Industrial enamel is designed for durability and resistance to harsh conditions, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications such as machinery and automotive parts. Decorative enamel prioritizes aesthetic qualities, offering vibrant colors and glossy finishes suited for artistic and ornamental objects. Choosing between industrial and decorative enamel depends on whether functionality or visual appeal is the primary requirement.
Table of Comparison
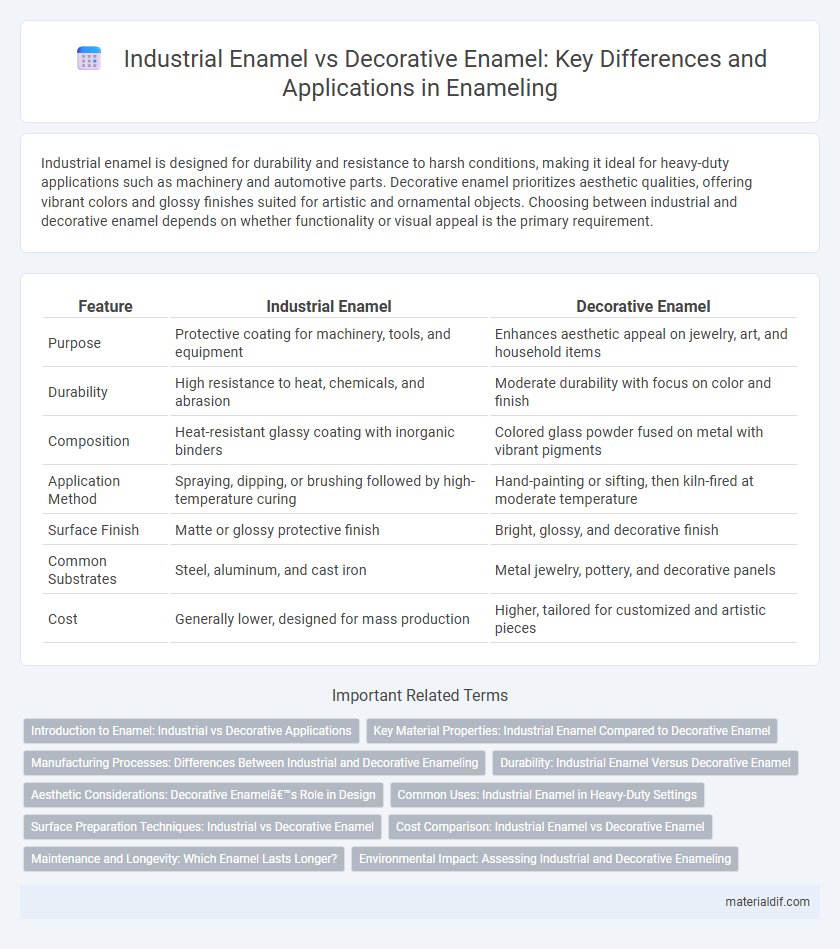
| Feature | Industrial Enamel | Decorative Enamel |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protective coating for machinery, tools, and equipment | Enhances aesthetic appeal on jewelry, art, and household items |
| Durability | High resistance to heat, chemicals, and abrasion | Moderate durability with focus on color and finish |
| Composition | Heat-resistant glassy coating with inorganic binders | Colored glass powder fused on metal with vibrant pigments |
| Application Method | Spraying, dipping, or brushing followed by high-temperature curing | Hand-painting or sifting, then kiln-fired at moderate temperature |
| Surface Finish | Matte or glossy protective finish | Bright, glossy, and decorative finish |
| Common Substrates | Steel, aluminum, and cast iron | Metal jewelry, pottery, and decorative panels |
| Cost | Generally lower, designed for mass production | Higher, tailored for customized and artistic pieces |
Introduction to Enamel: Industrial vs Decorative Applications
Industrial enamel features robust chemical and thermal resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications such as cookware, automotive parts, and machinery coatings. Decorative enamel prioritizes aesthetic appeal with vibrant colors and glossy finishes, commonly used in jewelry, art pieces, and household items. Both types leverage the glassy, smooth surface qualities of enamel but differ significantly in formulation to meet their specific functional demands.
