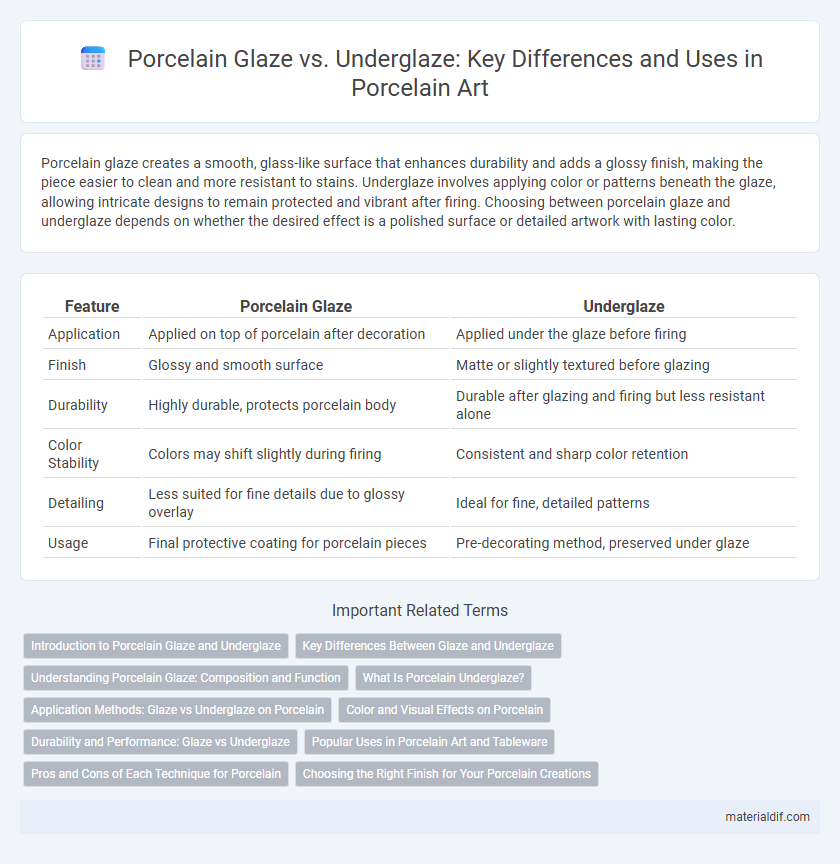
Porcelain glaze creates a smooth, glass-like surface that enhances durability and adds a glossy finish, making the piece easier to clean and more resistant to stains. Underglaze involves applying color or patterns beneath the glaze, allowing intricate designs to remain protected and vibrant after firing. Choosing between porcelain glaze and underglaze depends on whether the desired effect is a polished surface or detailed artwork with lasting color.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Porcelain Glaze | Underglaze |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Applied on top of porcelain after decoration | Applied under the glaze before firing |
| Finish | Glossy and smooth surface | Matte or slightly textured before glazing |
| Durability | Highly durable, protects porcelain body | Durable after glazing and firing but less resistant alone |
| Color Stability | Colors may shift slightly during firing | Consistent and sharp color retention |
| Detailing | Less suited for fine details due to glossy overlay | Ideal for fine, detailed patterns |
| Usage | Final protective coating for porcelain pieces | Pre-decorating method, preserved under glaze |
Introduction to Porcelain Glaze and Underglaze
Porcelain glaze is a glass-like coating applied to ceramics that enhances durability, provides a smooth surface, and gives porcelain its characteristic glossy or matte finish. Underglaze refers to colored decoration painted on the porcelain body before glazing, allowing intricate designs to be sealed beneath a transparent glaze layer. The interaction between porcelain glaze and underglaze creates vibrant, long-lasting artwork that resists fading and wear.
Key Differences Between Glaze and Underglaze
Porcelain glaze forms a glassy, protective surface on ceramics that enhances durability and imparts a glossy or matte finish, while underglaze consists of colored pigments applied beneath the glaze for detailed, lasting decoration. Glaze undergoes melting during firing to create a smooth, sealed coating that resists staining and water absorption, whereas underglaze colors fuse into the porcelain body but remain visible through the transparent glaze. Key differences include their composition and function: glaze acts as a surface sealant and aesthetic enhancer, whereas underglaze provides intricate design with color stability under high temperatures.
