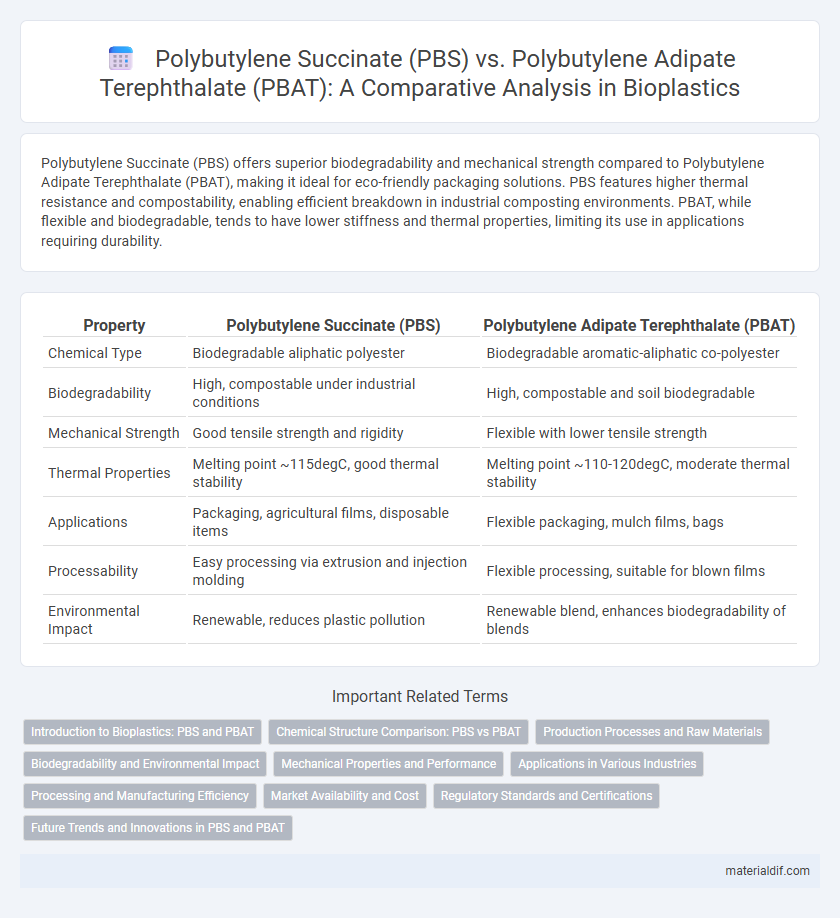
Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) offers superior biodegradability and mechanical strength compared to Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate (PBAT), making it ideal for eco-friendly packaging solutions. PBS features higher thermal resistance and compostability, enabling efficient breakdown in industrial composting environments. PBAT, while flexible and biodegradable, tends to have lower stiffness and thermal properties, limiting its use in applications requiring durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) | Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate (PBAT) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Type | Biodegradable aliphatic polyester | Biodegradable aromatic-aliphatic co-polyester |
| Biodegradability | High, compostable under industrial conditions | High, compostable and soil biodegradable |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength and rigidity | Flexible with lower tensile strength |
| Thermal Properties | Melting point ~115degC, good thermal stability | Melting point ~110-120degC, moderate thermal stability |
| Applications | Packaging, agricultural films, disposable items | Flexible packaging, mulch films, bags |
| Processability | Easy processing via extrusion and injection molding | Flexible processing, suitable for blown films |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, reduces plastic pollution | Renewable blend, enhances biodegradability of blends |
Introduction to Bioplastics: PBS and PBAT
Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) and Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate (PBAT) are prominent biodegradable polyesters used in bioplastic applications, offering eco-friendly alternatives to traditional plastics. PBS is derived from succinic acid and 1,4-butanediol, known for its high crystallinity, thermal stability, and rigidity, making it suitable for packaging and agricultural films. In contrast, PBAT is a copolymer synthesized from adipic acid, terephthalic acid, and 1,4-butanediol, valued for its flexibility, toughness, and compostability in various packaging and mulch film uses.
