Cork composite combines natural cork granules with binders, offering enhanced durability and resistance to wear compared to solid cork. Solid cork provides a softer, more natural feel with superior insulation properties but may be less resistant to heavy foot traffic. Choosing between cork composite and solid cork depends on balancing durability needs with the desired aesthetic and comfort for your space.
Table of Comparison
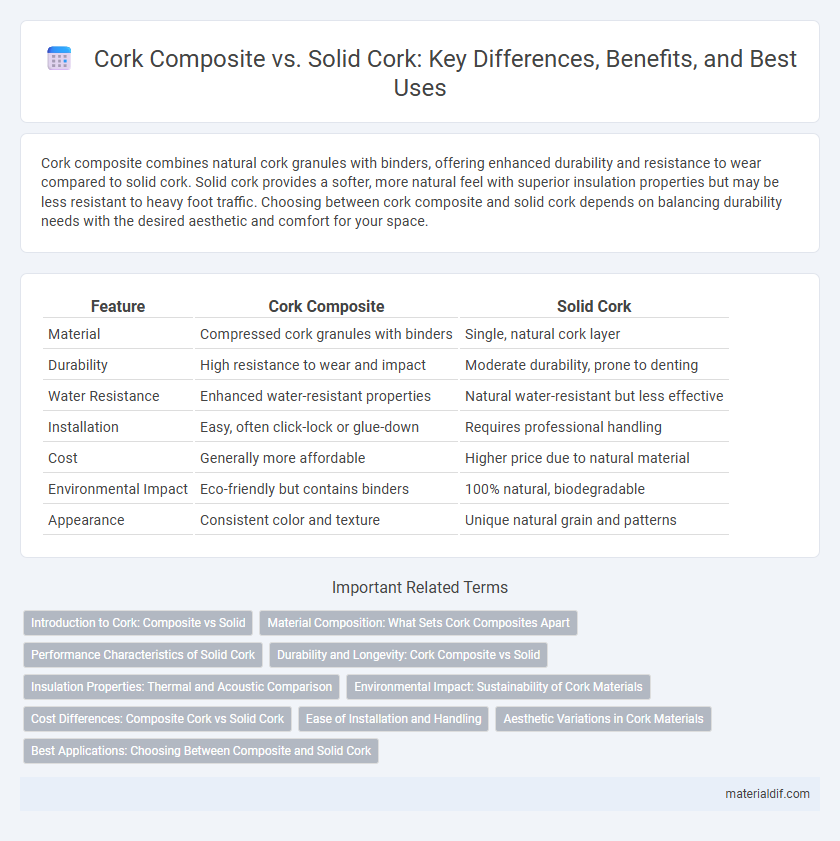
| Feature | Cork Composite | Solid Cork |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Compressed cork granules with binders | Single, natural cork layer |
| Durability | High resistance to wear and impact | Moderate durability, prone to denting |
| Water Resistance | Enhanced water-resistant properties | Natural water-resistant but less effective |
| Installation | Easy, often click-lock or glue-down | Requires professional handling |
| Cost | Generally more affordable | Higher price due to natural material |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly but contains binders | 100% natural, biodegradable |
| Appearance | Consistent color and texture | Unique natural grain and patterns |
Introduction to Cork: Composite vs Solid
Composite cork consists of cork granules bound with adhesive agents, offering improved flexibility and durability, making it ideal for flooring and insulation applications. Solid cork is harvested in thick, uniform slabs directly from cork oak bark, prized for its natural thermal properties, resilience, and eco-friendly advantages. Both types showcase cork's sustainable qualities but differ in structure and suitability depending on the specific use case.
Material Composition: What Sets Cork Composites Apart
Cork composites combine natural cork granules with synthetic resins or binders, enhancing durability and flexibility compared to solid cork, which consists solely of natural cork bark. The inclusion of polymers or adhesives in cork composites improves resistance to moisture, impact, and wear while maintaining lightweight and insulating properties. This engineered material offers a versatile alternative for applications requiring greater strength and customization without compromising the eco-friendly benefits of traditional cork.
Performance Characteristics of Solid Cork
Solid cork offers superior durability and impact resistance compared to cork composite, making it ideal for high-traffic flooring applications. Its natural cellular structure provides excellent thermal insulation and acoustic properties, enhancing comfort in both residential and commercial spaces. Solid cork's resilience against moisture and wear ensures long-term performance, maintaining its aesthetic appeal over time.
Durability and Longevity: Cork Composite vs Solid
Cork composite offers enhanced durability by combining natural cork with synthetic materials, making it more resistant to wear and moisture compared to solid cork. Solid cork provides excellent cushioning and is naturally renewable but tends to be softer and more prone to dents and damage over time. For long-term use in high-traffic areas, cork composite outperforms solid cork due to its improved structural integrity and resistance to environmental factors.
Insulation Properties: Thermal and Acoustic Comparison
Cork composite and solid cork both offer excellent insulation properties, but solid cork typically provides superior thermal resistance due to its natural cellular structure that traps air efficiently. In terms of acoustic insulation, cork composite often incorporates additional materials that can enhance sound dampening, making it a versatile option for reducing noise transmission. When selecting between the two, consider solid cork for optimal thermal insulation and cork composite for tailored acoustic performance in building projects.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability of Cork Materials
Composite cork combines cork particles with binders, reducing natural cork usage but introducing synthetic elements that can impact biodegradability and recycling. Solid cork, harvested sustainably from cork oak bark without harming the tree, offers a renewable, biodegradable material with a lower environmental footprint. Choosing solid cork supports biodiversity, carbon sequestration, and long-term cork oak forest conservation, enhancing overall sustainability.
Cost Differences: Composite Cork vs Solid Cork
Composite cork typically costs less than solid cork due to its manufacturing process, which combines cork granules with adhesives or resins to optimize material usage and reduce waste. Solid cork, harvested directly from cork oak bark, involves more labor-intensive extraction and processing, resulting in higher prices. For budget-conscious projects in Cork, composite cork offers an affordable alternative without significantly compromising the natural benefits of cork material.
Ease of Installation and Handling
Composite cork offers superior ease of installation compared to solid cork due to its lightweight structure and consistent density, allowing for quicker cutting and fitting. Solid cork, while durable, is denser and heavier, which can complicate handling and extend installation time. The engineered nature of composite cork reduces waste and errors, streamlining the overall process for builders and DIY enthusiasts.
Aesthetic Variations in Cork Materials
Cork composites offer a diverse range of aesthetic variations, featuring patterns and textures that combine natural cork granules with resins for enhanced visual appeal and durability. Solid cork, derived directly from cork bark, provides a more authentic and organic look with unique variations in color, grain, and texture due to its natural growth process. These differences make cork composites suitable for contemporary designs requiring consistency, while solid cork is preferred for projects emphasizing natural beauty and sustainability.
Best Applications: Choosing Between Composite and Solid Cork
Solid cork offers superior durability and water resistance, making it ideal for flooring in high-traffic areas and wet environments like kitchens and bathrooms. Composite cork combines natural cork with synthetic materials, enhancing flexibility and cost-effectiveness, which suits wall panels, underlayment, and decorative applications. Selecting between composite and solid cork depends on the specific performance requirements, such as resilience, moisture resistance, and budget constraints.
Cork composite vs Solid cork Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com