Rayon dyeing offers vibrant, rich colors due to its high absorbency, allowing dyes to penetrate fibers deeply for lasting results. Nylon dyeing, while also capable of producing bright hues, often requires more complex dyeing processes because of nylon's lower moisture absorption. Both fibers benefit from reactive and acid dyes, but rayon typically achieves better colorfastness and uniformity compared to nylon.
Table of Comparison
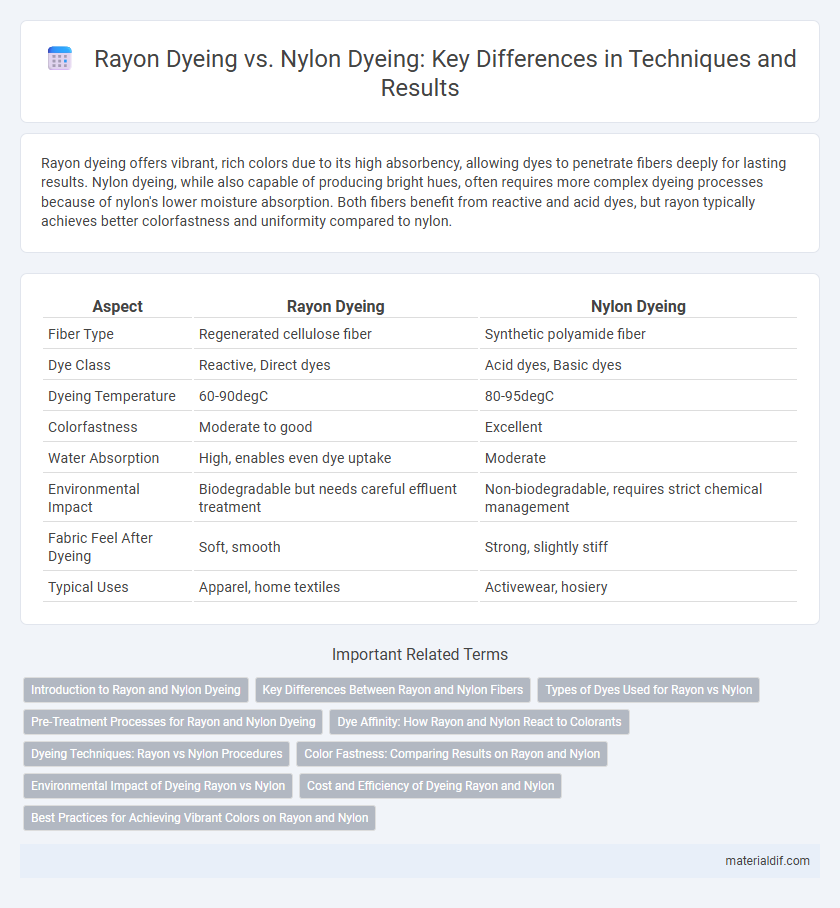
| Aspect | Rayon Dyeing | Nylon Dyeing |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Type | Regenerated cellulose fiber | Synthetic polyamide fiber |
| Dye Class | Reactive, Direct dyes | Acid dyes, Basic dyes |
| Dyeing Temperature | 60-90degC | 80-95degC |
| Colorfastness | Moderate to good | Excellent |
| Water Absorption | High, enables even dye uptake | Moderate |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable but needs careful effluent treatment | Non-biodegradable, requires strict chemical management |
| Fabric Feel After Dyeing | Soft, smooth | Strong, slightly stiff |
| Typical Uses | Apparel, home textiles | Activewear, hosiery |
Introduction to Rayon and Nylon Dyeing
Rayon dyeing involves the application of dyes to regenerated cellulose fibers, which have high absorbency and affinity for reactive and direct dyes, resulting in vibrant and rich color saturation. Nylon dyeing, on the other hand, targets synthetic polyamide fibers that require acid dyes to achieve deep, uniform coloration with excellent wash and light fastness. The choice of dyeing process depends on the fiber's chemical composition, fiber morphology, and desired end-use properties such as durability and colorfastness.
Key Differences Between Rayon and Nylon Fibers
Rayon fibers, derived from regenerated cellulose, exhibit excellent moisture absorbency and a soft, breathable texture, making them ideal for dyeing with vibrant, deep colors using reactive dyes. In contrast, nylon, a synthetic polyamide fiber, demonstrates higher strength, durability, and elasticity but requires acid dyes or disperse dyes for effective coloration due to its hydrophobic nature. The dyeing processes differ significantly: rayon achieves uniform dye uptake and colorfastness through water-based dye baths, while nylon necessitates careful pH control and temperature to ensure consistent dye penetration and minimize color fading.
