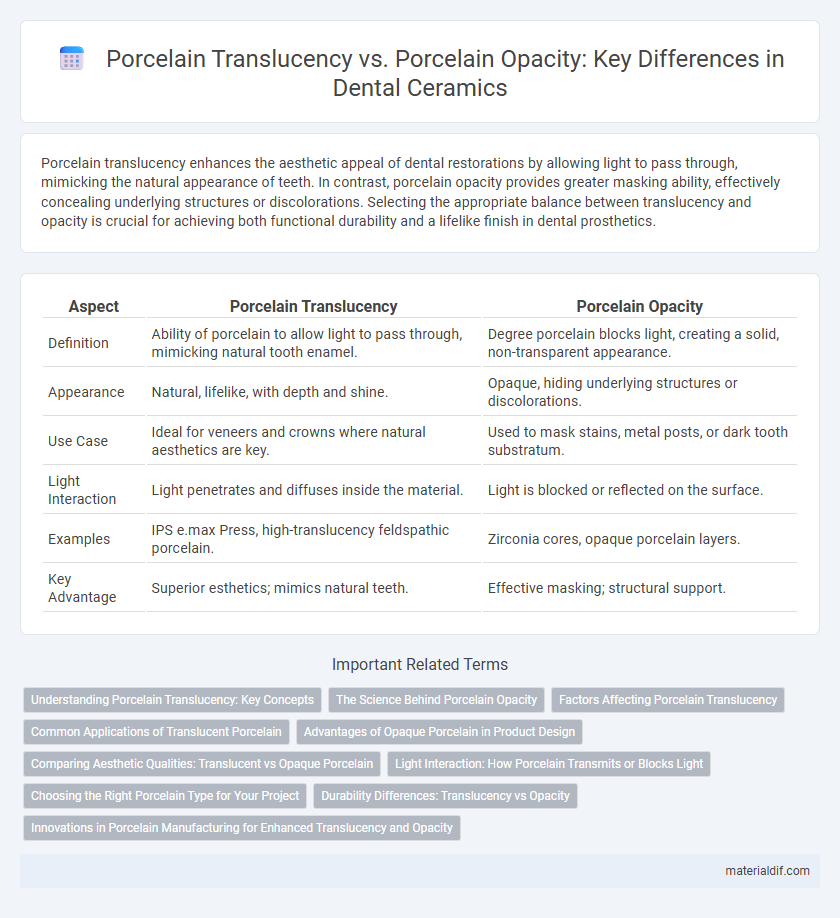
Porcelain translucency enhances the aesthetic appeal of dental restorations by allowing light to pass through, mimicking the natural appearance of teeth. In contrast, porcelain opacity provides greater masking ability, effectively concealing underlying structures or discolorations. Selecting the appropriate balance between translucency and opacity is crucial for achieving both functional durability and a lifelike finish in dental prosthetics.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Porcelain Translucency | Porcelain Opacity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability of porcelain to allow light to pass through, mimicking natural tooth enamel. | Degree porcelain blocks light, creating a solid, non-transparent appearance. |
| Appearance | Natural, lifelike, with depth and shine. | Opaque, hiding underlying structures or discolorations. |
| Use Case | Ideal for veneers and crowns where natural aesthetics are key. | Used to mask stains, metal posts, or dark tooth substratum. |
| Light Interaction | Light penetrates and diffuses inside the material. | Light is blocked or reflected on the surface. |
| Examples | IPS e.max Press, high-translucency feldspathic porcelain. | Zirconia cores, opaque porcelain layers. |
| Key Advantage | Superior esthetics; mimics natural teeth. | Effective masking; structural support. |
Understanding Porcelain Translucency: Key Concepts
Porcelain translucency refers to the ability of light to penetrate and diffuse through the ceramic material, creating a lifelike depth and natural appearance essential in dental restorations and fine china. In contrast, porcelain opacity limits light transmission, producing a more solid, opaque look that effectively masks underlying structures or imperfections. Understanding porcelain translucency involves analyzing factors such as particle size, ceramic composition, and firing temperature, which collectively influence the balance between translucency and opacity for optimal aesthetic and functional outcomes.
