Heat-resistant quartz offers superior durability by withstanding higher temperatures without cracking, unlike regular quartz which may suffer damage under extreme heat. This makes heat-resistant quartz ideal for kitchen surfaces near stoves or fireplaces where thermal stress is common. Its enhanced composition ensures long-lasting elegance and performance in environments requiring both beauty and resilience.
Table of Comparison
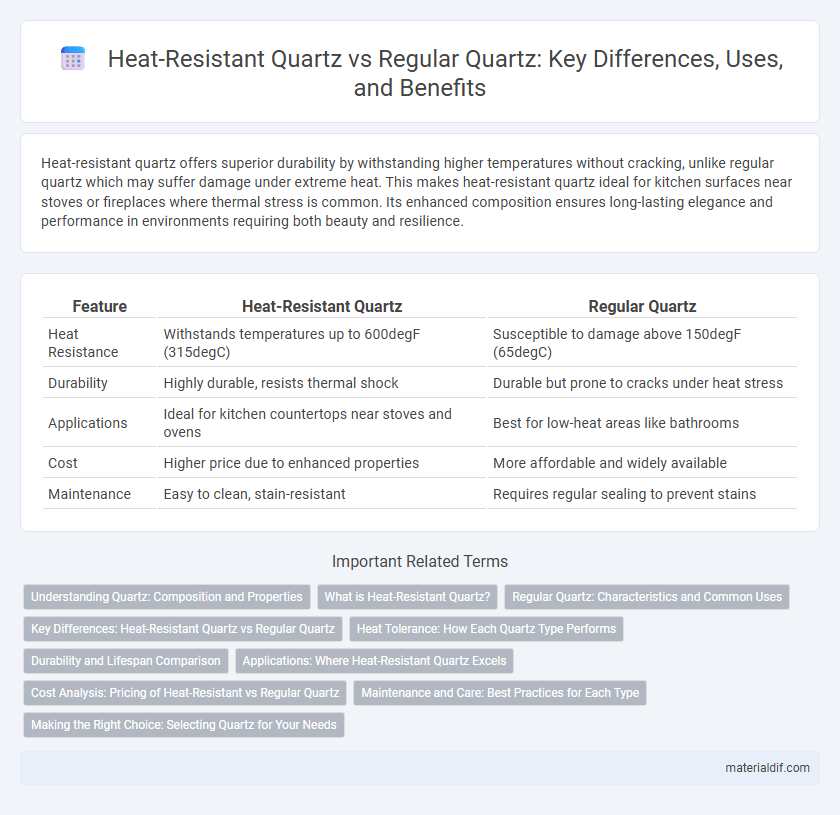
| Feature | Heat-Resistant Quartz | Regular Quartz |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Withstands temperatures up to 600degF (315degC) | Susceptible to damage above 150degF (65degC) |
| Durability | Highly durable, resists thermal shock | Durable but prone to cracks under heat stress |
| Applications | Ideal for kitchen countertops near stoves and ovens | Best for low-heat areas like bathrooms |
| Cost | Higher price due to enhanced properties | More affordable and widely available |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, stain-resistant | Requires regular sealing to prevent stains |
Understanding Quartz: Composition and Properties
Heat-resistant quartz is engineered with enhanced thermal stability by incorporating higher purity silicon dioxide and controlled trace elements, enabling it to withstand temperatures above 1200degF without structural degradation. Regular quartz, composed primarily of silicon dioxide (SiO2) with natural impurities, exhibits brittleness and may crack or discolor under high heat. Understanding the crystalline structure and chemical composition differences between these quartz types is crucial for applications requiring thermal durability and aesthetic stability.
What is Heat-Resistant Quartz?
Heat-resistant quartz is engineered to withstand higher temperatures than regular quartz, making it ideal for kitchen countertops and fireplace surrounds where exposure to heat is common. This variant is manufactured using advanced resins and mineral blends that improve thermal stability and prevent cracking or discoloration under heat stress. Regular quartz, while durable and scratch-resistant, is not designed to handle extreme temperatures and may suffer damage if exposed to hot pots or pans directly.
