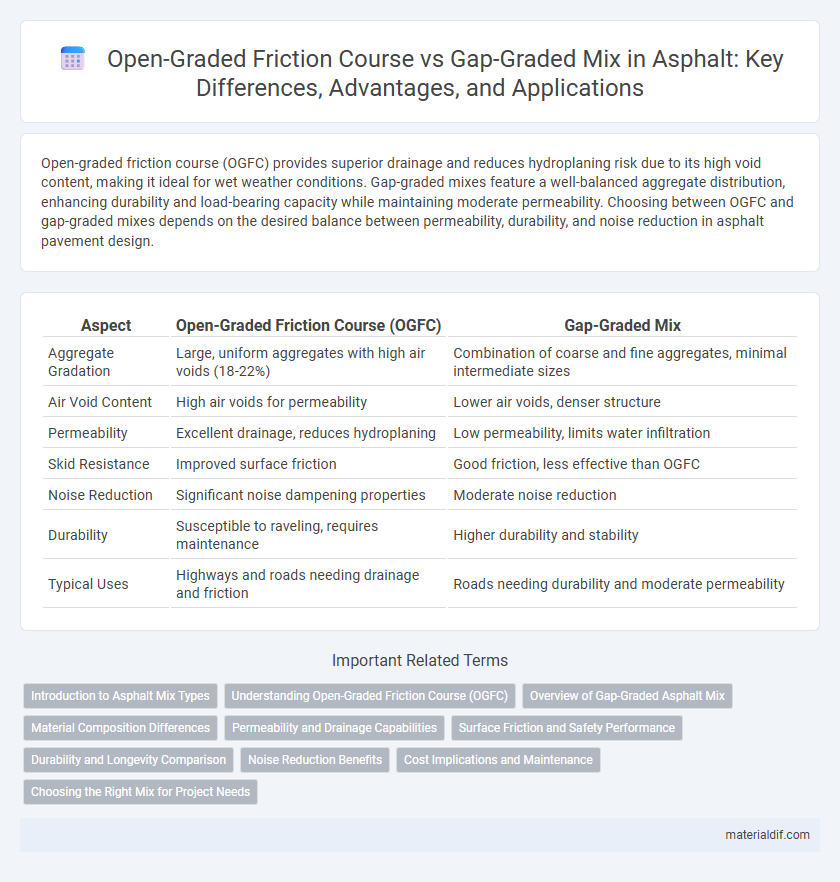
Open-graded friction course (OGFC) provides superior drainage and reduces hydroplaning risk due to its high void content, making it ideal for wet weather conditions. Gap-graded mixes feature a well-balanced aggregate distribution, enhancing durability and load-bearing capacity while maintaining moderate permeability. Choosing between OGFC and gap-graded mixes depends on the desired balance between permeability, durability, and noise reduction in asphalt pavement design.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Open-Graded Friction Course (OGFC) | Gap-Graded Mix |
|---|---|---|
| Aggregate Gradation | Large, uniform aggregates with high air voids (18-22%) | Combination of coarse and fine aggregates, minimal intermediate sizes |
| Air Void Content | High air voids for permeability | Lower air voids, denser structure |
| Permeability | Excellent drainage, reduces hydroplaning | Low permeability, limits water infiltration |
| Skid Resistance | Improved surface friction | Good friction, less effective than OGFC |
| Noise Reduction | Significant noise dampening properties | Moderate noise reduction |
| Durability | Susceptible to raveling, requires maintenance | Higher durability and stability |
| Typical Uses | Highways and roads needing drainage and friction | Roads needing durability and moderate permeability |
Introduction to Asphalt Mix Types
Open-graded friction course (OGFC) asphalt mix features large, interconnected air voids that enhance water drainage and improve surface friction, making it ideal for wet conditions. Gap-graded asphalt mix contains a combination of coarse and fine aggregates with minimal intermediate sizes, optimizing durability and resistance to deformation under heavy traffic. Both mix types play crucial roles in pavement performance, with OGFC prioritizing surface safety and gap-graded mixes emphasizing structural strength.
