Brass extrusion produces high-strength, uniform profiles by forcing heated brass through a die, ideal for precise, long, and complex shapes. Brass casting, involving molten metal poured into molds, allows for intricate designs and large components but may result in less material consistency. Choosing between these methods depends on the required dimensional accuracy, mechanical properties, and production volume.
Table of Comparison
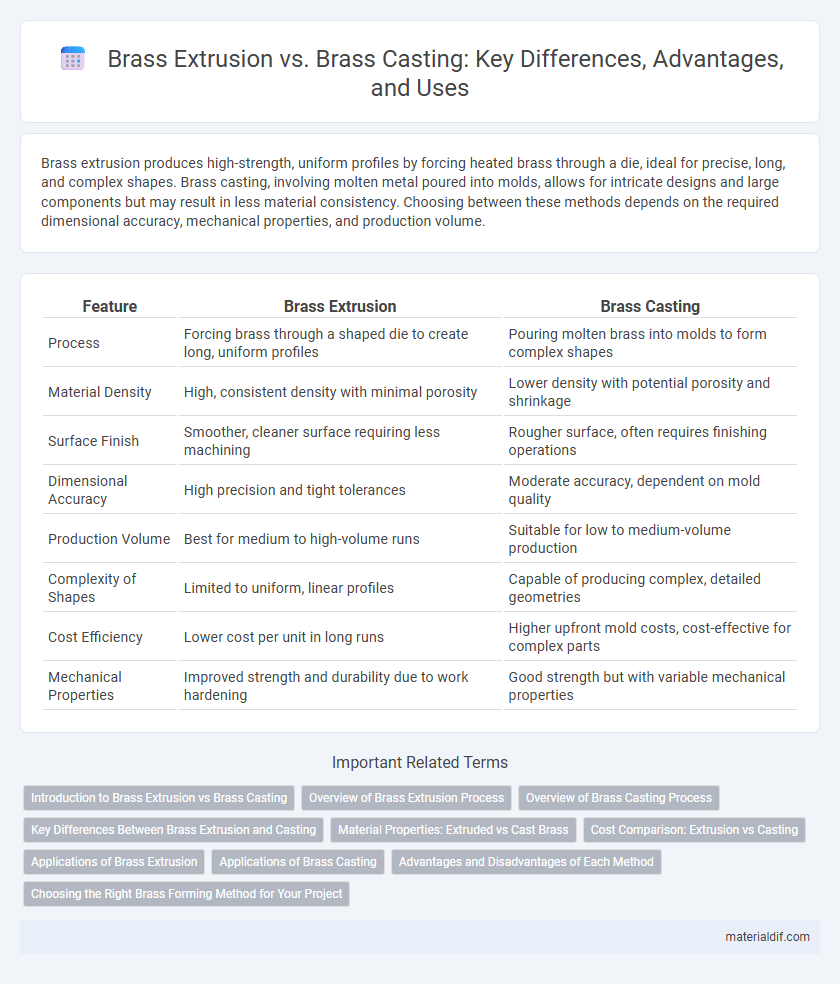
| Feature | Brass Extrusion | Brass Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Forcing brass through a shaped die to create long, uniform profiles | Pouring molten brass into molds to form complex shapes |
| Material Density | High, consistent density with minimal porosity | Lower density with potential porosity and shrinkage |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, cleaner surface requiring less machining | Rougher surface, often requires finishing operations |
| Dimensional Accuracy | High precision and tight tolerances | Moderate accuracy, dependent on mold quality |
| Production Volume | Best for medium to high-volume runs | Suitable for low to medium-volume production |
| Complexity of Shapes | Limited to uniform, linear profiles | Capable of producing complex, detailed geometries |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower cost per unit in long runs | Higher upfront mold costs, cost-effective for complex parts |
| Mechanical Properties | Improved strength and durability due to work hardening | Good strength but with variable mechanical properties |
Introduction to Brass Extrusion vs Brass Casting
Brass extrusion involves forcing heated brass through a die to create uniform cross-sectional profiles, offering precise control over dimensions and mechanical properties. Brass casting, on the other hand, melts brass and pours it into molds to form complex shapes, suitable for intricate designs but with less dimensional accuracy. Understanding these fundamental differences helps in selecting the appropriate manufacturing process for specific industrial applications.
