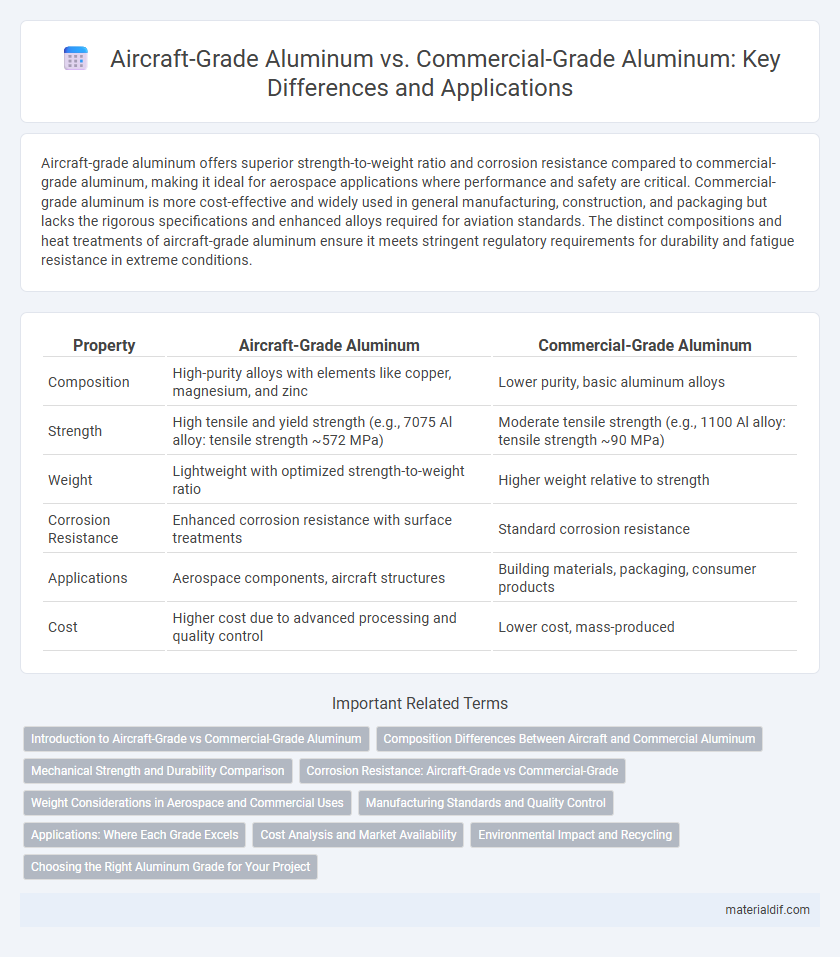
Aircraft-grade aluminum offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance compared to commercial-grade aluminum, making it ideal for aerospace applications where performance and safety are critical. Commercial-grade aluminum is more cost-effective and widely used in general manufacturing, construction, and packaging but lacks the rigorous specifications and enhanced alloys required for aviation standards. The distinct compositions and heat treatments of aircraft-grade aluminum ensure it meets stringent regulatory requirements for durability and fatigue resistance in extreme conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aircraft-Grade Aluminum | Commercial-Grade Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | High-purity alloys with elements like copper, magnesium, and zinc | Lower purity, basic aluminum alloys |
| Strength | High tensile and yield strength (e.g., 7075 Al alloy: tensile strength ~572 MPa) | Moderate tensile strength (e.g., 1100 Al alloy: tensile strength ~90 MPa) |
| Weight | Lightweight with optimized strength-to-weight ratio | Higher weight relative to strength |
| Corrosion Resistance | Enhanced corrosion resistance with surface treatments | Standard corrosion resistance |
| Applications | Aerospace components, aircraft structures | Building materials, packaging, consumer products |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced processing and quality control | Lower cost, mass-produced |
Introduction to Aircraft-Grade vs Commercial-Grade Aluminum
Aircraft-grade aluminum, primarily in the 2000 and 7000 series alloys, offers superior strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance essential for aerospace applications. Commercial-grade aluminum includes a broader range of alloys such as the 1000 and 3000 series, optimized for general use with more emphasis on formability and cost-effectiveness rather than extreme performance. The high tensile strength and fatigue resistance of aircraft-grade aluminum make it the preferred choice for structural components in aircraft manufacturing.
