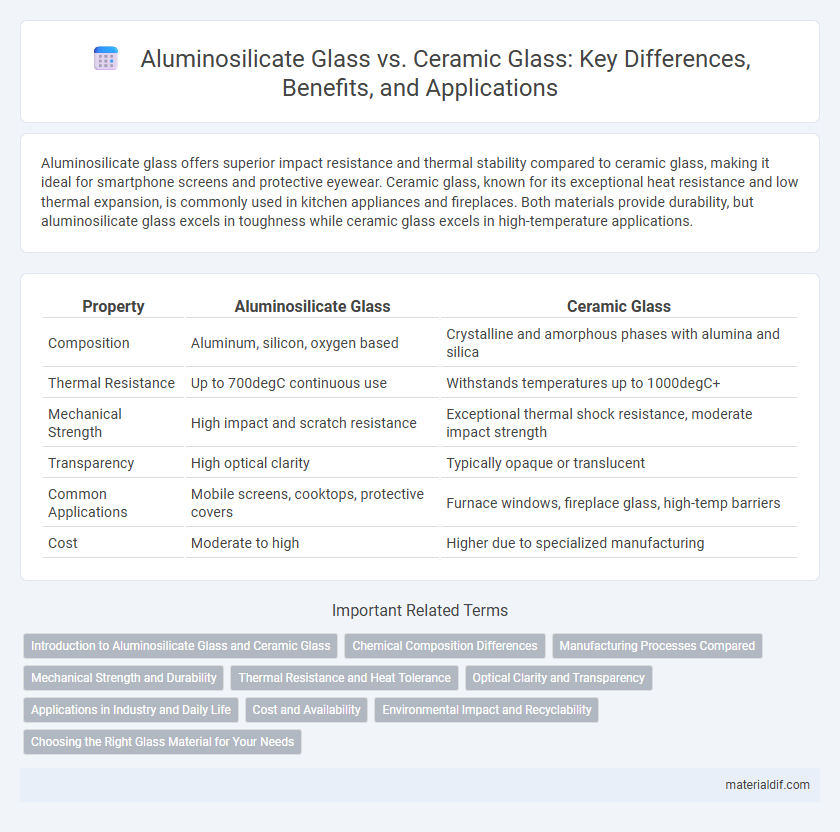
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior impact resistance and thermal stability compared to ceramic glass, making it ideal for smartphone screens and protective eyewear. Ceramic glass, known for its exceptional heat resistance and low thermal expansion, is commonly used in kitchen appliances and fireplaces. Both materials provide durability, but aluminosilicate glass excels in toughness while ceramic glass excels in high-temperature applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aluminosilicate Glass | Ceramic Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Aluminum, silicon, oxygen based | Crystalline and amorphous phases with alumina and silica |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 700degC continuous use | Withstands temperatures up to 1000degC+ |
| Mechanical Strength | High impact and scratch resistance | Exceptional thermal shock resistance, moderate impact strength |
| Transparency | High optical clarity | Typically opaque or translucent |
| Common Applications | Mobile screens, cooktops, protective covers | Furnace windows, fireplace glass, high-temp barriers |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Higher due to specialized manufacturing |
Introduction to Aluminosilicate Glass and Ceramic Glass
Aluminosilicate glass consists of aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, offering exceptional thermal resistance and high mechanical strength ideal for smartphone screens and protective covers. Ceramic glass, containing crystalline structures within a glass matrix, provides superior heat resistance and durability for applications like stove tops and fireplace doors. Both materials excel in toughness and heat tolerance but serve distinct industrial needs based on their composition and performance characteristics.
Chemical Composition Differences
Aluminosilicate glass contains a high concentration of aluminum oxide (Al2O3) and silicon dioxide (SiO2), enhancing its thermal and chemical durability compared to traditional glass types. Ceramic glass, composed mainly of crystalline phases like alumina (Al2O3) and silica (SiO2), often includes zirconia (ZrO2) or other metal oxides, providing superior heat resistance and mechanical strength through its polycrystalline structure. The key difference lies in aluminosilicate glass's amorphous network versus ceramic glass's partially crystalline matrix, influencing their respective thermal shock resistance and chemical stability.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Aluminosilicate glass is produced through a melting process at high temperatures, followed by rapid cooling to enhance strength and thermal resistance, commonly utilizing batch mixing and melting furnaces. Ceramic glass manufacturing involves controlled crystallization through heat-treatment or nucleation processes, transforming the glass into a glass-ceramic composite with improved mechanical properties and thermal stability. The key distinction lies in aluminosilicate glass being primarily an amorphous solid formed by conventional glass melting, whereas ceramic glass undergoes additional heat treatments to develop crystalline phases within the glass matrix.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Aluminosilicate glass exhibits high mechanical strength and scratch resistance, making it ideal for smartphone screens and protective covers. Ceramic glass offers superior thermal durability and resistance to thermal shock, widely used in cooktops and fireplace doors. Both materials provide enhanced durability, but aluminosilicate glass excels in impact resistance while ceramic glass endures extreme temperature variations.
Thermal Resistance and Heat Tolerance
Aluminosilicate glass exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to ceramic glass, withstanding rapid temperature changes up to 700degC without cracking. Its high heat tolerance makes it ideal for applications requiring durability against thermal shock, such as in smartphone screens and cookware. Ceramic glass, while capable of enduring high temperatures around 600degC, is less resistant to sudden temperature fluctuations, limiting its use in environments with extreme thermal cycling.
Optical Clarity and Transparency
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior optical clarity and higher transparency compared to ceramic glass, making it ideal for applications requiring clear, distortion-free viewing. Its molecular structure reduces light scattering and enhances light transmission, while ceramic glass often exhibits slight haziness due to its crystalline composition. This results in aluminosilicate glass being the preferred choice for high-precision optical devices and display panels.
Applications in Industry and Daily Life
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for smartphone screens, cookware, and aerospace components. Ceramic glass excels in high-temperature environments, commonly used in stove tops, furnace windows, and protective glass for industrial ovens. Both materials cater to demanding applications requiring durability, heat resistance, and scratch protection across various industrial and daily life settings.
Cost and Availability
Aluminosilicate glass offers a cost-effective solution with widespread availability due to its simpler manufacturing process and common raw materials. Ceramic glass tends to be more expensive and less readily available, as it requires specialized production techniques and higher purity components. Industries prioritizing budget and supply continuity often favor aluminosilicate glass over ceramic glass despite the latter's superior thermal resistance.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Aluminosilicate glass features a lower environmental impact due to its energy-efficient manufacturing process and high durability, leading to extended product lifespan and reduced waste. Ceramic glass, while offering excellent thermal resistance, typically requires higher energy inputs during production and faces challenges in recyclability due to its crystalline structure. The superior recyclability of aluminosilicate glass enables more effective reuse in industrial recycling streams, minimizing landfill contribution and conserving raw materials.
Choosing the Right Glass Material for Your Needs
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior impact resistance and thermal shock tolerance, making it ideal for electronic screens and protective covers requiring durability. Ceramic glass excels with high heat resistance and chemical stability, suited for cookware and fireplace doors exposed to extreme temperatures. Selecting between aluminosilicate and ceramic glass depends on prioritizing either mechanical strength and scratch resistance or exceptional heat endurance and chemical inertness.
Aluminosilicate glass vs Ceramic glass Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com