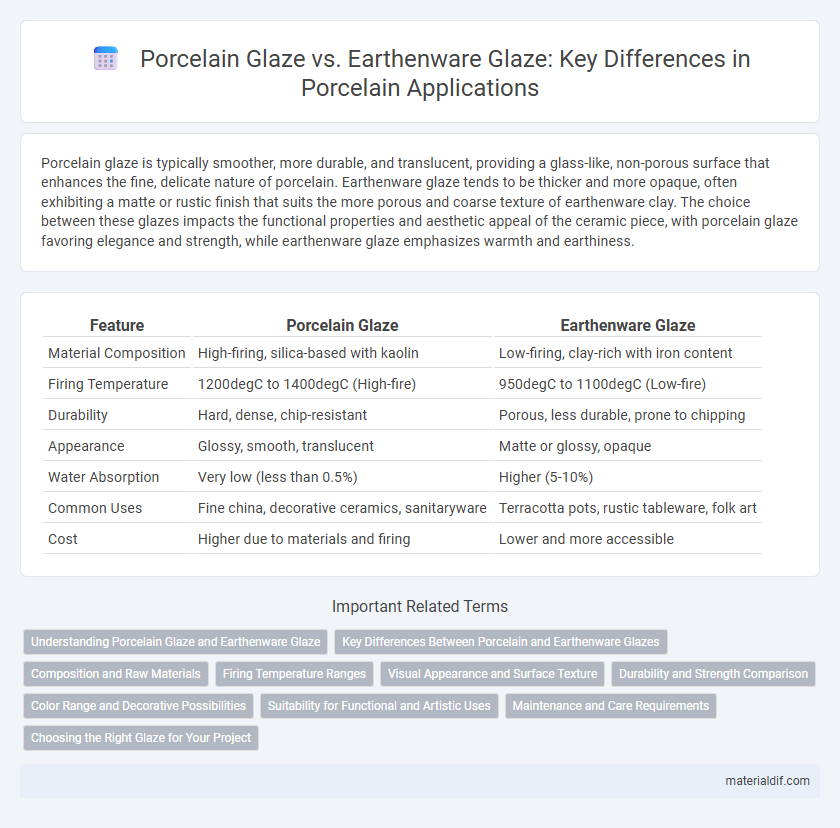
Porcelain glaze is typically smoother, more durable, and translucent, providing a glass-like, non-porous surface that enhances the fine, delicate nature of porcelain. Earthenware glaze tends to be thicker and more opaque, often exhibiting a matte or rustic finish that suits the more porous and coarse texture of earthenware clay. The choice between these glazes impacts the functional properties and aesthetic appeal of the ceramic piece, with porcelain glaze favoring elegance and strength, while earthenware glaze emphasizes warmth and earthiness.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Porcelain Glaze | Earthenware Glaze |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High-firing, silica-based with kaolin | Low-firing, clay-rich with iron content |
| Firing Temperature | 1200degC to 1400degC (High-fire) | 950degC to 1100degC (Low-fire) |
| Durability | Hard, dense, chip-resistant | Porous, less durable, prone to chipping |
| Appearance | Glossy, smooth, translucent | Matte or glossy, opaque |
| Water Absorption | Very low (less than 0.5%) | Higher (5-10%) |
| Common Uses | Fine china, decorative ceramics, sanitaryware | Terracotta pots, rustic tableware, folk art |
| Cost | Higher due to materials and firing | Lower and more accessible |
Understanding Porcelain Glaze and Earthenware Glaze
Porcelain glaze is typically smooth, glass-like, and highly vitrified, providing a non-porous, durable surface ideal for fine china and artistic ceramics. Earthenware glaze, on the other hand, is often thicker and more porous due to the lower firing temperatures, resulting in a less durable but more rustic finish. Understanding the differences in composition and firing processes between porcelain glaze and earthenware glaze is crucial for selecting the appropriate finish for functional or decorative pottery.