Composition Differences Between Aircraft and Commercial Aluminum
Aircraft-grade aluminum predominantly consists of high-strength alloys such as 2024, 6061, and 7075, containing elements like copper, magnesium, and zinc to enhance tensile strength and corrosion resistance. Commercial-grade aluminum typically features lower alloy content and is primarily composed of 1000 series pure aluminum or 3000 series alloys, focusing more on malleability and conductivity than structural performance. The precise elemental composition in aircraft-grade aluminum allows it to meet rigorous aerospace standards for durability, weight, and safety.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Aircraft-grade aluminum, typically alloyed with elements like copper, magnesium, and zinc, offers superior mechanical strength and enhanced fatigue resistance compared to commercial-grade aluminum, which often lacks these reinforcing additives. The tensile strength of aircraft-grade alloys can exceed 70,000 psi, significantly outperforming commercial-grade aluminum that generally ranges between 30,000 to 50,000 psi. Durability in aircraft-grade aluminum includes better corrosion resistance and damage tolerance essential for aerospace applications, while commercial-grade aluminum suits general construction but falls short under high-stress conditions.
Corrosion Resistance: Aircraft-Grade vs Commercial-Grade
Aircraft-grade aluminum, specifically alloys like 7075 and 2024, exhibit superior corrosion resistance due to their precise alloying elements and controlled heat treatment processes, which enhance durability in harsh aerospace environments. Commercial-grade aluminum, such as 1100 and 3003 series, generally offers lower corrosion resistance, making it more suitable for less demanding applications where exposure to corrosive elements is limited. The enhanced corrosion resistance of aircraft-grade aluminum significantly extends the lifespan and safety of components used in aviation.
Weight Considerations in Aerospace and Commercial Uses
Aircraft-grade aluminum alloys, such as 2024 and 7075, are engineered for high strength-to-weight ratios essential in aerospace applications where reducing weight directly improves fuel efficiency and payload capacity. Commercial-grade aluminum, including 1100 and 3003 alloys, prioritizes corrosion resistance and formability, making them suitable for general consumer goods where weight is less critical. The significant weight savings achieved by aircraft-grade aluminum contribute to superior aerodynamic performance and increased operational range compared to heavier commercial-grade alternatives.
Manufacturing Standards and Quality Control
Aircraft-grade aluminum undergoes rigorous manufacturing standards involving strict alloy composition and enhanced heat treatment processes to ensure superior strength, corrosion resistance, and fatigue performance. Quality control for this grade includes comprehensive non-destructive testing methods such as ultrasonic inspection and X-ray analysis, ensuring adherence to aerospace specifications like AMS and ASTM certifications. In contrast, commercial-grade aluminum follows less stringent standards with broader alloy variations and simpler quality control protocols, typically suitable for consumer products and structural applications with lower stress demands.
Applications: Where Each Grade Excels
Aircraft-grade aluminum, primarily composed of high-strength alloys such as 7075 and 2024, excels in aerospace applications requiring exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and resistance to fatigue and corrosion. Commercial-grade aluminum, often alloyed with elements like silicon and magnesium in grades such as 6061 and 3003, is ideal for construction, automotive, and packaging industries due to its corrosion resistance, formability, and cost-effectiveness. The superior mechanical properties of aircraft-grade aluminum make it indispensable for structural aircraft components, while commercial-grade aluminum is preferred for everyday products where durability and ease of fabrication are prioritized.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Aircraft-grade aluminum, primarily 2024 and 7075 alloys, commands higher prices due to superior strength-to-weight ratios and stringent manufacturing standards essential for aerospace applications. Commercial-grade aluminum, such as 6061 alloy, is widely available at lower costs, suitable for general construction and manufacturing but lacks the advanced mechanical properties required for aircraft. Market availability of commercial-grade aluminum is robust with extensive supply chains, whereas aircraft-grade aluminum is more specialized, limited in volume, and subject to supply fluctuations impacting cost and procurement timelines.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Aircraft-grade aluminum typically exhibits higher purity and enhanced alloying elements, resulting in improved strength-to-weight ratios that promote fuel efficiency and reduce carbon emissions in aviation. Its recycling process demands more energy due to specialized alloy compositions but maintains a significant potential for reuse, contributing to lower environmental impact over an aircraft's lifecycle. Commercial-grade aluminum, while easier to recycle with less energy input, generally offers lower performance metrics, potentially leading to higher operational emissions when integrated into less efficient applications.
Choosing the Right Aluminum Grade for Your Project
Aircraft-grade aluminum offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced corrosion resistance, making it ideal for high-performance applications requiring durability and precision. Commercial-grade aluminum, while more cost-effective and easier to work with, suits general construction and manufacturing projects where extreme mechanical properties are less critical. Selecting the appropriate aluminum grade depends on project requirements such as load-bearing capacity, environmental exposure, and budget constraints.
Aircraft-Grade Aluminum vs Commercial-Grade Aluminum Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com