Feldspathic ceramics are prized for their translucency and natural glass-like appearance, making them ideal for aesthetic dental restorations. Kaolin, a type of white clay, enhances the plasticity and workability of ceramic mixtures, improving molding precision and surface smoothness. Understanding the balance between feldspathic content and kaolin is essential for optimizing strength, durability, and esthetic qualities in ceramic products.
Table of Comparison
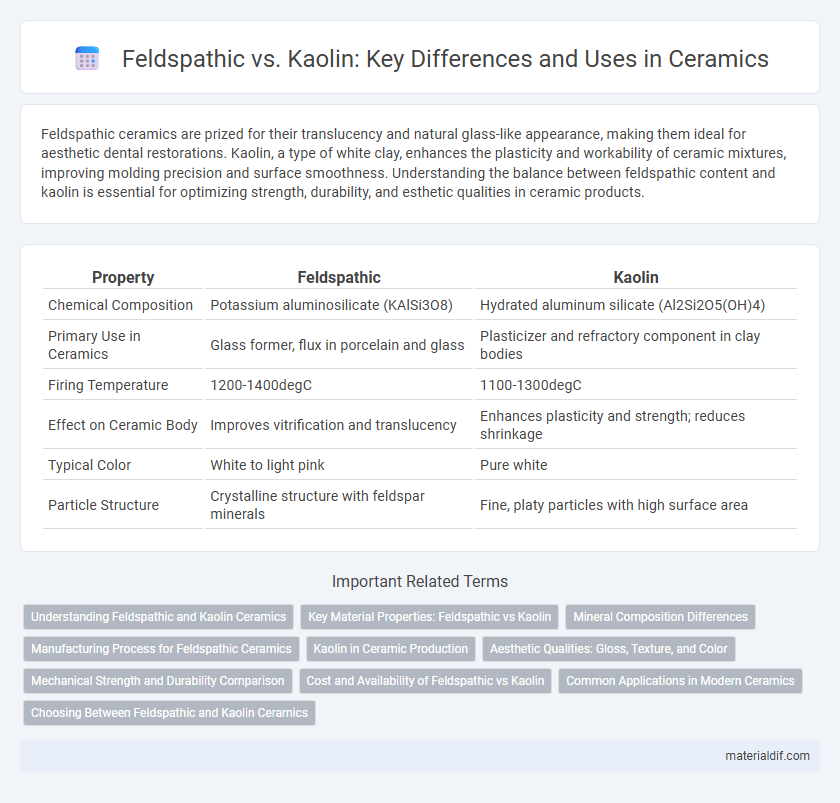
| Property | Feldspathic | Kaolin |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Potassium aluminosilicate (KAlSi3O8) | Hydrated aluminum silicate (Al2Si2O5(OH)4) |
| Primary Use in Ceramics | Glass former, flux in porcelain and glass | Plasticizer and refractory component in clay bodies |
| Firing Temperature | 1200-1400degC | 1100-1300degC |
| Effect on Ceramic Body | Improves vitrification and translucency | Enhances plasticity and strength; reduces shrinkage |
| Typical Color | White to light pink | Pure white |
| Particle Structure | Crystalline structure with feldspar minerals | Fine, platy particles with high surface area |
Understanding Feldspathic and Kaolin Ceramics
Feldspathic ceramics are composed primarily of feldspar minerals, which provide high glass content, excellent translucency, and superior strength, making them ideal for dental restorations and fine porcelain. Kaolin ceramics consist mainly of kaolinite clay, offering high plasticity, whiteness, and thermal stability, important for shaping and firing processes in pottery and technical ceramics. Understanding the distinct mineral compositions and properties of feldspathic versus kaolin ceramics helps optimize their applications in art, engineering, and medical fields.
Key Material Properties: Feldspathic vs Kaolin
Feldspathic ceramics exhibit high alumina content, enhancing strength and thermal stability, making them ideal for durable, high-temperature applications. Kaolin, rich in silica and alumina with fine particle size, provides excellent plasticity and whiteness, optimizing it for detailed shaping and smooth surface finishes. The choice between feldspathic and kaolin hinges on balancing mechanical strength versus workability and aesthetic qualities in ceramic production.
