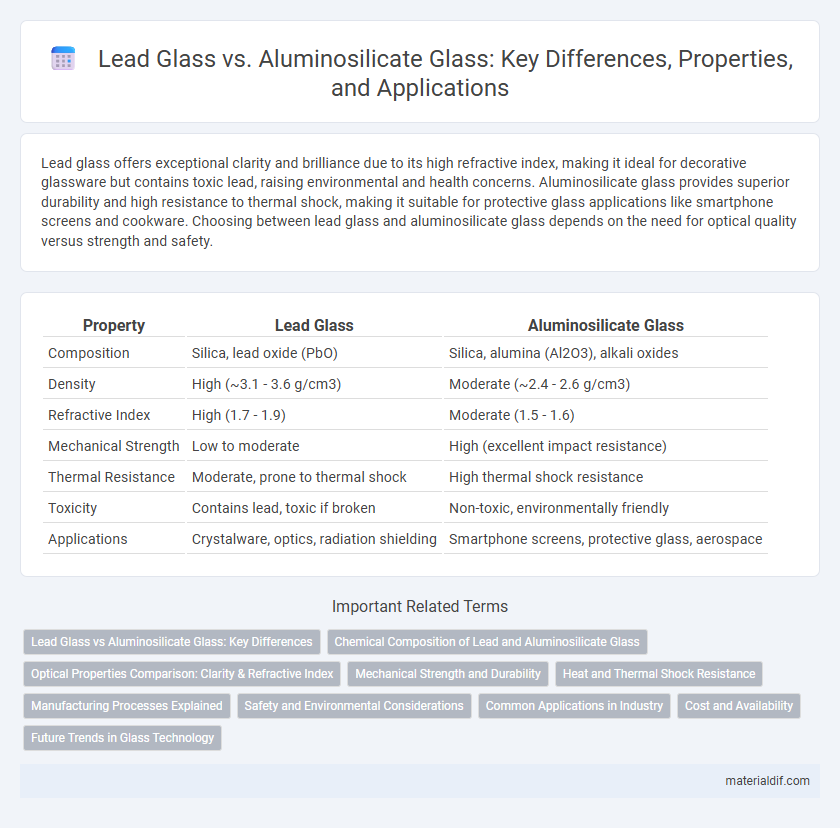
Lead glass offers exceptional clarity and brilliance due to its high refractive index, making it ideal for decorative glassware but contains toxic lead, raising environmental and health concerns. Aluminosilicate glass provides superior durability and high resistance to thermal shock, making it suitable for protective glass applications like smartphone screens and cookware. Choosing between lead glass and aluminosilicate glass depends on the need for optical quality versus strength and safety.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lead Glass | Aluminosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica, lead oxide (PbO) | Silica, alumina (Al2O3), alkali oxides |
| Density | High (~3.1 - 3.6 g/cm3) | Moderate (~2.4 - 2.6 g/cm3) |
| Refractive Index | High (1.7 - 1.9) | Moderate (1.5 - 1.6) |
| Mechanical Strength | Low to moderate | High (excellent impact resistance) |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate, prone to thermal shock | High thermal shock resistance |
| Toxicity | Contains lead, toxic if broken | Non-toxic, environmentally friendly |
| Applications | Crystalware, optics, radiation shielding | Smartphone screens, protective glass, aerospace |
Lead Glass vs Aluminosilicate Glass: Key Differences
Lead glass contains a high percentage of lead oxide, which increases its density, brilliance, and refractive index, making it ideal for decorative items like crystal glassware. Aluminosilicate glass, composed primarily of aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, offers superior durability, scratch resistance, and thermal stability, commonly used in smartphone screens and protective covers. The key difference lies in lead glass's optical clarity and weight versus aluminosilicate's mechanical strength and resilience.
Chemical Composition of Lead and Aluminosilicate Glass
Lead glass contains a high percentage of lead oxide (PbO), typically ranging from 18% to 40%, which enhances its density, refractive index, and brilliance. Aluminosilicate glass is primarily composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2) and aluminum oxide (Al2O3), with alumina content often between 5% and 15%, providing superior thermal resistance and mechanical strength. The distinct chemical compositions result in lead glass being favored for optical clarity and brilliance, while aluminosilicate glass is preferred for durability and heat resistance in industrial applications.
Optical Properties Comparison: Clarity & Refractive Index
Lead glass exhibits a higher refractive index, ranging from 1.7 to 1.9, resulting in greater brilliance and clarity compared to aluminosilicate glass, which typically has a refractive index of around 1.5. The increased lead content enhances light dispersion in lead glass, producing superior clarity and a characteristic sparkle ideal for decorative applications. Aluminosilicate glass offers good optical clarity but lacks the high refractive qualities of lead glass, making it better suited for durability-focused uses rather than optical brilliance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Lead glass exhibits lower mechanical strength and durability compared to aluminosilicate glass due to its higher lead oxide content, which increases density but reduces structural integrity. Aluminosilicate glass contains aluminum oxide, enhancing its resistance to impacts, scratches, and thermal stress, making it ideal for protective screens and high-performance glassware. The superior toughness and chemical durability of aluminosilicate glass result in longer-lasting applications in harsh environments.
Heat and Thermal Shock Resistance
Lead glass typically exhibits lower heat and thermal shock resistance due to its higher lead oxide content, which reduces its melting point and makes it more susceptible to sudden temperature changes. Aluminosilicate glass contains aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, resulting in superior thermal stability and resistance to rapid temperature fluctuations, making it ideal for applications requiring high heat tolerance. The enhanced thermal shock resistance of aluminosilicate glass ensures better durability in environments exposed to extreme and sudden temperature variations.
Manufacturing Processes Explained
Lead glass manufacturing involves melting raw materials like silica, lead oxide, and alkali at high temperatures, followed by controlled cooling to enhance refractive index and clarity. Aluminosilicate glass production requires the fusion of alumina and silica with precise temperature control to achieve superior thermal and chemical durability. Both processes utilize specialized furnaces and cooling techniques that impact the final glass properties and applications.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Lead glass contains toxic lead oxide, posing significant environmental hazards during disposal and recycling, whereas aluminosilicate glass offers a safer alternative with lower toxicity and improved chemical durability. Aluminosilicate glass also exhibits higher resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress, enhancing safety in applications prone to impact or temperature fluctuations. The absence of lead in aluminosilicate glass reduces health risks for workers and consumers, making it a more sustainable choice in glass manufacturing.
Common Applications in Industry
Lead glass is widely used in optical lenses, radiation shielding, and decorative items due to its high density and excellent refractive index. Aluminosilicate glass, known for its superior thermal resistance and strength, is commonly applied in smartphone screens, aerospace windows, and chemical storage containers. Both types of glass offer distinct advantages tailored to their specialized industrial applications.
Cost and Availability
Lead glass typically costs more due to its higher lead content and specialized manufacturing process, making it less widely available compared to aluminosilicate glass. Aluminosilicate glass offers greater affordability and is produced in larger quantities, benefiting from more common raw materials and widespread industrial uses. Cost-efficiency and broader market availability make aluminosilicate glass a preferred choice for mass production and consumer applications.
Future Trends in Glass Technology
Lead glass offers superior optical clarity and radiation shielding, while aluminosilicate glass excels in strength and thermal resistance, driving future innovations in glass technology. Emerging trends emphasize developing hybrid glass compositions that combine lead glass's refractive properties with aluminosilicate's durability for advanced applications in optics and electronics. Research in nanotechnology and environmentally friendly production methods is accelerating the creation of multifunctional glass with enhanced performance and sustainability.
Lead glass vs Aluminosilicate glass Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com