Chemical Structure Comparison: PBS vs PBAT
Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) consists of linear aliphatic polyester chains derived from succinic acid and 1,4-butanediol, offering high crystallinity and thermal stability. Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate (PBAT) is a copolyester comprising adipic acid, terephthalic acid, and 1,4-butanediol, featuring both aliphatic and aromatic segments that provide enhanced flexibility and biodegradability. The aromatic terephthalate units in PBAT reduce crystallinity relative to PBS, resulting in a softer material with improved elongation properties.
Production Processes and Raw Materials
Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) is synthesized through the polycondensation of succinic acid and 1,4-butanediol, both of which can be derived from renewable biomass sources such as glucose fermentation. Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate (PBAT) results from the copolymerization of adipic acid, terephthalic acid, and 1,4-butanediol, with terephthalic acid primarily obtained from petrochemical feedstocks. The production of PBS typically involves more sustainable biomass-derived raw materials, whereas PBAT production relies significantly on petrochemical components, impacting the overall environmental footprint of each bioplastic.
Biodegradability and Environmental Impact
Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) offers superior biodegradability compared to Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate (PBAT), breaking down more efficiently in soil and compost environments due to its aliphatic polyester structure. PBS demonstrates lower environmental impact by releasing fewer greenhouse gases during degradation and being derived more frequently from renewable biomass sources. While PBAT provides flexibility in applications, its slower degradation rate and higher petroleum-based content contribute to a longer environmental footprint.
Mechanical Properties and Performance
Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) exhibits higher tensile strength and better thermal stability compared to Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate (PBAT), making it suitable for applications requiring rigidity and heat resistance. PBAT offers superior flexibility and elongation at break, contributing to better impact resistance and stretchability in flexible packaging and compostable films. Both polymers demonstrate biodegradability, but PBS typically delivers enhanced mechanical performance in load-bearing applications, while PBAT excels in applications needing elasticity and softness.
Applications in Various Industries
Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) is widely used in packaging, agricultural films, and disposable tableware due to its biodegradability and mechanical strength, making it suitable for environmentally friendly products. Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate (PBAT) finds extensive application in compostable bags, flexible packaging, and food service items owing to its excellent flexibility and high elongation properties. Industries such as agriculture, food packaging, and consumer goods leverage PBS for its thermal stability, while PBAT is preferred in applications requiring softness and biodegradability.
Processing and Manufacturing Efficiency
Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) offers superior processing efficiency due to its higher melting point and crystallization rate, facilitating faster mold cycle times in injection molding and extrusion. Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate (PBAT), while more flexible and biodegradable, requires lower processing temperatures and longer cooling times, potentially reducing throughput in manufacturing. PBS's thermal stability and crystallinity make it preferable for large-scale production aimed at packaging and compostable products.
Market Availability and Cost
Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) is gaining market availability due to its biodegradability and compatibility with composting standards, albeit at a higher production cost compared to conventional plastics. Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate (PBAT) is widely accessible in global markets, often favored for its lower cost and flexibility in blending with other bioplastics, which reduces overall material expenses. Cost-effectiveness and supply chain maturity make PBAT a preferred choice for large-scale packaging applications, while PBS appeals to niche markets prioritizing environmental sustainability.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) meets international regulatory standards such as ASTM D6400 and EN 13432 for compostability, ensuring its suitability for food-contact applications and industrial composting. Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate (PBAT) also complies with these certifications but is often preferred for flexible packaging due to its enhanced biodegradability under various conditions. Both bioplastics hold certifications from organizations like TUV Austria and BPI, validating their environmental performance and aiding manufacturers in meeting global sustainability regulations.
Future Trends and Innovations in PBS and PBAT
Future trends in Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) emphasize increasing its biodegradability and mechanical strength through bio-based monomers and enzymatic synthesis, targeting packaging and agricultural applications. Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate (PBAT) innovations focus on enhancing its flexibility and compostability by blending with starch and other biopolymers, improving performance in single-use plastics. Emerging research explores nanocomposite integration and chemical recycling techniques for both PBS and PBAT to advance sustainability and circular economy goals in the bioplastics industry.
Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) vs Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate (PBAT) Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com