Understanding Open-Graded Friction Course (OGFC)
Open-Graded Friction Course (OGFC) is a porous asphalt mix designed to improve surface drainage and reduce hydroplaning by allowing water to pass through the pavement surface. Unlike Gap-Graded Mixes, OGFC features a single size aggregate with high air void content, enhancing skid resistance and noise reduction. Its open structure minimizes water splash and spray, promoting safer driving conditions in wet weather.
Overview of Gap-Graded Asphalt Mix
Gap-graded asphalt mix features a well-defined particle size distribution designed to create a dense, tightly interlocked aggregate structure that enhances load-bearing capacity and durability. This mix type balances air voids and binder content to improve rut resistance and long-term performance under traffic stress. Unlike open-graded friction courses, gap-graded mixes provide superior structural support while maintaining adequate permeability to manage water drainage.
Material Composition Differences
Open-graded friction course (OGFC) primarily consists of larger aggregate sizes with a high void content, enhancing permeability and drainage by allowing water to flow through the pavement surface. Gap-graded mixes combine coarse and fine aggregates while minimizing intermediate sizes, resulting in a denser matrix that improves durability and load distribution. The material composition in OGFC emphasizes porosity for skid resistance and water runoff, whereas gap-graded mixes focus on achieving a balance of strength and flexibility through improved particle packing.
Permeability and Drainage Capabilities
Open-graded friction courses exhibit high permeability due to their large interconnected voids, enabling superior drainage and reducing hydroplaning risks on asphalt pavements. Gap-graded mixes feature a more compact aggregate structure with moderate permeability, balancing drainage efficiency and load-bearing capacity. Enhanced permeability in open-graded friction courses results in faster water evacuation, improving surface safety and pavement longevity compared to gap-graded mixes.
Surface Friction and Safety Performance
Open-graded friction course (OGFC) provides superior surface friction by enhancing water drainage and reducing hydroplaning risks, which significantly improves safety performance in wet conditions. Gap-graded mix offers a denser structure that provides better durability but lower surface friction due to reduced air voids and slower water permeability. Enhanced skid resistance of OGFC directly contributes to safer driving environments, especially on high-traffic roadways prone to moisture buildup.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Open-graded friction course (OGFC) asphalt provides superior drainage and reduces surface water buildup, enhancing skid resistance but generally exhibits lower durability due to higher air void content that increases susceptibility to oxidation and raveling. Gap-graded mixes deliver improved density and structural integrity with lower air voids, resulting in greater resistance to deformation, cracking, and aging, thereby extending pavement longevity under heavy traffic loads. Comparative studies indicate that while OGFC enhances safety through better friction, gap-graded asphalt outperforms in durability and lifecycle costs, making it preferable for long-term pavement performance.
Noise Reduction Benefits
Open-graded friction course (OGFC) asphalt exhibits superior noise reduction benefits by allowing air to flow through its porous structure, effectively minimizing tire-pavement interaction noise. Gap-graded mixes, with their denser composition, reduce noise less efficiently due to lower air void content restricting sound absorption. Consequently, OGFC pavements are preferred in urban areas aiming to lower traffic noise pollution and enhance roadway acoustics.
Cost Implications and Maintenance
Open-graded friction course (OGFC) typically incurs higher initial costs due to specialized materials and construction techniques but reduces long-term maintenance expenses by improving drainage and reducing hydroplaning risks. Gap-graded mix often has lower upfront costs but may require more frequent maintenance to address rutting and surface wear, leading to increased lifecycle expenses. Selecting between OGFC and gap-graded mixes depends on balancing initial budget constraints with projected maintenance savings and roadway performance goals.
Choosing the Right Mix for Project Needs
Open-graded friction course (OGFC) offers superior water drainage and skid resistance, making it ideal for wet climates and high-traffic areas requiring enhanced safety. Gap-graded mixes provide a denser structure with increased load-bearing capacity, suitable for projects demanding durability and resistance to deformation under heavy loads. Selecting the right mix depends on balancing performance needs like permeability, skid resistance, and structural strength to ensure optimal pavement longevity and safety.
Open-graded friction course vs Gap-graded mix Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com