Regular Quartz: Characteristics and Common Uses
Regular quartz is a crystalline mineral composed primarily of silicon dioxide, notable for its hardness of 7 on the Mohs scale and excellent chemical stability. Commonly used in countertops, watches, and electronic components, it offers durability and aesthetic appeal but lacks the enhanced thermal resistance found in heat-resistant quartz variants. Its susceptibility to thermal shock limits its application in high-temperature environments, making it ideal for everyday household and industrial uses with moderate heat exposure.
Key Differences: Heat-Resistant Quartz vs Regular Quartz
Heat-resistant quartz features enhanced thermal stability, allowing it to withstand temperatures up to 300degC without discoloration or structural damage, unlike regular quartz which may crack or discolor under high heat. The manufacturing process of heat-resistant quartz incorporates special resins and fillers to improve heat resistance, making it ideal for kitchen countertops and industrial applications. Regular quartz offers durability and aesthetic appeal but lacks the advanced thermal properties required for high-temperature environments.
Heat Tolerance: How Each Quartz Type Performs
Heat-resistant quartz withstands temperatures up to 600degF without damage, making it ideal for kitchen or industrial applications requiring high heat tolerance. Regular quartz typically tolerates heat only up to around 150degF to 200degF before discoloration, cracking, or other damage occurs. The enhanced heat resistance in heat-resistant quartz results from advanced resin formulations and manufacturing processes that increase durability under thermal stress.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Heat-resistant quartz exhibits significantly enhanced durability compared to regular quartz, maintaining structural integrity under high temperatures up to 300degC without discoloration or cracking. This type of quartz extends lifespan by resisting thermal shock and surface damage, whereas regular quartz may degrade or warp when exposed to sudden heat changes. Consequently, heat-resistant quartz is ideal for environments requiring both aesthetic longevity and superior thermal performance.
Applications: Where Heat-Resistant Quartz Excels
Heat-resistant quartz is specifically engineered to withstand high temperatures, making it ideal for kitchen countertops near stoves, fireplace surrounds, and laboratory surfaces where thermal shock is common. Regular quartz, while durable and scratch-resistant, lacks this high thermal tolerance and is prone to discoloration or damage when exposed to direct heat. Industries requiring both aesthetic appeal and heat resistance often prefer heat-resistant quartz for its ability to maintain structural integrity and appearance under extreme temperature conditions.
Cost Analysis: Pricing of Heat-Resistant vs Regular Quartz
Heat-resistant quartz typically commands a higher price compared to regular quartz due to its enhanced durability and ability to withstand elevated temperatures without damage. The manufacturing process for heat-resistant quartz involves specialized treatments, increasing production costs and thus retail prices. Investing in heat-resistant quartz may offer long-term value by reducing replacement costs in high-heat environments despite the initial premium.
Maintenance and Care: Best Practices for Each Type
Heat-resistant quartz requires specialized maintenance to preserve its thermal durability, avoiding sudden temperature changes and using mild, non-abrasive cleaners to prevent surface damage. Regular quartz demands routine cleaning with pH-balanced detergents and immediate spill removal to maintain its non-porous surface and prevent staining. Both types benefit from using cutting boards and trivets to extend lifespan and retain aesthetic quality.
Making the Right Choice: Selecting Quartz for Your Needs
Heat-resistant quartz offers enhanced durability and thermal stability, ideal for kitchen countertops exposed to high temperatures, while regular quartz suits low-heat applications with excellent scratch resistance and aesthetic appeal. Consider surface hardness, temperature tolerance up to 300degF (150degC) for heat-resistant variants, and maintenance requirements when selecting quartz. Matching quartz properties to specific needs ensures longevity and performance tailored to residential or commercial use.
Heat-Resistant Quartz vs Regular Quartz Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com