Understanding Porcelain Glaze: Composition and Function
Porcelain glaze is a vitreous coating composed primarily of silica, alumina, and fluxes that fuse at high temperatures to create a smooth, glass-like surface enhancing durability and water resistance. Unlike underglaze, which is a colored decoration applied beneath the glaze, porcelain glaze serves both protective and aesthetic functions by sealing the porous body and providing a glossy or matte finish. The chemical composition and firing temperature determine the glaze's texture, color clarity, and adhesion, making it essential for porcelain's strength and visual appeal.
What Is Porcelain Underglaze?
Porcelain underglaze is a decorative technique where colored pigments are applied directly onto the porcelain body before glazing and firing, resulting in durable, vivid designs beneath a clear, glossy surface. Unlike porcelain glaze, which serves as a smooth, protective coating, underglaze ensures intricate patterns remain protected and resistant to wear over time. This method enhances porcelain's aesthetic appeal while maintaining its functional integrity in items such as dinnerware and art pieces.
Application Methods: Glaze vs Underglaze on Porcelain
Porcelain glaze is applied as a liquid coating that fuses with the ceramic surface during firing, creating a smooth, glass-like finish that enhances durability and aesthetic appeal. Underglaze is painted or stamped onto the porcelain body before glazing, allowing detailed designs to remain crisp and protected beneath the transparent glaze layer. The glaze application method involves dipping, spraying, or brushing, while underglaze requires precision in design placement followed by a clear glaze overlay to seal the decoration.
Color and Visual Effects on Porcelain
Porcelain glaze creates a smooth, glossy surface that enhances color depth and adds a reflective sheen, intensifying visual appeal with a glass-like finish. Underglaze, applied before glazing, allows for precise, detailed designs and vibrant colors that remain sharp under the final glaze layer. The interplay of underglaze patterns with the translucent glaze results in rich textures and layered visual effects unique to porcelain artistry.
Durability and Performance: Glaze vs Underglaze
Porcelain glaze provides a durable, glass-like coating that enhances resistance to scratches, stains, and moisture, making it ideal for everyday use and high-traffic applications. Underglaze, applied beneath the glaze layer, offers vibrant, long-lasting colors but depends on the overlying glaze for protection and durability. While both contribute to the overall performance of porcelain, glaze ensures the surface strength and durability, whereas underglaze primarily affects aesthetic longevity.
Popular Uses in Porcelain Art and Tableware
Porcelain glaze provides a smooth, glossy finish that enhances durability and gives tableware a sleek, polished look, making it ideal for functional items like plates, bowls, and cups. Underglaze features vibrant, permanent pigments applied beneath a clear glaze, commonly used in intricate porcelain art and decorative pieces to achieve detailed designs without compromising the smooth surface. Popular uses of porcelain glaze emphasize protective qualities and shine in everyday use, while underglaze is favored by artists for its versatility in creating colorful, long-lasting patterns.
Pros and Cons of Each Technique for Porcelain
Porcelain glaze provides a glossy, protective surface that enhances durability, resists stains, and brings out vibrant colors, but it may sometimes obscure fine painted details beneath. Underglaze allows for precise, detailed decoration with colors that remain vivid after firing, yet it is less resistant to scratching and wear compared to glazed finishes. Choosing between porcelain glaze and underglaze depends on the desired aesthetic effect, durability needs, and whether surface texture or detailed painting is prioritized.
Choosing the Right Finish for Your Porcelain Creations
Porcelain glaze provides a smooth, glossy finish that enhances durability and waterproofs the surface, making it ideal for functional items like dinnerware and vases. Underglaze offers vibrant, detailed designs that fuse seamlessly beneath a clear protective glaze, perfect for intricate artwork and decorative pieces. Selecting between porcelain glaze and underglaze depends on whether you prioritize surface resilience or detailed, colorful patterns in your porcelain creations.
Porcelain Glaze vs Underglaze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com