Polymer-bonded quartz offers enhanced durability and resistance to heat and chemicals compared to resin-bonded quartz, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Resin-bonded quartz provides excellent aesthetics with a smoother finish and greater design flexibility, often preferred in decorative surfaces. Choosing between polymer and resin bonds depends on the required performance characteristics and the intended use environment.
Table of Comparison
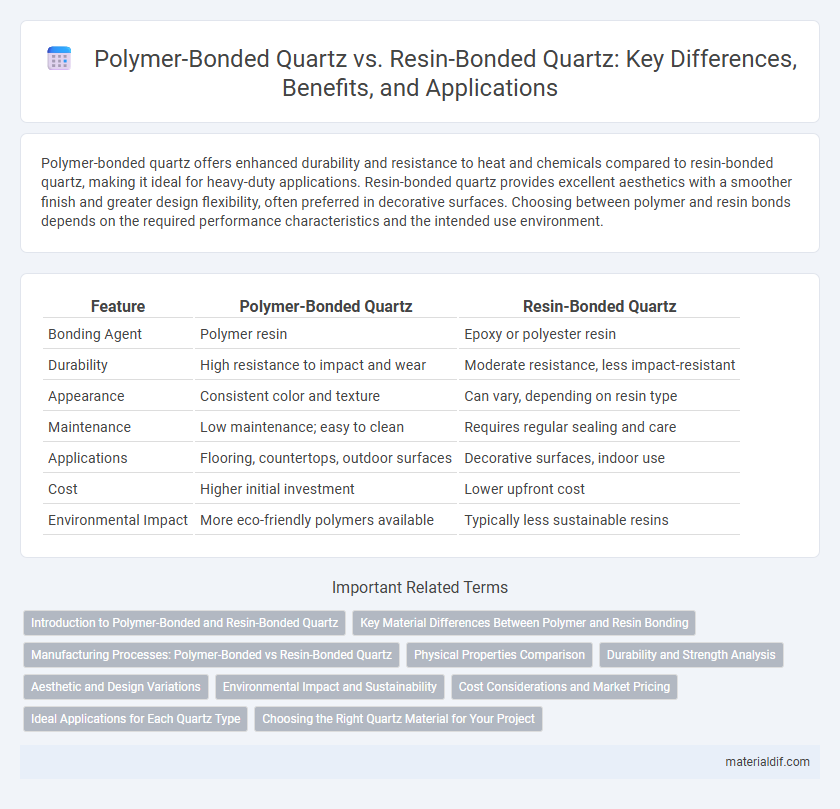
| Feature | Polymer-Bonded Quartz | Resin-Bonded Quartz |
|---|---|---|
| Bonding Agent | Polymer resin | Epoxy or polyester resin |
| Durability | High resistance to impact and wear | Moderate resistance, less impact-resistant |
| Appearance | Consistent color and texture | Can vary, depending on resin type |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; easy to clean | Requires regular sealing and care |
| Applications | Flooring, countertops, outdoor surfaces | Decorative surfaces, indoor use |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Environmental Impact | More eco-friendly polymers available | Typically less sustainable resins |
Introduction to Polymer-Bonded and Resin-Bonded Quartz
Polymer-bonded quartz combines crushed quartz aggregates with a polymer resin binder, creating a durable, non-porous surface ideal for countertops and flooring due to its high resistance to stains and scratches. Resin-bonded quartz uses a resin adhesive to bind quartz particles, emphasizing enhanced mechanical strength and flexibility, making it suitable for applications requiring impact resistance and structural integrity. Both types leverage the natural hardness of quartz but differ in binder composition, affecting their performance characteristics and ideal usage scenarios.
Key Material Differences Between Polymer and Resin Bonding
Polymer-bonded quartz utilizes synthetic polymers as the adhesive matrix, offering enhanced chemical resistance and flexibility compared to resin-bonded quartz, which typically employs thermosetting resins like polyester or epoxy. The polymer bonding in polymer-bonded quartz provides superior durability against thermal expansion and mechanical stress, while resin-bonded quartz offers excellent surface hardness and chemical stability. Key material differences include the polymer's ability to absorb vibrations and resist cracking, contrasted with resin bonding's higher rigidity and resistance to solvents.
