Cartridge brass, typically composed of 70% copper and 30% zinc, offers superior strength and corrosion resistance compared to yellow brass, which usually contains about 60% copper and 40% zinc. This higher copper content in cartridge brass enhances its ability to withstand high pressures, making it ideal for ammunition casings and industrial applications. Yellow brass's increased zinc content provides greater malleability and a brighter appearance, making it suitable for decorative items and musical instruments.
Table of Comparison
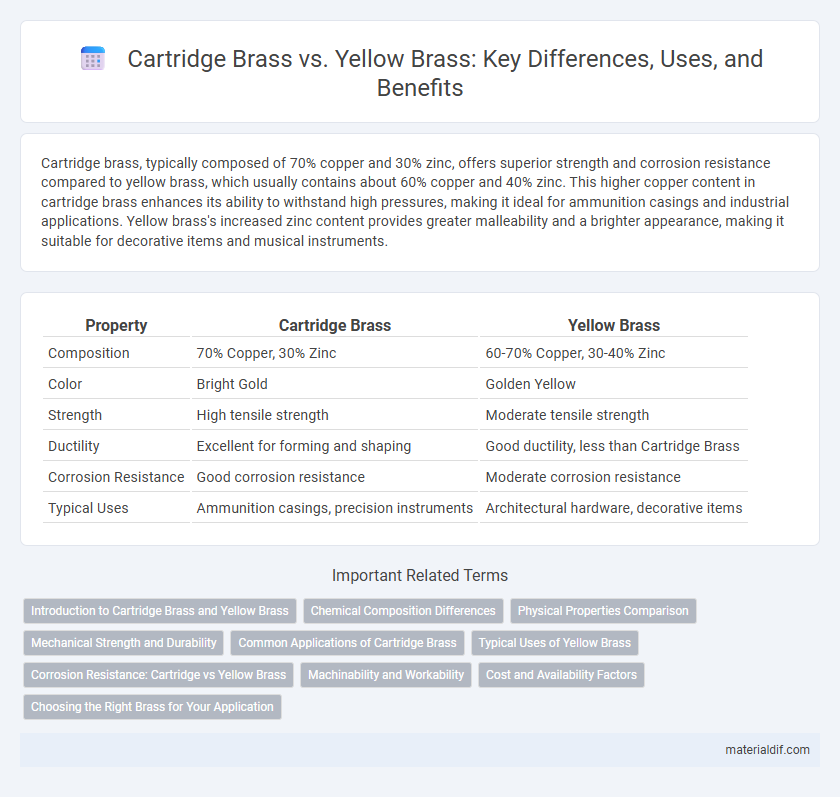
| Property | Cartridge Brass | Yellow Brass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | 70% Copper, 30% Zinc | 60-70% Copper, 30-40% Zinc |
| Color | Bright Gold | Golden Yellow |
| Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Ductility | Excellent for forming and shaping | Good ductility, less than Cartridge Brass |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good corrosion resistance | Moderate corrosion resistance |
| Typical Uses | Ammunition casings, precision instruments | Architectural hardware, decorative items |
Introduction to Cartridge Brass and Yellow Brass
Cartridge brass, primarily composed of 70% copper and 30% zinc, offers excellent ductility and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for ammunition casings and precision components. Yellow brass, typically containing 60-63% copper and 37-40% zinc, features higher strength and moderate machinability, widely used in plumbing fittings and decorative hardware. The distinct alloy compositions influence their mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and typical applications in various industrial sectors.
Chemical Composition Differences
Cartridge brass typically consists of about 70% copper and 30% zinc, offering a balance of strength and ductility suited for ammunition casings. Yellow brass contains approximately 60-63% copper and 37-40% zinc, making it more malleable and corrosion-resistant for decorative applications. The higher zinc content in yellow brass lowers the copper percentage, influencing its color and mechanical properties compared to cartridge brass.
Physical Properties Comparison
Cartridge brass, typically composed of 70% copper and 30% zinc, exhibits higher tensile strength and superior corrosion resistance compared to yellow brass, which contains about 60-65% copper and 35-40% zinc. Yellow brass offers greater malleability and ductility, making it ideal for intricate forming applications, whereas cartridge brass is favored for its durability and wear resistance in ammunition casings. The density of cartridge brass is approximately 8.4 g/cm3, slightly higher than yellow brass, which ranges around 8.3 g/cm3, reflecting differences in material composition and structural integrity.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Cartridge brass, typically composed of 70% copper and 30% zinc, exhibits superior mechanical strength and durability compared to yellow brass, which contains roughly 60-70% copper with a higher zinc content. The balanced zinc concentration in cartridge brass enhances its tensile strength and resistance to wear, making it ideal for high-stress applications like ammunition casings. Yellow brass, while corrosion-resistant, generally has lower tensile strength and is less resilient under mechanical stress, limiting its use in high-durability scenarios.
Common Applications of Cartridge Brass
Cartridge brass, composed primarily of 70% copper and 30% zinc, is widely used in ammunition casings due to its excellent corrosion resistance and high ductility. Its ability to withstand high pressure without cracking makes it ideal for cartridges in firearms and shell casings in the defense industry. Beyond ammunition, cartridge brass is also utilized in electrical connectors and decorative hardware, benefiting from its superior formability and polish.
Typical Uses of Yellow Brass
Yellow Brass, commonly composed of approximately 70% copper and 30% zinc, is widely used in decorative applications, plumbing fittings, and musical instruments due to its bright gold-like appearance and corrosion resistance. Its excellent machinability and acoustic properties make it ideal for manufacturing locks, gears, and valves, where durability and aesthetic appeal are crucial. Unlike cartridge brass, which is preferred for ammunition casings, yellow brass is favored in architectural hardware and ornamental trims for its visual attractiveness and functional reliability.
Corrosion Resistance: Cartridge vs Yellow Brass
Cartridge brass, typically composed of 70% copper and 30% zinc, exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to yellow brass, which generally contains about 60-65% copper with higher zinc content. The lower zinc percentage in cartridge brass enhances its resistance to dezincification, making it ideal for applications exposed to moisture and corrosive environments. Yellow brass, while versatile and cost-effective, is more prone to corrosion and dezincification, reducing its durability in harsh conditions.
Machinability and Workability
Cartridge brass, typically composed of 70% copper and 30% zinc, offers superior machinability due to its higher zinc content, making it ideal for precision components and ammunition casings. Yellow brass, with a zinc content around 33%, exhibits enhanced workability and corrosion resistance but is slightly harder to machine compared to cartridge brass. The balance between machinability and workability makes cartridge brass preferred for fine machining tasks, while yellow brass is favored in applications requiring better forming and durability.
Cost and Availability Factors
Cartridge brass, primarily composed of 70% copper and 30% zinc, is widely used in ammunition casings due to its excellent ductility and corrosion resistance, which commands a higher cost compared to yellow brass. Yellow brass, with a typical composition of 65% copper and 35% zinc, is more readily available and cost-effective for general manufacturing and decorative applications. The higher zinc content in yellow brass enhances machinability and reduces raw material expenses, making it a preferred choice where budget constraints and abundant supply are critical factors.
Choosing the Right Brass for Your Application
Cartridge brass, typically composed of 70% copper and 30% zinc, offers excellent ductility and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for ammunition casings and precision components. Yellow brass, with a slightly lower copper content around 60-65%, provides superior strength and machinability, suited for plumbing fixtures, musical instruments, and decorative items. Selecting the right brass alloy depends on balancing factors such as mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and workability to meet specific application requirements.
Cartridge Brass vs Yellow Brass Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com