Kevlar offers exceptional impact resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for protective gear and ballistic applications, while carbon fiber provides superior stiffness and high tensile strength, suited for aerospace and automotive components. Kevlar's ability to absorb energy without fracturing contrasts with carbon fiber's tendency to be more brittle but structurally rigid. Choosing between Kevlar and carbon fiber depends on whether the application requires more toughness or enhanced rigidity and light weight.
Table of Comparison
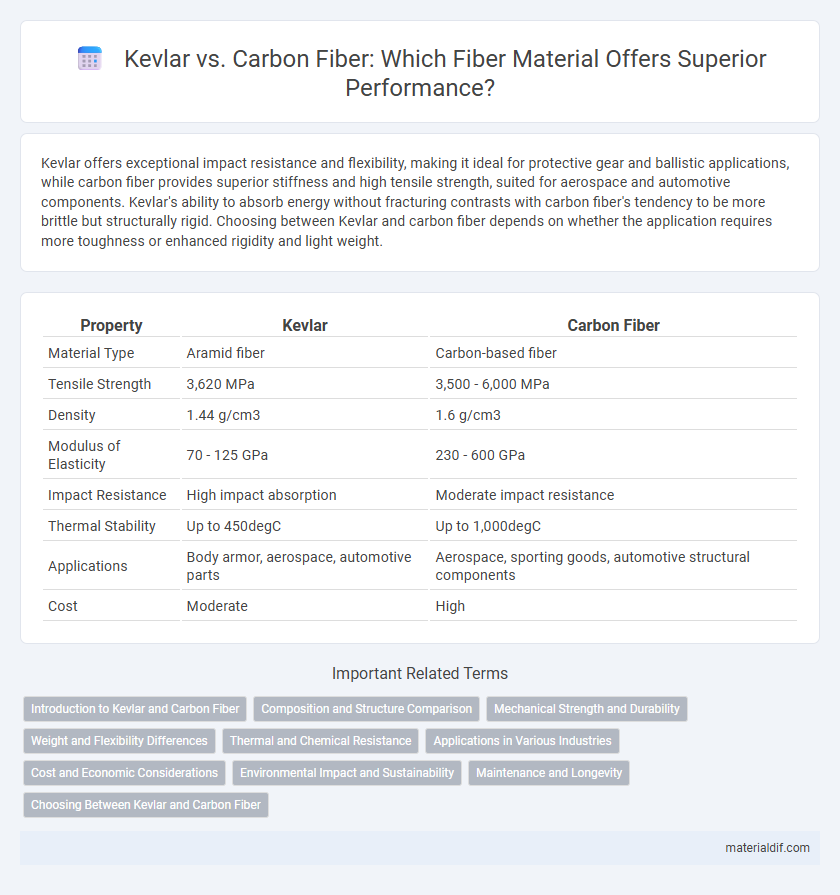
| Property | Kevlar | Carbon Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Aramid fiber | Carbon-based fiber |
| Tensile Strength | 3,620 MPa | 3,500 - 6,000 MPa |
| Density | 1.44 g/cm3 | 1.6 g/cm3 |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 70 - 125 GPa | 230 - 600 GPa |
| Impact Resistance | High impact absorption | Moderate impact resistance |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 450degC | Up to 1,000degC |
| Applications | Body armor, aerospace, automotive parts | Aerospace, sporting goods, automotive structural components |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
Introduction to Kevlar and Carbon Fiber
Kevlar and carbon fiber are advanced materials renowned for their high strength-to-weight ratios and durability. Kevlar, a synthetic aromatic polyamide fiber, is prized for its exceptional impact resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for body armor and protective gear. Carbon fiber consists of thin strands of carbon atoms bonded in a crystalline formation, offering superior stiffness and tensile strength widely utilized in aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods applications.
Composition and Structure Comparison
Kevlar is an aramid fiber composed of poly-paraphenylene terephthalamide, featuring a tightly woven, highly oriented molecular structure that provides exceptional tensile strength and impact resistance. Carbon fiber consists of thin strands of carbon atoms bonded in a crystalline structure aligned parallel to the fiber axis, resulting in high stiffness, low weight, and excellent heat resistance. The differing molecular arrangements lead Kevlar to excel in flexibility and energy absorption, while carbon fiber offers superior rigidity and compressive strength.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Kevlar exhibits exceptional tensile strength and high impact resistance, making it highly durable under dynamic loads and abrasion. Carbon fiber offers superior stiffness and higher compressive strength, excelling in rigidity and lightweight structural applications. Both materials provide excellent mechanical strength, but Kevlar outperforms in impact durability while carbon fiber leads in stiffness and compressive performance.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Kevlar offers superior flexibility and impact resistance compared to carbon fiber, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under stress. Carbon fiber is significantly lighter, with a density around 1.6 g/cm3 versus Kevlar's approximately 1.44 g/cm3, but excels in stiffness and tensile strength. The choice between Kevlar and carbon fiber depends on balancing lightweight performance against flexibility needs in composite materials.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Kevlar offers superior thermal resistance with a decomposition temperature around 500degC, maintaining strength under high heat, whereas carbon fiber typically withstands temperatures up to 650degC but may degrade with rapid thermal cycling. Chemically, Kevlar resists a broad range of solvents, oils, and fuels, making it highly resistant to chemical corrosion compared to carbon fiber, which is generally inert but can be vulnerable to oxidation and acidic environments. These properties position Kevlar as the preferred choice for applications requiring durable thermal and chemical protection, while carbon fiber excels in environments demanding higher thermal stability with less chemical exposure.
Applications in Various Industries
Kevlar excels in ballistic protection and aerospace due to its high tensile strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for body armor and aircraft components. Carbon fiber dominates automotive and sports equipment industries by offering exceptional stiffness and lightweight properties that enhance performance and fuel efficiency. Both materials serve critical roles in construction and marine sectors, where durability and weight savings are essential.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Kevlar offers a cost advantage over carbon fiber due to its lower raw material expenses and simpler manufacturing process, making it more economical for large-scale applications. Carbon fiber demands higher upfront investment but provides superior strength-to-weight ratios, potentially reducing long-term costs in high-performance industries like aerospace and automotive. Evaluating budget constraints and performance requirements is essential when choosing between Kevlar and carbon fiber for optimal economic efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Kevlar production consumes less energy compared to carbon fiber, resulting in a lower carbon footprint during manufacturing. Kevlar is partially recyclable through chemical processes, whereas carbon fiber recycling remains limited and energy-intensive, contributing to waste challenges. Both materials offer durability that extends product life, but Kevlar's biodegradability potential makes it a more sustainable option in high-performance fiber applications.
Maintenance and Longevity
Kevlar's high resistance to abrasion and impact makes it exceptionally durable with minimal maintenance requirements, ideal for applications exposed to harsh conditions. Carbon fiber offers superior stiffness and strength but is more susceptible to cracking and requires regular inspections and careful handling to ensure longevity. Both materials excel in durability, yet Kevlar generally demands less upkeep, extending its functional life in environments where wear and tear are significant factors.
Choosing Between Kevlar and Carbon Fiber
Choosing between Kevlar and carbon fiber depends on the application's requirements for strength, weight, and impact resistance. Kevlar offers superior impact absorption and flexibility, making it ideal for ballistic protection and high-impact sports gear, while carbon fiber excels in stiffness and lightweight properties, preferred for aerospace, automotive, and high-performance sporting goods. Understanding these material differences ensures optimal performance and durability in specific fiber-reinforced composite applications.
Kevlar vs Carbon Fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com