Overview of Brass Extrusion Process
Brass extrusion involves forcing heated brass billets through a die to create continuous profiles with uniform cross-sections, enabling precise shapes and smooth surface finishes. This process offers enhanced mechanical properties due to the metal's work-hardening and grain flow alignment, resulting in improved strength and durability. Compared to brass casting, extrusion provides tighter dimensional tolerances and less material waste, making it ideal for producing complex, high-strength components.
Overview of Brass Casting Process
Brass casting involves pouring molten brass into a mold to create complex shapes with excellent dimensional accuracy and surface finish. This process is ideal for producing intricate components that are difficult to achieve through extrusion, such as valves, fittings, and decorative hardware. Key advantages include reduced machining requirements and the ability to manufacture parts with varying wall thicknesses and internal cavities.
Key Differences Between Brass Extrusion and Casting
Brass extrusion produces uniform, high-strength components by forcing heated brass through a die, resulting in enhanced mechanical properties and precise dimensional accuracy. Brass casting involves pouring molten brass into molds, allowing for complex shapes but generally yielding lower strength and surface finish compared to extrusion. Extrusion is preferred for long, consistent profiles, while casting suits intricate, detailed designs with less emphasis on structural performance.
Material Properties: Extruded vs Cast Brass
Extruded brass exhibits a more uniform grain structure, resulting in higher tensile strength and improved fatigue resistance compared to cast brass. The controlled cooling process in extrusion minimizes porosity and enhances mechanical properties, making it ideal for components requiring precise dimensional tolerances. Cast brass, while offering excellent corrosion resistance and workability, typically has a coarser grain structure and higher susceptibility to internal defects, impacting its overall strength and durability.
Cost Comparison: Extrusion vs Casting
Brass extrusion generally offers lower production costs compared to brass casting due to its streamlined manufacturing process and higher material efficiency, which reduces waste. Casting involves higher expenses related to mold creation and longer cooling times, increasing labor and energy costs. For large-scale production of uniform profiles, extrusion provides a cost-effective solution, while casting is more viable for complex shapes but at a higher overall cost.
Applications of Brass Extrusion
Brass extrusion is widely applied in manufacturing plumbing fittings, electrical connectors, and automotive components due to its ability to produce complex, precise profiles with excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy. This process enables the creation of long, uniform shapes ideal for structural applications, such as architectural trim and heat exchanger tubes, where strength and corrosion resistance are critical. Brass extrusion offers superior mechanical properties and consistency compared to casting, making it suitable for industries requiring high-quality, durable brass parts.
Applications of Brass Casting
Brass casting is widely used in applications requiring complex shapes and intricate details such as plumbing fittings, electrical connectors, and decorative hardware. Its superior dimensional accuracy and surface finish make it ideal for producing durable components in automotive parts, valves, and musical instruments. Brass casting supports high-volume production runs with consistent quality critical in industrial and consumer goods manufacturing.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Method
Brass extrusion offers precise dimensional control, improved mechanical properties, and superior surface finish, making it ideal for high-strength applications, but it involves higher tooling costs and is less suitable for complex shapes. Brass casting allows for intricate geometries and reduced manufacturing costs for large, complex parts but often results in lower strength and surface quality compared to extruded components. Choosing between brass extrusion and casting depends on balancing production volume, part complexity, mechanical requirements, and cost efficiency.
Choosing the Right Brass Forming Method for Your Project
Brass extrusion offers precise dimensional control and excellent mechanical properties, making it ideal for complex profiles and high-strength applications. Brass casting provides versatility in shape and size with lower initial tooling costs, suitable for intricate designs and lower production volumes. Evaluating project requirements such as part complexity, volume, and mechanical performance is crucial when choosing between brass extrusion and casting.
Brass Extrusion vs Brass Casting Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com