Manufacturing Processes: Polymer-Bonded vs Resin-Bonded Quartz
Polymer-bonded quartz involves mixing quartz aggregates with a polymer-based adhesive, which is then cured under controlled temperature and pressure to achieve high strength and durability. Resin-bonded quartz typically uses synthetic resins such as epoxy or polyester to bind the quartz particles, with curing processes often performed at ambient or slightly elevated temperatures for faster production cycles. The manufacturing differences impact the mechanical properties and application suitability, with polymer-bonded quartz generally offering better chemical resistance and resin-bonded quartz providing enhanced flexibility in finishing options.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polymer-bonded quartz exhibits higher tensile strength and better impact resistance compared to resin-bonded quartz, making it more durable in demanding applications. Resin-bonded quartz typically offers superior heat resistance and chemical stability, suitable for environments exposed to high temperatures and corrosive substances. Both materials demonstrate excellent hardness and wear resistance, but polymer-bonded quartz often provides enhanced flexibility and reduced brittleness.
Durability and Strength Analysis
Polymer-bonded quartz exhibits superior durability and strength due to its enhanced resistance to impact and abrasion compared to resin-bonded quartz, which typically has a lower tensile strength and is more prone to surface wear. The chemical composition of polymer binders contributes to improved mechanical properties, making polymer-bonded quartz ideal for heavy-use applications requiring long-lasting performance. In contrast, resin-bonded quartz is better suited for decorative purposes where mechanical stress is minimal.
Aesthetic and Design Variations
Polymer-bonded quartz offers a wider range of vibrant colors and intricate patterns, enabling highly customizable and decorative surfaces for modern interior design. Resin-bonded quartz typically features a finer texture with a more consistent color palette, ideal for sleek, minimalist aesthetics and uniform finishes. The choice between polymer and resin bonding directly influences the visual complexity and tactile appeal of quartz surfaces in architectural applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polymer-bonded quartz surfaces utilize synthetic resins that often contain non-biodegradable components, resulting in a higher environmental footprint compared to resin-bonded quartz, which incorporates bio-based or natural resins with improved recyclability. The production process of resin-bonded quartz typically emits fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs), enhancing indoor air quality and reducing ecological toxicity. Lifecycle assessments reveal that resin-bonded quartz offers superior sustainability by enabling easier material recovery and reducing landfill waste.
Cost Considerations and Market Pricing
Polymer-bonded quartz typically commands higher market prices due to its superior durability and aesthetic appeal compared to resin-bonded quartz, which is more budget-friendly but less resilient. The cost considerations for polymer-bonded quartz involve higher raw material and manufacturing expenses resulting from advanced polymer integration techniques. Resin-bonded quartz appeals to cost-sensitive consumers seeking quartz surfaces at lower price points, influencing its competitive pricing in the mid-range quartz countertop market.
Ideal Applications for Each Quartz Type
Polymer-bonded quartz is ideal for applications requiring high chemical resistance and enhanced mechanical strength, such as laboratory countertops, industrial flooring, and precision instrument surfaces. Resin-bonded quartz suits decorative and architectural uses, including kitchen countertops, wall cladding, and bathroom vanities, where aesthetic appeal and ease of fabrication are prioritized. Selecting between polymer-bonded and resin-bonded quartz depends on the specific performance demands and environmental conditions of the intended application.
Choosing the Right Quartz Material for Your Project
Polymer-bonded quartz offers enhanced durability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-traffic surfaces and industrial applications. Resin-bonded quartz provides greater flexibility and ease of installation, suitable for residential countertops and decorative uses. Selecting the right quartz material depends on project requirements such as strength, appearance, and environmental exposure to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Polymer-Bonded Quartz vs Resin-Bonded Quartz Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com