Low-denier fiber offers superior softness and flexibility, making it ideal for lightweight garments and delicate textiles. High-denier fiber provides enhanced durability and strength, suitable for heavy-duty applications like outdoor gear and upholstery. Choosing between low-denier and high-denier fibers depends on the required balance between comfort and toughness.
Table of Comparison
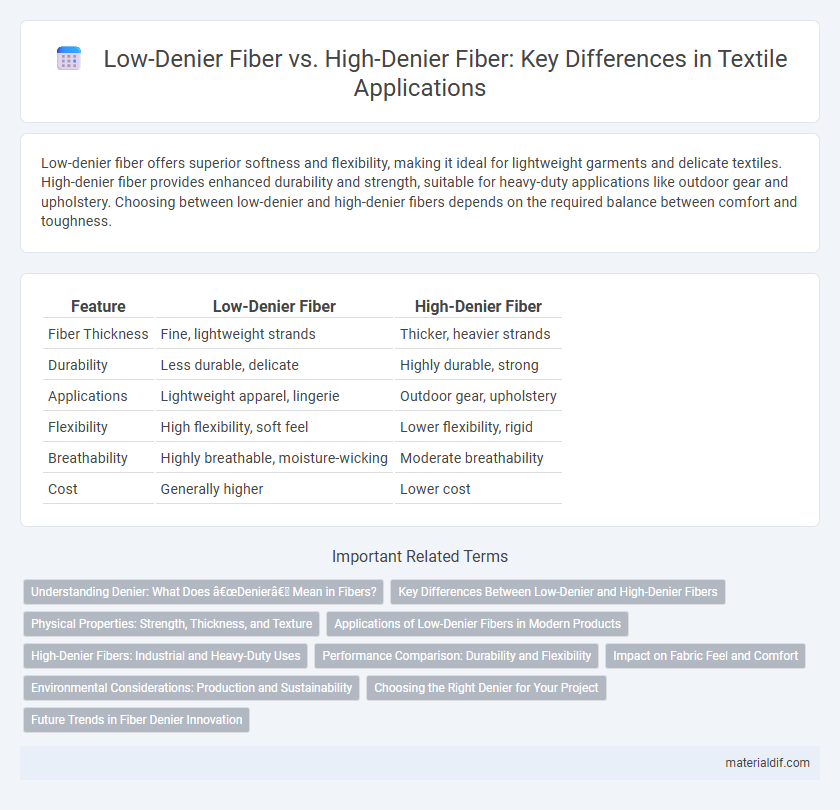
| Feature | Low-Denier Fiber | High-Denier Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Thickness | Fine, lightweight strands | Thicker, heavier strands |
| Durability | Less durable, delicate | Highly durable, strong |
| Applications | Lightweight apparel, lingerie | Outdoor gear, upholstery |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, soft feel | Lower flexibility, rigid |
| Breathability | Highly breathable, moisture-wicking | Moderate breathability |
| Cost | Generally higher | Lower cost |
Understanding Denier: What Does “Denier” Mean in Fibers?
Denier measures the thickness or density of individual fibers, defined as the mass in grams per 9,000 meters of fiber. Low-denier fibers are finer and lighter, offering softness and flexibility ideal for lightweight textiles. High-denier fibers are thicker and stronger, providing durability and resistance suited for heavy-duty fabrics and industrial applications.
Key Differences Between Low-Denier and High-Denier Fibers
Low-denier fiber features thinner, lighter strands that offer greater softness, flexibility, and breathability, making them ideal for lightweight garments and delicate textiles. High-denier fiber consists of thicker, more robust strands that provide enhanced durability, strength, and resistance to wear, suitable for heavy-duty applications such as outdoor gear and upholstery. The key differences between low-denier and high-denier fibers include fiber thickness, tensile strength, weight, and end-use performance characteristics.
Physical Properties: Strength, Thickness, and Texture
Low-denier fiber exhibits finer thickness, resulting in a softer texture and less strength compared to high-denier fiber, which is thicker and more durable. High-denier fiber provides enhanced tensile strength and resilience, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring robust physical properties. The texture of low-denier fibers feels smooth and lightweight, while high-denier fibers offer a coarser, sturdier feel due to their increased thickness.
Applications of Low-Denier Fibers in Modern Products
Low-denier fibers, characterized by their fine and lightweight structure, are essential in the production of high-performance athletic apparel, where breathability and moisture-wicking properties enhance comfort and functionality. These fibers are extensively used in technical textiles such as parachutes and airbags, offering superior strength-to-weight ratios that improve safety and efficiency. Their application in medical textiles, including bandages and surgical gowns, leverages their softness and flexibility for better patient outcomes and comfort.
High-Denier Fibers: Industrial and Heavy-Duty Uses
High-denier fibers, characterized by their thick and robust yarns, are essential for industrial and heavy-duty applications requiring enhanced durability and strength. These fibers offer superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength, making them ideal for manufacturing products such as conveyor belts, heavy-duty sacks, and safety harnesses. Their enhanced structural integrity supports performance in demanding environments, ensuring long-lasting reliability and safety.
Performance Comparison: Durability and Flexibility
Low-denier fiber exhibits superior flexibility due to its finer strands, making it ideal for applications requiring lightweight and pliable materials, while high-denier fiber excels in durability, offering enhanced resistance to abrasion and tensile strength for heavy-duty uses. The lower thickness of low-denier fibers enables better drape and softness but compromises on long-term wear resistance compared to the coarser, more robust high-denier fibers. Choosing between low-denier and high-denier fiber depends on balancing the need for flexibility versus durability in specific performance requirements.
Impact on Fabric Feel and Comfort
Low-denier fiber creates lightweight, soft fabrics with a smooth texture, enhancing breathability and comfort against the skin. High-denier fiber produces thicker, more durable textiles that offer greater warmth and resistance but may feel coarser and less flexible. Choosing between low and high denier impacts fabric feel significantly, balancing softness with durability based on end-use requirements.
Environmental Considerations: Production and Sustainability
Low-denier fiber production consumes significantly less raw material and energy, resulting in a lower carbon footprint compared to high-denier fiber, which requires more resources and generates higher emissions. Low-denier fibers promote sustainability by enabling lightweight fabrics that reduce transportation fuel consumption and waste during manufacturing. High-denier fibers, often used for heavy-duty applications, have a longer lifecycle that can offset some environmental impacts, but their initial production remains resource-intensive.
Choosing the Right Denier for Your Project
Low-denier fiber offers a lightweight, soft texture ideal for delicate fabrics and detailed designs, enhancing comfort and flexibility. High-denier fiber provides superior durability and strength, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications like outdoor gear and upholstery. Selecting the right denier depends on balancing project requirements such as strength, flexibility, and aesthetic appeal for optimal performance.
Future Trends in Fiber Denier Innovation
Future trends in fiber denier innovation emphasize the development of ultra-low-denier fibers to enhance fabric softness and breathability, meeting consumer demand for lightweight performance textiles. Advances in nanotechnology and polymer engineering enable precise control over fiber diameter, resulting in high-strength, durable fibers with reduced environmental impact. The integration of smart materials within low-denier fibers paves the way for multifunctional textiles used in wearable technology and sustainable fashion.
Low-Denier Fiber vs High-Denier Fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com