Mineral Composition Differences
Feldspathic ceramics primarily contain feldspar minerals, which are rich in silica, alumina, and alkali oxides, contributing to their glass-forming properties and high thermal stability. Kaolin-based ceramics rely on kaolinite clay, characterized by a high content of alumina and silica but with minimal alkali content, resulting in a more refractory and plastic material. The mineral composition differences influence the sintering behavior, firing temperature, and final mechanical strength of ceramic products.
Manufacturing Process for Feldspathic Ceramics
Feldspathic ceramics are manufactured through a precise process involving the melting and cooling of feldspar combined with silica and clay, which creates a glassy matrix that enhances strength and translucency. The raw materials are carefully ground, mixed, and fired at high temperatures, typically between 1200degC and 1400degC, to achieve optimal vitrification and durability. Compared to kaolin-based ceramics, feldspathic ceramics demand strict control during firing to prevent warping and ensure a dense, homogenous structure ideal for dental and fine ceramic applications.
Kaolin in Ceramic Production
Kaolin, a highly pure white clay mineral composed primarily of kaolinite, plays a crucial role in ceramic production by enhancing the plasticity, whiteness, and firing properties of ceramic bodies. Its fine particle size and chemical stability improve the strength and translucency of porcelain and fine china, distinguishing it from feldspathic materials, which mainly act as fluxes to lower the melting point of the mixture. The high alumina content in kaolin contributes to ceramic durability and resistance to thermal shock, making it indispensable in advanced ceramics manufacturing.
Aesthetic Qualities: Gloss, Texture, and Color
Feldspathic ceramics exhibit a high gloss finish with a smooth, glass-like texture, offering a natural translucency that closely mimics tooth enamel. Kaolin-based ceramics provide a matte to satin surface with a finer, more uniform texture, resulting in a softer, less reflective appearance. Color-wise, feldspathic materials offer a wider range of translucency and depth, while kaolin ceramics tend to present more opaque and consistent hues ideal for layering techniques.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Feldspathic ceramics exhibit higher mechanical strength due to their dense microstructure and enhanced vitrification, resulting in superior resistance to cracking and wear. Kaolin-based ceramics, while offering excellent thermal stability and whiteness, tend to have lower strength and are more prone to brittleness under mechanical stress. The durability of feldspathic ceramics surpasses that of kaolin ceramics, making them preferable for applications requiring robust structural integrity.
Cost and Availability of Feldspathic vs Kaolin
Feldspathic materials tend to be more widely available and cost-effective due to abundant natural reserves and simpler mining processes, making them favorable for large-scale ceramic production. Kaolin, while more expensive, offers higher purity and consistency but is limited by regional deposits, often increasing transportation costs and supply chain complexity. Manufacturers balance these factors, choosing feldspathic substitutes when cost efficiency is critical and kaolin when superior ceramic quality is required.
Common Applications in Modern Ceramics
Feldspathic materials are widely used in the production of porcelain and vitreous ceramics due to their excellent fluxing properties, which lower the melting point and enhance strength and translucency. Kaolin, a primary clay component, is essential in creating whiteware, sanitaryware, and fine china for its plasticity and high refractory nature, enabling precise shaping and durability during firing. Modern ceramic manufacturing often combines feldspathic fluxes with kaolin to balance workability and final product hardness in applications such as tiles, tableware, and advanced technical ceramics.
Choosing Between Feldspathic and Kaolin Ceramics
Choosing between feldspathic and kaolin ceramics depends on the desired properties for the final product; feldspathic ceramics offer superior translucency and aesthetic appeal, making them ideal for dental veneers and fine porcelain. Kaolin ceramics, on the other hand, provide higher strength and durability due to their alumina content, suitable for functional pottery and technical applications. Understanding the thermal expansion and firing temperatures of each material ensures optimal performance and longevity in ceramic manufacturing.
Feldspathic vs Kaolin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com