Types of Dyes Used for Rayon vs Nylon
Rayon dyeing primarily utilizes reactive dyes, sulfur dyes, and vat dyes, which offer excellent color fastness and vibrant hues on cellulose-based fibers due to their strong chemical bonding with the fiber structure. In contrast, nylon dyeing commonly employs acid dyes and basic dyes, taking advantage of nylon's polyamide structure that allows ionic interactions for rich and even coloration. The choice of dyes is crucial because rayon's cellulose composition requires dyes that form covalent bonds, while nylon's protein-like structure favors acidic dye formulations for optimal dye uptake and durability.
Pre-Treatment Processes for Rayon and Nylon Dyeing
Pre-treatment processes for rayon dyeing typically involve scouring and bleaching to remove natural impurities like waxes, pectins, and residual spinning oils, ensuring uniform dye absorption and enhanced fabric brightness. In nylon dyeing, pre-treatment focuses on desalting and removing lubricants or finishes applied during manufacturing to improve dye uptake and minimize uneven coloration. Both fibers require careful pH and temperature control during pre-treatment to optimize dye affinity and achieve consistent, vibrant shades.
Dye Affinity: How Rayon and Nylon React to Colorants
Rayon exhibits high dye affinity due to its hydrophilic nature, allowing it to absorb water-based dyes like reactive and direct dyes efficiently, resulting in vibrant and uniform coloration. Nylon, being a synthetic polymer with less hydrophilicity, requires acid dyes or disperse dyes to achieve strong dye fixation and rich color depth. The varying chemical structures of rayon and nylon directly influence their dyeing processes, making dye selection crucial for optimal color fastness and brightness.
Dyeing Techniques: Rayon vs Nylon Procedures
Rayon dyeing typically involves reactive and direct dyes that bond well with its cellulose fibers, requiring precise temperature control and longer fixation times to ensure deep, vibrant colors. Nylon dyeing uses acid dyes that penetrate the polyamide structure efficiently at higher temperatures, resulting in bright and durable finishes. The fundamental difference lies in the chemical affinity and fiber composition, dictating specific dye types and process conditions for optimal coloration.
Color Fastness: Comparing Results on Rayon and Nylon
Rayon dyeing typically exhibits moderate color fastness due to its semi-synthetic cellulose fibers, which absorb dyes well but can fade with prolonged exposure to sunlight and washing. Nylon, a synthetic polyamide fiber, generally demonstrates superior color fastness because of its stronger dye-fiber bonds, especially when acid dyes are used, resulting in vibrant colors that resist fading and bleeding. In comparative tests, nylon fabrics consistently show higher resistance to color loss under abrasion, light, and washing conditions than rayon, making nylon preferable for applications requiring durable color retention.
Environmental Impact of Dyeing Rayon vs Nylon
Rayon dyeing generally has a higher environmental impact compared to nylon dyeing due to the use of large volumes of water and toxic chemicals in the viscose process, which can result in significant water pollution if not properly treated. Nylon dyeing typically requires less water and energy but involves synthetic chemicals that can also contribute to environmental degradation through chemical runoff and greenhouse gas emissions. Sustainable practices such as closed-loop systems and eco-friendly dyes are critical in reducing the environmental footprint of both rayon and nylon dyeing processes.
Cost and Efficiency of Dyeing Rayon and Nylon
Rayon dyeing typically incurs lower costs due to its higher absorbency, allowing dyes to penetrate more easily and reducing the amount of dye and energy required. Nylon dyeing demands more intensive processes, including prolonged heating and specialized dyes, which increase both time and operational expenses. Efficiency in dyeing rayon surpasses nylon, resulting in quicker turnaround and lower resource consumption in textile manufacturing.
Best Practices for Achieving Vibrant Colors on Rayon and Nylon
Achieving vibrant colors on rayon requires using reactive dyes or acid dyes combined with precise temperature control to ensure deep penetration and colorfastness. Nylon dyeing benefits from acid dyes and proper pre-treatment, such as mordanting, to enhance color vibrancy and durability. Consistent pH control and post-dye fixation processes optimize color retention and minimize fading for both fiber types.
Rayon Dyeing vs Nylon Dyeing Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com