The Science Behind Porcelain Opacity
Porcelain opacity is determined by the material's microstructure and the presence of crystalline phases that scatter light, reducing translucency and increasing opacity. The addition of feldspar, kaolin, and other minerals influences the degree of light absorption and reflection within the porcelain matrix. Understanding the interaction between light and these microscopic components is essential for controlling the balance between aesthetic translucency and functional opacity in dental and artistic porcelain applications.
Factors Affecting Porcelain Translucency
Porcelain translucency is influenced by factors such as particle size, crystallinity, and the thickness of the porcelain layer, which determine the degree of light transmission and diffusion. Higher translucency results from smaller particle sizes and a more amorphous structure, allowing light to pass through with minimal scattering, while increased crystallinity and thickness contribute to opacity by reflecting and absorbing light. The uniformity of the porcelain matrix and the incorporation of opacifiers or pigments also play critical roles in modulating translucency for aesthetic and functional dental applications.
Common Applications of Translucent Porcelain
Translucent porcelain is widely used in dental restorations such as veneers, crowns, and inlays due to its ability to mimic the natural appearance of tooth enamel by allowing light to pass through. This material enhances aesthetic outcomes, especially in anterior teeth, providing a lifelike translucency that opaque porcelain cannot achieve. Opaque porcelain, conversely, is preferred for masking discolored tooth structures or metal substructures in posterior restorations where aesthetics are less critical.
Advantages of Opaque Porcelain in Product Design
Opaque porcelain offers superior concealment of underlying structures, allowing designers to mask imperfections or color inconsistencies in product bases effectively. This characteristic enhances the visual uniformity and richness of the final product, creating a more polished and refined appearance in ceramics and dental restorations. Its ability to block light transmission ensures durability and color stability, making opaque porcelain ideal for creating bold, vividly colored designs that maintain their aesthetic appeal over time.
Comparing Aesthetic Qualities: Translucent vs Opaque Porcelain
Translucent porcelain mimics the natural depth and light diffusion of tooth enamel, providing a lifelike and radiant appearance ideal for aesthetic dental restorations. Opaque porcelain, while less light-permeable, excels at masking underlying discolorations and metal frameworks, delivering uniform color and strength. Comparing aesthetic qualities, translucent porcelain offers superior realism and brilliance, whereas opaque porcelain prioritizes coverage and durability in restorative applications.
Light Interaction: How Porcelain Transmits or Blocks Light
Porcelain translucency refers to its ability to transmit light, allowing some light to pass through the material and create a natural, lifelike appearance in dental restorations and fine china. Porcelain opacity blocks light, providing a more solid, non-transparent effect that masks underlying structures or materials. The balance between translucency and opacity in porcelain significantly influences light interaction, affecting aesthetic outcomes and functional properties in various applications.
Choosing the Right Porcelain Type for Your Project
Porcelain translucency significantly affects the aesthetic outcome, with translucent porcelain mimicking natural tooth enamel by allowing light to pass through, ideal for anterior restorations requiring lifelike appearance. Opacity in porcelain enhances the masking of underlying structures, making opaque varieties suitable for cases involving discolored teeth or metal substructures in posterior restorations. Selecting the right porcelain type depends on the balance between desired esthetics, durability, and the clinical situation, ensuring optimal integration and performance in dental prosthetics.
Durability Differences: Translucency vs Opacity
Porcelain translucency enhances aesthetic appeal by mimicking natural tooth enamel but may slightly compromise durability due to its thinner, more brittle structure. Porcelain opacity improves strength and resistance to fracture, making it ideal for high-stress dental restorations or areas requiring maximum durability. Balancing translucency and opacity is crucial in dental ceramics to ensure both natural appearance and long-lasting performance.
Innovations in Porcelain Manufacturing for Enhanced Translucency and Opacity
Innovations in porcelain manufacturing, such as advanced nanotechnology and refined particle sizing, have significantly enhanced the translucency of dental and artistic porcelains, allowing for more lifelike and natural light diffusion. Contrarily, specific formulations incorporating opacifying agents like zirconia and alumina improve opacity, providing better masking of underlying structures in dental restorations. These technological advancements enable customized translucency and opacity levels, optimizing both aesthetic and functional outcomes in porcelain applications.
Porcelain translucency vs Porcelain opacity Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com