Crystal glass is renowned for its clarity and brilliance due to the high lead content, which enhances light refraction and weight. Lead-free glass offers a safer, environmentally friendly alternative without sacrificing durability but often has less sparkle compared to traditional lead crystal. Both materials serve different preferences, with lead-free glass prioritized for health and sustainability, while crystal glass remains preferred for luxury and visual appeal.
Table of Comparison
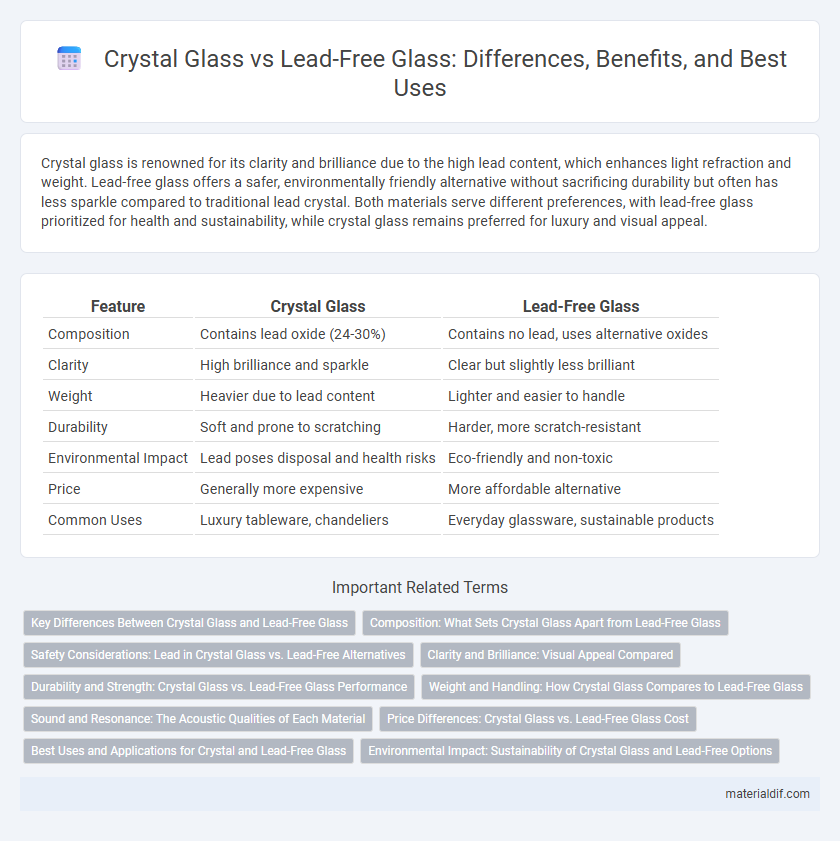
| Feature | Crystal Glass | Lead-Free Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Contains lead oxide (24-30%) | Contains no lead, uses alternative oxides |
| Clarity | High brilliance and sparkle | Clear but slightly less brilliant |
| Weight | Heavier due to lead content | Lighter and easier to handle |
| Durability | Soft and prone to scratching | Harder, more scratch-resistant |
| Environmental Impact | Lead poses disposal and health risks | Eco-friendly and non-toxic |
| Price | Generally more expensive | More affordable alternative |
| Common Uses | Luxury tableware, chandeliers | Everyday glassware, sustainable products |
Key Differences Between Crystal Glass and Lead-Free Glass
Crystal glass contains lead oxide, which enhances its clarity, weight, and sparkle, while lead-free glass achieves similar brilliance using alternative metal oxides like barium or zinc. Lead-free glass is safer for food and drink contact, environmentally friendly, and often more durable against chipping compared to traditional lead crystal. The refractive index of lead crystal typically ranges from 1.52 to 1.57, whereas lead-free glass usually ranges slightly lower, between 1.49 and 1.52, affecting its light dispersion and brilliance.
