Aluminosilicate glass offers superior strength and thermal resistance compared to traditional silicate glass due to its enhanced chemical composition. This makes aluminosilicate glass ideal for durable glass pet containers that require resistance to impact and temperature fluctuations. Silicate glass, while more common and cost-effective, lacks the toughness and scratch resistance found in aluminosilicate variants.
Table of Comparison
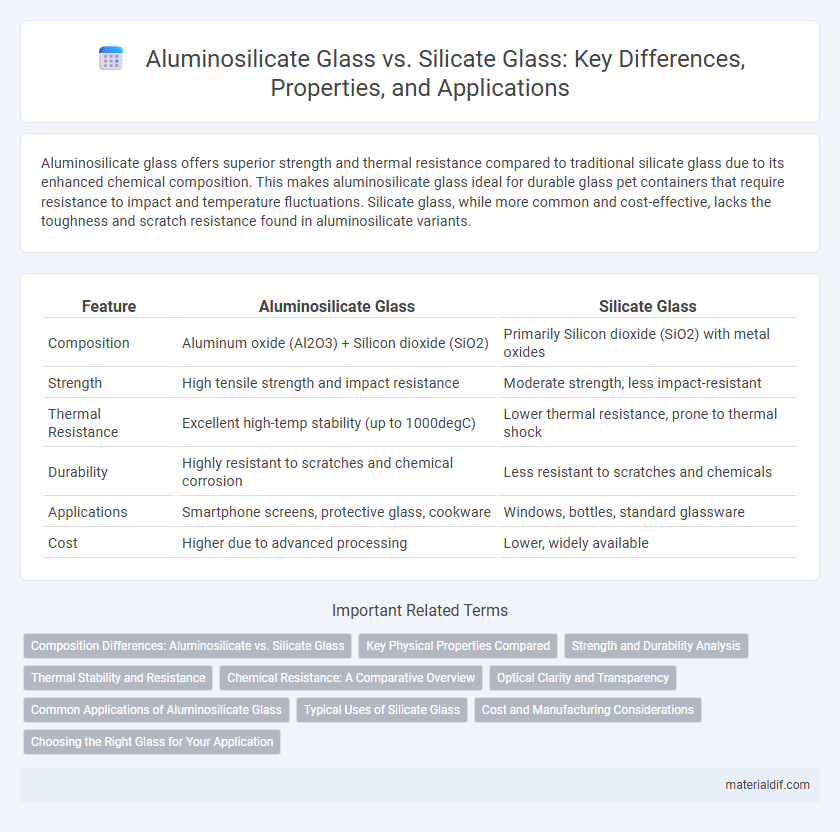
| Feature | Aluminosilicate Glass | Silicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Aluminum oxide (Al2O3) + Silicon dioxide (SiO2) | Primarily Silicon dioxide (SiO2) with metal oxides |
| Strength | High tensile strength and impact resistance | Moderate strength, less impact-resistant |
| Thermal Resistance | Excellent high-temp stability (up to 1000degC) | Lower thermal resistance, prone to thermal shock |
| Durability | Highly resistant to scratches and chemical corrosion | Less resistant to scratches and chemicals |
| Applications | Smartphone screens, protective glass, cookware | Windows, bottles, standard glassware |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced processing | Lower, widely available |
Composition Differences: Aluminosilicate vs. Silicate Glass
Aluminosilicate glass contains a significant proportion of aluminum oxide (Al2O3) combined with silicon dioxide (SiO2), enhancing its strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance compared to traditional silicate glass, which primarily consists of silicon dioxide with various metal oxides like sodium oxide and calcium oxide. The incorporation of alumina in aluminosilicate glass alters the network structure, resulting in improved mechanical properties and higher resistance to thermal shock. In contrast, silicate glass is more susceptible to thermal and chemical degradation due to its simpler silicon-oxygen network and lower alumina content.
Key Physical Properties Compared
Aluminosilicate glass exhibits higher thermal resistance and mechanical strength compared to conventional silicate glass, making it more durable under extreme conditions. Its enhanced chemical stability and lower thermal expansion coefficient reduce the risk of cracking during rapid temperature changes. Silicate glass, while more affordable, typically shows lower hardness and increased susceptibility to thermal shock.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Aluminosilicate glass exhibits superior strength and durability compared to traditional silicate glass due to its enhanced chemical composition incorporating aluminum oxide, which increases resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress. The densely packed molecular structure of aluminosilicate glass contributes to higher scratch resistance and improved impact tolerance, making it ideal for smartphones and protective screens. In contrast, silicate glass, primarily composed of silicon dioxide, offers less robustness and is more prone to fracture under pressure or rapid temperature changes.
Thermal Stability and Resistance
Aluminosilicate glass exhibits superior thermal stability and resistance compared to traditional silicate glass due to its enhanced chemical composition, which includes aluminum oxide that increases its melting point and reduces thermal expansion. This makes aluminosilicate glass highly resistant to thermal shock, allowing it to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking. Its robust thermal properties are ideal for applications in smartphone screens, cookware, and high-performance windows where heat resistance is critical.
Chemical Resistance: A Comparative Overview
Aluminosilicate glass exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to traditional silicate glass due to its enhanced aluminum oxide content, which significantly improves durability against acidic and alkaline environments. This type of glass is less prone to leaching and surface degradation, making it ideal for industrial applications where exposure to harsh chemicals is frequent. In contrast, conventional silicate glass is more susceptible to corrosion and chemical attack, limiting its use in aggressive chemical settings.
Optical Clarity and Transparency
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior optical clarity and transparency compared to traditional silicate glass due to its enhanced thermal and chemical stability, which reduces light scattering and color distortion. The unique alumina and silica composition results in higher refractive index uniformity, providing clearer and brighter visual performance ideal for high-precision optical applications. Silicate glass, while commonly used, tends to exhibit slight haze and lower light transmission, making aluminosilicate glass the preferred choice for advanced optical devices and displays.
Common Applications of Aluminosilicate Glass
Aluminosilicate glass is widely used in smartphone and tablet screens due to its superior strength and scratch resistance compared to silicate glass. It also serves in aerospace and automotive industries for durable, heat-resistant windows and protective covers. Its chemical durability makes it ideal for laboratory glassware and high-performance optical components.
Typical Uses of Silicate Glass
Silicate glass, primarily composed of silica (SiO2) with various metal oxides, is widely used in everyday applications such as windows, bottles, and tableware due to its affordability and ease of manufacture. Its excellent optical clarity and chemical durability make it suitable for use in lenses, glass containers, and architectural panels. Unlike aluminosilicate glass, silicate glass generally exhibits lower thermal resistance, limiting its use in high-stress thermal environments but excelling in mass-produced consumer products.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Aluminosilicate glass exhibits higher thermal and chemical durability than conventional silicate glass, yet its manufacturing process involves more complex and energy-intensive techniques, increasing production costs. The raw material cost for aluminosilicate glass is generally higher due to the inclusion of aluminum oxide, while silicate glass benefits from abundant silica sand and simpler melting procedures that reduce expenses. Choosing between the two depends on the application's tolerance for cost versus performance, with aluminosilicate favored in high-stress environments despite its elevated manufacturing investment.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Application
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and mechanical strength compared to standard silicate glass, making it ideal for high-stress applications such as electronics and aerospace. Silicate glass, while more cost-effective and easier to mold, is best suited for everyday uses like windows and containers where extreme durability is less critical. Selecting the appropriate glass depends on balancing factors like temperature tolerance, impact resistance, and budget requirements.
Aluminosilicate glass vs Silicate glass Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com