Key Material Properties: Industrial Enamel Compared to Decorative Enamel
Industrial enamel exhibits superior hardness, chemical resistance, and thermal stability compared to decorative enamel, making it ideal for harsh environments and heavy-duty applications. Its formulation includes high-quality frits and inorganic pigments designed to withstand corrosion, abrasion, and extreme temperatures, whereas decorative enamel prioritizes aesthetic qualities like color vibrancy and smooth finishes. The enhanced durability of industrial enamel ensures extended service life in machinery, appliances, and protective coatings, while decorative enamel is optimized for appearance on consumer goods and art.
Manufacturing Processes: Differences Between Industrial and Decorative Enameling
Industrial enamel manufacturing involves applying thick, durable coatings through high-temperature firing to provide corrosion resistance and mechanical protection for machinery and equipment. Decorative enameling processes emphasize fine, detailed designs with thinner enamel layers applied using techniques like cloisonne or painting, followed by lower temperature firing to preserve intricate artwork. These differences in manufacturing impact enamel composition, firing temperatures, and surface finish quality tailored to either functional durability or aesthetic appeal.
Durability: Industrial Enamel Versus Decorative Enamel
Industrial enamel offers superior durability due to its chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for harsh environments and heavy-duty applications. Decorative enamel, while visually appealing with a glossy finish and vibrant colors, typically sacrifices some durability and is more prone to chipping and fading under mechanical stress and exposure. The formulation differences in industrial enamel emphasize toughness and longevity, whereas decorative enamel prioritizes aesthetic qualities over extreme durability.
Aesthetic Considerations: Decorative Enamel’s Role in Design
Decorative enamel enhances aesthetic appeal through vibrant colors, intricate patterns, and glossy finishes that elevate product design and consumer attraction. Industrial enamel prioritizes durability, corrosion resistance, and heat protection, often resulting in more subdued visual qualities tailored for functional performance. The choice of decorative enamel allows designers to merge art with utility, creating visually striking surfaces without compromising structural integrity.
Common Uses: Industrial Enamel in Heavy-Duty Settings
Industrial enamel is commonly used in heavy-duty settings such as machinery, automotive parts, and appliances due to its exceptional durability, corrosion resistance, and heat tolerance. Unlike decorative enamel, which prioritizes aesthetic appeal and is often applied to jewelry or household items, industrial enamel provides robust protection against wear, chemicals, and environmental damage. This makes it indispensable for coating metal surfaces exposed to harsh industrial conditions, ensuring longevity and functional performance.
Surface Preparation Techniques: Industrial vs Decorative Enamel
Industrial enamel surface preparation involves rigorous cleaning and abrasive blasting to ensure strong adhesion and resistance to corrosion in harsh environments. Decorative enamel requires meticulous polishing and degreasing, prioritizing smoothness and clarity for aesthetic appeal. Both techniques emphasize surface cleanliness but differ in their approach, driven by the enamel's functional versus ornamental purpose.
Cost Comparison: Industrial Enamel vs Decorative Enamel
Industrial enamel typically incurs higher costs than decorative enamel due to its enhanced durability, chemical resistance, and thermal stability designed for harsh environments. Decorative enamel emphasizes aesthetics and surface finish, often utilizing less expensive materials and simpler application processes, resulting in lower overall expenses. Evaluating total cost involves considering long-term performance requirements alongside initial material and labor costs.
Maintenance and Longevity: Which Enamel Lasts Longer?
Industrial enamel, designed for harsh environments, offers superior durability and resistance to corrosion, heat, and abrasion compared to decorative enamel. Decorative enamel emphasizes aesthetic appeal, often sacrificing some longevity due to thinner coatings and less robust formulations. Maintenance requirements for industrial enamel are minimal, ensuring longer service life, while decorative enamel may require more frequent touch-ups to maintain appearance.
Environmental Impact: Assessing Industrial and Decorative Enameling
Industrial enamel coatings typically involve high-temperature processes that emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and heavy metals, contributing to environmental pollution and requiring stringent waste management protocols. Decorative enamel applications often use lower-temperature techniques with fewer hazardous emissions, resulting in a comparatively reduced ecological footprint. Evaluating the environmental impact of enameling necessitates analyzing energy consumption, emission levels, and waste generation specific to each application type.
industrial enamel vs decorative enamel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com