Key Differences Between Porcelain and Earthenware Glazes
Porcelain glaze is typically smoother, more glass-like, and fired at higher temperatures between 1200degC and 1400degC, resulting in a harder, non-porous surface resistant to stains and scratches. In contrast, earthenware glaze is fired at lower temperatures around 1000degC to 1150degC, producing a more porous, less durable finish with greater susceptibility to chipping and wear. The chemical composition of porcelain glazes usually includes higher silica and alumina content, enhancing vitrification, whereas earthenware glazes contain more fluxes to melt at lower temperatures.
Composition and Raw Materials
Porcelain glaze is primarily composed of refined kaolin, silica, and feldspar, creating a smooth, glassy surface that vitrifies at high firing temperatures above 1200degC. Earthenware glaze contains a higher proportion of fluxes like lead oxide or borax, combined with clay and silica, allowing it to mature at lower temperatures around 900-1100degC, resulting in a more porous and less durable finish. The raw materials in porcelain glaze emphasize purity and a controlled particle size, whereas earthenware glaze incorporates more impurities and coarse materials suited for its lower firing range.
Firing Temperature Ranges
Porcelain glaze typically requires higher firing temperatures between 1200degC and 1400degC, resulting in a durable, glass-like surface with enhanced strength and translucency. Earthenware glaze fires at lower temperatures, usually ranging from 950degC to 1150degC, producing a more porous, matte finish that is less vitrified compared to porcelain. The distinct firing temperature ranges directly influence the physical properties and durability of each glaze type.
Visual Appearance and Surface Texture
Porcelain glaze typically offers a smooth, glossy finish with a translucent quality that enhances its delicate and refined appearance, while earthenware glaze tends to be thicker, more opaque, and often matte or satin in texture. The surface of porcelain glaze is usually glass-like and cool to the touch, providing a sleek, polished feel, whereas earthenware glaze may exhibit slight irregularities and a more rustic, tactile texture. Porcelain's glaze often results in a pristine, elegant look ideal for fine tableware, contrasting with the warmer, more casual visual character of earthenware.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Porcelain glaze exhibits superior durability and strength compared to earthenware glaze due to its dense, vitrified surface that resists chipping and scratching. Earthenware glaze, being more porous and less vitrified, tends to be more susceptible to wear and damage over time. The higher firing temperature of porcelain glaze contributes significantly to its enhanced hardness and longevity in everyday use.
Color Range and Decorative Possibilities
Porcelain glaze offers a broader and more vibrant color range compared to earthenware glaze, allowing for intricate and refined decorative effects due to its smooth, glass-like surface. Earthenware glazes tend to have a more limited palette, often appearing matte or opaque, which restricts the variety of color intensity and detail achievable in decoration. The high firing temperature of porcelain glaze enhances color stability and depth, making it ideal for detailed artistic designs and complex layering techniques.
Suitability for Functional and Artistic Uses
Porcelain glaze offers a smooth, glass-like finish ideal for both functional items like dinnerware and delicate artistic pieces due to its durability and resistance to stains. Earthenware glaze, while porous and less durable, provides a rustic charm suitable for decorative art and low-impact functional objects such as planters and ornamental bowls. The choice between porcelain and earthenware glazes depends on the balance between aesthetic appeal and practical use, with porcelain preferred for longevity and earthenware favored for creative expression.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Porcelain glaze offers a non-porous, highly durable surface that resists staining and requires minimal maintenance compared to earthenware glaze, which is more porous and prone to chipping. Earthenware glaze often demands regular sealing and careful handling to prevent moisture absorption and damage. Porcelain's smooth, vitrified finish allows for easy cleaning with mild detergents, while earthenware needs gentle care to avoid glaze deterioration over time.
Choosing the Right Glaze for Your Project
Porcelain glaze offers a smooth, glass-like finish with high durability and resistance to stains, making it ideal for fine, detailed work requiring a polished surface. Earthenware glaze, which is typically more porous and less durable, provides a rustic, matte look suited for decorative or functional pieces where texture and earthiness are desired. Selecting the right glaze depends on the project's functional requirements and aesthetic preferences, balancing durability with the desired surface finish.
Porcelain Glaze vs Earthenware Glaze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com