Composition: What Sets Crystal Glass Apart from Lead-Free Glass
Crystal glass contains a high percentage of lead oxide, typically 24% to 30%, which enhances its brilliance, weight, and clarity. Lead-free glass replaces lead oxide with alternatives like barium oxide or potassium oxide, making it safer and environmentally friendly but with slightly less sparkle. The unique composition of crystal glass results in superior refraction and resonance, distinguishing it from lead-free varieties used in eco-conscious manufacturing.
Safety Considerations: Lead in Crystal Glass vs. Lead-Free Alternatives
Lead crystal glass contains lead oxide, which enhances brilliance but poses potential health risks through lead exposure, especially with prolonged contact or use in drinkware. Lead-free glass substitutes lead with safer materials like barium or zinc oxides, reducing toxicity while maintaining clarity and durability. Consumers prioritizing safety should opt for lead-free alternatives to minimize lead ingestion hazards without compromising on aesthetic quality.
Clarity and Brilliance: Visual Appeal Compared
Crystal glass exhibits superior clarity and brilliance due to its higher refractive index, often exceeding 1.5, which enhances light dispersion and creates a sparkling visual appeal. Lead-free glass, designed to replicate these qualities, uses alternative materials like barium or zinc oxides to achieve similar clarity while maintaining eco-friendliness and safety. The visual difference remains notable, with crystal glass delivering more pronounced brilliance and scintillation, making it preferred for luxury glassware and decorative pieces.
Durability and Strength: Crystal Glass vs. Lead-Free Glass Performance
Crystal glass typically exhibits superior durability and strength due to its lead content, which increases density and resistance to chipping and breaking. Lead-free glass, often made with alternative formulations such as barium or potassium, provides comparable strength while being more environmentally friendly and safer for health. Both materials offer high-performance benefits, but crystal glass remains preferred for luxury glassware where enhanced durability and clarity are prioritized.
Weight and Handling: How Crystal Glass Compares to Lead-Free Glass
Crystal glass typically weighs more than lead-free glass due to its higher density from lead content, which results in a heavier, sturdier feel. Lead-free glass is lighter and easier to handle, making it more practical for everyday use and safer in environments where breakage risk is high. The difference in weight affects the balance and comfort during use, with crystal often favored for its substantial, luxurious tactile experience.
Sound and Resonance: The Acoustic Qualities of Each Material
Crystal glass produces a bright, sustained ringing tone that makes it preferred for fine glassware and musical instruments due to its higher lead content enhancing density and resonance. Lead-free glass, while safer and more environmentally friendly, offers a softer sound with shorter resonance times because of its lower density and different molecular structure. The distinct acoustic qualities of each material influence their suitability in applications where sound clarity and duration are critical.
Price Differences: Crystal Glass vs. Lead-Free Glass Cost
Crystal glass typically commands a higher price than lead-free glass due to its traditional manufacturing process and higher density caused by lead content. Lead-free glass offers a more affordable alternative while maintaining clarity and durability, benefiting from eco-friendly production methods. Consumers often choose lead-free glass for cost efficiency and environmental considerations without significantly compromising visual quality.
Best Uses and Applications for Crystal and Lead-Free Glass
Crystal glass, with its high refractive index and clarity, is best used in luxury drinkware, decorative items, and fine chandeliers due to its brilliance and weight. Lead-free glass, favored for its environmental and health benefits, is ideal for everyday glassware, food containers, and laboratory equipment where durability and safety are essential. Both materials excel in distinct applications, with crystal glass emphasizing aesthetics and lead-free glass prioritizing sustainability and practicality.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability of Crystal Glass and Lead-Free Options
Crystal glass often contains lead oxide, which poses environmental concerns due to lead's toxicity and challenges in recycling, impacting soil and water quality. Lead-free glass alternatives use safer materials like barium or zinc, reducing hazardous waste and improving recyclability for sustainable production. Choosing lead-free glass supports eco-friendly manufacturing and minimizes environmental pollution, aligning with sustainable consumption goals.
Crystal glass vs Lead-free glass Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com