Ceramic insulators offer superior mechanical strength and resistance to high temperatures compared to glass insulators, making them ideal for heavy-duty electrical applications. Unlike glass insulators, ceramics provide enhanced durability against environmental stressors such as pollution and moisture. Their ability to maintain dielectric properties under harsh conditions ensures reliable performance in power transmission and distribution systems.
Table of Comparison
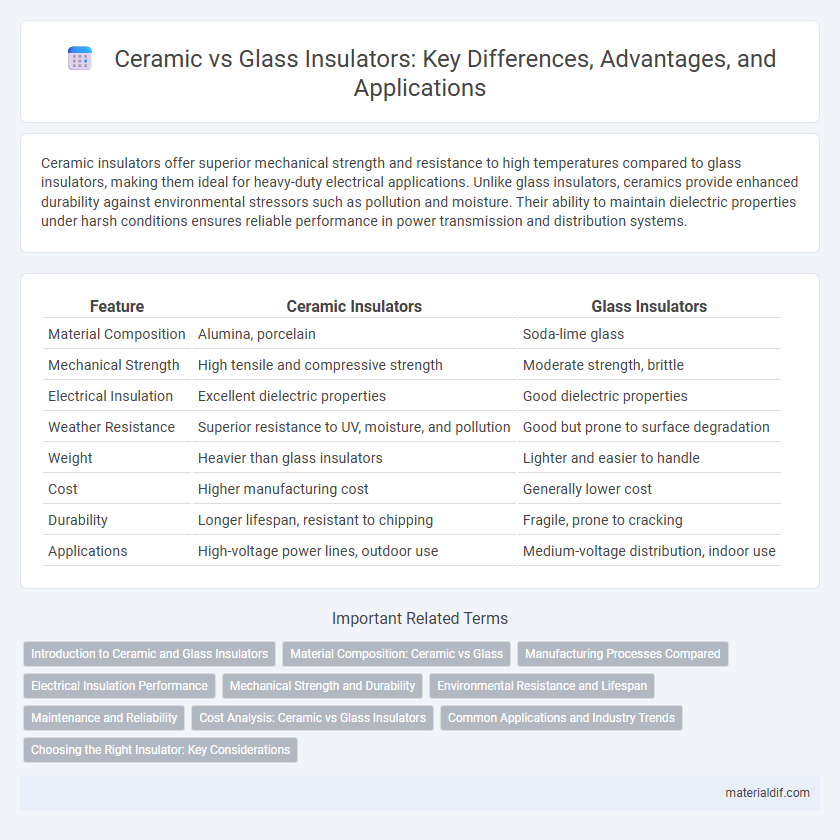
| Feature | Ceramic Insulators | Glass Insulators |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Alumina, porcelain | Soda-lime glass |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile and compressive strength | Moderate strength, brittle |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric properties | Good dielectric properties |
| Weather Resistance | Superior resistance to UV, moisture, and pollution | Good but prone to surface degradation |
| Weight | Heavier than glass insulators | Lighter and easier to handle |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Generally lower cost |
| Durability | Longer lifespan, resistant to chipping | Fragile, prone to cracking |
| Applications | High-voltage power lines, outdoor use | Medium-voltage distribution, indoor use |
Introduction to Ceramic and Glass Insulators
Ceramic insulators and glass insulators both serve critical roles in electrical systems by providing high dielectric strength and mechanical support. Ceramic insulators, made from porcelain, exhibit superior thermal stability, excellent resistance to weathering, and strong insulation properties under high voltage conditions. Glass insulators offer benefits such as visibility of internal damage and lower manufacturing costs but generally have lower mechanical strength and are more prone to breakage compared to ceramic insulators.
Material Composition: Ceramic vs Glass
Ceramic insulators are primarily composed of alumina, silica, and feldspar, which provide excellent mechanical strength and thermal stability. Glass insulators consist mainly of silica with varying amounts of alkali and alkaline earth metals, offering superior electrical insulation but less resistance to mechanical stress. The crystalline structure of ceramic allows for higher durability and resistance to environmental degradation compared to the amorphous structure of glass.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Ceramic insulators are produced through high-temperature firing of clay and other raw materials, resulting in a dense, durable structure with excellent electrical insulation properties. Glass insulators are manufactured by melting raw materials like silica sand and soda ash, then shaping and cooling the molten glass to form a brittle but smooth and transparent product. The ceramic process allows for better mechanical strength and resistance to weathering, while glass manufacturing emphasizes clarity and ease of molding complex shapes.
Electrical Insulation Performance
Ceramic insulators exhibit superior electrical insulation performance compared to glass insulators due to their higher dielectric strength and enhanced resistance to electrical stress and moisture. The microstructure of ceramics offers better durability under high voltage conditions, minimizing leakage currents and surface contamination issues. Glass insulators, while effective, are more prone to failures from cracking and lower resistance to environmental factors, making ceramics a preferred choice in modern high voltage applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Ceramic insulators exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to glass insulators, making them more resistant to impact and mechanical stress in high-voltage applications. Their enhanced durability allows for better performance in harsh environmental conditions, including extreme temperature variations and pollution. Unlike glass insulators, ceramic materials are less prone to cracking and chipping, ensuring longer service life and reduced maintenance costs.
Environmental Resistance and Lifespan
Ceramic insulators exhibit superior environmental resistance compared to glass insulators, effectively withstanding UV radiation, temperature fluctuations, and pollution without degradation. Their robust composition ensures a longer lifespan, often surpassing 40 years in harsh outdoor conditions. Glass insulators, while resistant to corrosion, are more susceptible to mechanical stress and environmental wear, resulting in a comparatively shorter service life.
Maintenance and Reliability
Ceramic insulators demonstrate superior durability and require less frequent maintenance compared to glass insulators due to their high resistance to weathering and mechanical stress. Their non-porous surface minimizes contamination buildup, enhancing long-term reliability in harsh environmental conditions. Glass insulators, while providing good visibility for damage detection, often face brittleness and increased risk of cracking, leading to higher maintenance demands and potential service interruptions.
Cost Analysis: Ceramic vs Glass Insulators
Ceramic insulators generally offer a lower initial cost compared to glass insulators, making them an economical choice for high-voltage applications. While glass insulators provide superior mechanical strength and longer lifespan, the higher manufacturing and replacement expenses often result in increased overall costs. Maintenance costs for ceramic insulators tend to be lower due to their resistance to surface damage and environmental degradation, influencing total cost of ownership favorably.
Common Applications and Industry Trends
Ceramic insulators are predominantly used in high-voltage power transmission and distribution due to their superior mechanical strength and excellent thermal performance, making them ideal for outdoor electrical insulations in substations and overhead lines. Glass insulators, favored for their high dielectric strength and visibility of internal faults, find common applications in railway electrification and telecommunication lines where durability under environmental stress is crucial. Industry trends indicate a growing preference for composite insulators combining ceramic and glass properties to enhance performance, reduce weight, and improve resistance to pollution and mechanical wear.
Choosing the Right Insulator: Key Considerations
Ceramic insulators offer superior mechanical strength and better thermal stability compared to glass insulators, making them ideal for high-voltage applications and harsh environmental conditions. Glass insulators provide excellent visibility for detecting internal defects but are more prone to sudden breakage due to their brittle nature. When choosing the right insulator, factors such as mechanical load, environmental exposure, electrical performance, and maintenance requirements must be carefully evaluated to ensure long-term reliability and safety.
Ceramic insulators vs Glass insulators Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com