Brass alloys primarily consist of copper and zinc, offering excellent machinability, corrosion resistance, and a bright gold-like appearance, making them ideal for decorative and mechanical applications. Bronze alloys are mainly composed of copper and tin, providing superior hardness, wear resistance, and anti-corrosive properties, which suit them well for marine and industrial environments. The choice between brass and bronze depends on the required strength, corrosion resistance, and appearance in specific uses.
Table of Comparison
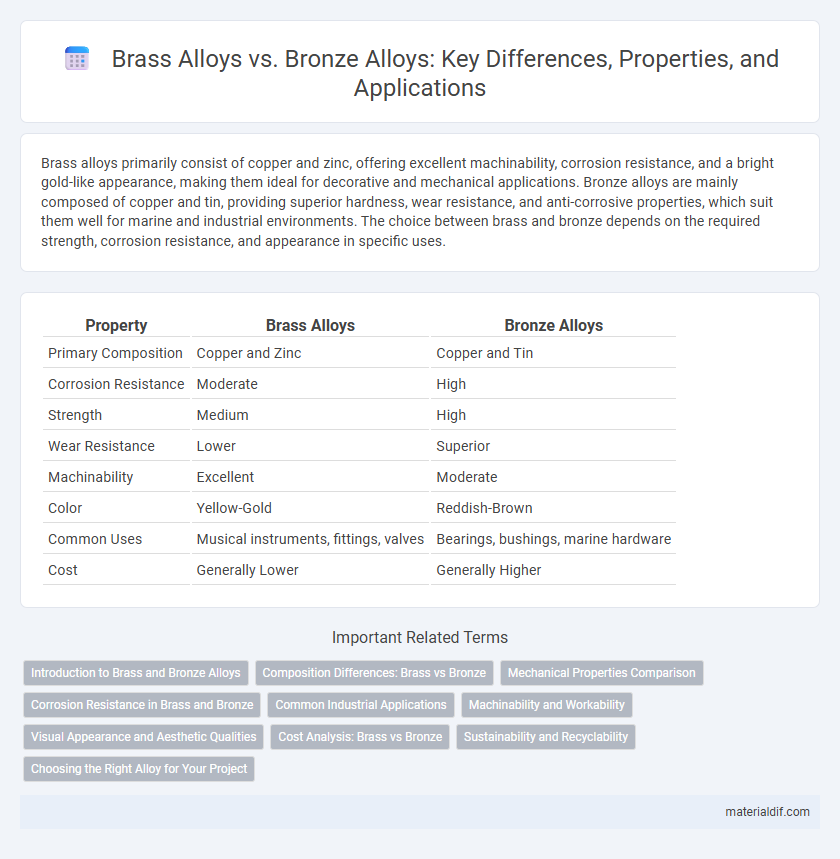
| Property | Brass Alloys | Bronze Alloys |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Composition | Copper and Zinc | Copper and Tin |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Strength | Medium | High |
| Wear Resistance | Lower | Superior |
| Machinability | Excellent | Moderate |
| Color | Yellow-Gold | Reddish-Brown |
| Common Uses | Musical instruments, fittings, valves | Bearings, bushings, marine hardware |
| Cost | Generally Lower | Generally Higher |
Introduction to Brass and Bronze Alloys
Brass alloys primarily consist of copper and zinc, offering excellent machinability and corrosion resistance ideal for decorative and mechanical applications. Bronze alloys, primarily composed of copper and tin, provide superior strength and wear resistance, making them suitable for heavy-duty and marine environments. Both alloys have distinct metallurgical properties that influence their performance in various industrial uses.
Composition Differences: Brass vs Bronze
Brass alloys primarily consist of copper and zinc, with zinc content typically ranging from 5% to 40%, which enhances machinability and corrosion resistance. Bronze alloys are mainly composed of copper and tin, usually containing 5% to 12% tin, providing greater hardness and wear resistance compared to brass. The differing secondary metals in brass and bronze directly impact their mechanical properties and suitability for various industrial applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Brass alloys typically exhibit higher ductility and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for applications requiring flexibility and environmental durability. Bronze alloys generally offer superior hardness and wear resistance due to their higher tin content, which enhances strength and reduces friction. The mechanical properties of bronze make it preferable for heavy-load and friction-prone components, while brass suits fittings and decorative uses demanding malleability.
Corrosion Resistance in Brass and Bronze
Brass alloys, primarily composed of copper and zinc, exhibit good corrosion resistance in non-aggressive environments but are prone to dezincification in acidic or marine conditions. Bronze alloys, mainly consisting of copper and tin, offer superior corrosion resistance, especially in seawater and industrial atmospheres, due to their stable oxide layer formation. The enhanced corrosion resistance of bronze makes it a preferred choice for marine applications and components exposed to harsh environments.
Common Industrial Applications
Brass alloys, primarily composed of copper and zinc, are widely used in plumbing fixtures, musical instruments, and decorative hardware due to their excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. Bronze alloys, consisting mainly of copper and tin, find common industrial applications in marine hardware, bearings, and bushings because of their superior wear resistance and strength. Both alloys serve crucial roles in manufacturing but are selected based on specific mechanical properties and environmental conditions.
Machinability and Workability
Brass alloys typically exhibit superior machinability due to their lower hardness and reduced tendency to cause tool wear, making them ideal for precision components and complex shapes. Bronze alloys, containing higher amounts of tin or other elements, offer enhanced wear resistance and strength but generally present more challenges during machining. Workability of brass is often better for cold forming processes, while bronze alloys excel in cast and forged applications requiring durability under stress.
Visual Appearance and Aesthetic Qualities
Brass alloys typically exhibit a bright, yellow-gold hue with excellent polishability, making them ideal for decorative items and architectural accents. Bronze alloys, characterized by a deeper, reddish-brown tone often enriched with copper and tin, present a more antique, rich appearance favored in sculptures and classical designs. The patina development on bronze enhances its visual texture over time, while brass maintains a consistently shiny finish.
Cost Analysis: Brass vs Bronze
Brass alloys generally have a lower production cost compared to bronze alloys due to the lower price of zinc, their primary alloying element, versus tin used in bronze. The availability and ease of recycling brass also contribute to its cost-effectiveness for manufacturing applications. Bronze alloys, while more expensive, offer superior corrosion resistance and wear properties, which can reduce lifecycle costs in marine and industrial environments.
Sustainability and Recyclability
Brass alloys, composed primarily of copper and zinc, offer high recyclability due to widespread industrial recovery systems, reducing the demand for virgin raw materials and lowering environmental impact. Bronze alloys, containing copper and tin or other elements, also exhibit good recyclability but face challenges due to the less common secondary metal recovery, which can limit sustainable reuse practices. Both alloys contribute to sustainability goals by extending product life cycles and enabling circular economy models, though brass's more established recycling infrastructure often provides a slight advantage.
Choosing the Right Alloy for Your Project
Brass alloys, composed mainly of copper and zinc, offer excellent machinability and corrosion resistance, ideal for applications requiring precision and aesthetic appeal. Bronze alloys, primarily copper and tin, provide superior wear resistance and strength, making them better suited for heavy-duty or marine environments. Selecting the right alloy depends on factors like mechanical properties, environmental exposure, and specific project requirements to ensure optimal performance and durability.
Brass alloys vs Bronze alloys Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com