are two primary types of glass fiber materials used in composite manufacturing, each distinguished by their chemical composition and mechanical properties. E-glass, or electrical glass, offers excellent electrical insulation and is cost-effective, making it suitable for general-purpose reinforcement. S-glass, known for its superior tensile strength and thermal resistance, is preferred in aerospace and high-performance applications where durability and strength are critical.
What is E-glass?
E-glass, or electrical-grade glass, is a type of fiberglass known for its excellent electrical insulating properties and high tensile strength, making it widely used in electronics and composite materials. It typically consists of silica, alumina, calcium oxide, and boron oxide, providing good thermal resistance and durability. E-glass is favored in applications requiring lightweight, strong, and non-conductive reinforcement, such as printed circuit boards and wind turbine blades.
What is S-glass?
S-glass is a high-strength fiberglass variant composed primarily of magnesium-aluminosilicate, renowned for its superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to conventional E-glass. It is widely used in aerospace, military, and high-performance sporting goods where enhanced mechanical properties and durability are critical. The enhanced fiber strength of S-glass results from its optimized chemical composition, making it ideal for applications requiring exceptional toughness and structural integrity.
Key Differences Between E-glass and S-glass
E-glass and S-glass differ primarily in their chemical composition and mechanical properties; E-glass, or electrical glass, contains higher amounts of silica and alumina, offering excellent electrical insulation and moderate tensile strength around 3.4 GPa. S-glass, or structural glass, has increased silica and magnesia content, resulting in superior tensile strength up to 4.9 GPa and enhanced impact resistance, making it ideal for aerospace and military applications. The thermal resistance of S-glass also surpasses that of E-glass, allowing it to perform better under high-stress and high-temperature conditions.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
E-glass offers excellent tensile strength around 3.45 GPa and good flexibility, making it suitable for general composite applications. S-glass surpasses E-glass with tensile strength up to 4.8 GPa and higher modulus of elasticity, providing superior impact resistance and durability in demanding environments. The enhanced mechanical properties of S-glass result in better performance for aerospace, military, and high-stress industrial uses compared to standard E-glass fibers.
Applications of E-glass
E-glass is predominantly used in applications such as fiberglass insulation, boat hulls, and wind turbine blades due to its excellent electrical insulating properties and cost-effectiveness. Its high tensile strength and chemical resistance make it ideal for reinforcing composites in automotive and aerospace industries. Industries prefer E-glass over S-glass when budget constraints are critical and extreme mechanical strength is less prioritized.
Applications of S-glass
S-glass is primarily utilized in aerospace, military, and high-performance automotive industries due to its superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to E-glass. Its enhanced durability and thermal stability make it ideal for structural components, ballistic protection, and composite reinforcements where high mechanical performance is critical. S-glass composites provide improved fatigue resistance, enabling longer service life in demanding applications such as aircraft fuselages, missile bodies, and sports equipment.
Cost Analysis: E-glass vs S-glass
E-glass offers a more cost-effective solution compared to S-glass, with prices typically 30-50% lower due to its widespread production and availability. S-glass, valued for its superior tensile strength and impact resistance, commands a premium price, often making it suitable for high-performance applications despite higher material costs. The choice between E-glass and S-glass in manufacturing hinges on balancing budget constraints against performance requirements in composites and structural reinforcements.
Durability and Performance Considerations
E-glass offers high electrical insulation and cost-effective durability suitable for general applications, while S-glass provides superior tensile strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for aerospace and military uses. The enhanced fiber strength of S-glass translates to better fatigue resistance and longer service life under demanding mechanical stress. Choosing between E-glass and S-glass depends on balancing performance requirements against budget constraints and application-specific durability needs.
Choosing Between E-glass and S-glass: Which is Best?
E-glass offers superior electrical insulation and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for general-purpose applications in composites and insulation. S-glass provides enhanced tensile strength and impact resistance, preferred in aerospace and military sectors where high-performance materials are critical. Selecting between E-glass and S-glass depends primarily on mechanical requirements, budget constraints, and specific application environments.
E-glass vs S-glass Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com