Low-iron porcelain offers superior translucency and a whiter, more refined appearance, making it ideal for artistic and delicate applications. High-iron porcelain contains more iron oxide, resulting in a stronger, more durable material with a warmer, earthier tone suitable for functional pottery and industrial uses. Selecting between low-iron and high-iron porcelain depends on the desired balance of aesthetic appeal and structural strength.
Table of Comparison
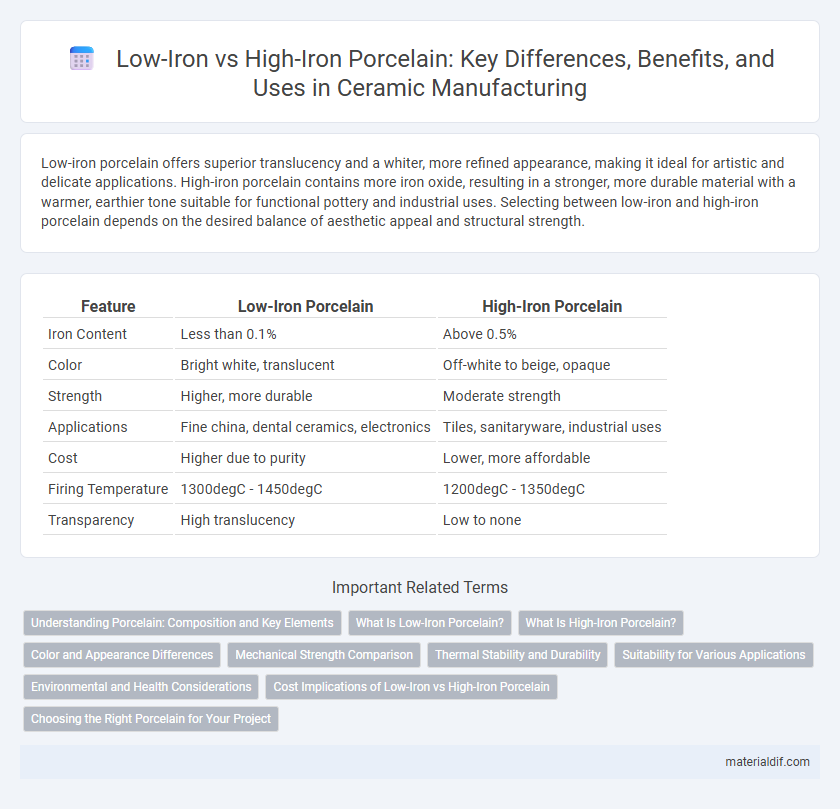
| Feature | Low-Iron Porcelain | High-Iron Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Iron Content | Less than 0.1% | Above 0.5% |
| Color | Bright white, translucent | Off-white to beige, opaque |
| Strength | Higher, more durable | Moderate strength |
| Applications | Fine china, dental ceramics, electronics | Tiles, sanitaryware, industrial uses |
| Cost | Higher due to purity | Lower, more affordable |
| Firing Temperature | 1300degC - 1450degC | 1200degC - 1350degC |
| Transparency | High translucency | Low to none |
Understanding Porcelain: Composition and Key Elements
Low-iron porcelain is prized for its translucent, bright white appearance due to minimal iron oxide content, making it ideal for fine china and artistic ceramics. High-iron porcelain contains greater amounts of iron oxide, resulting in a warmer, creamier hue and increased opacity, often preferred for utilitarian wares and rustic finishes. The iron content directly affects the porcelain's firing temperature, color, and translucency, influencing both aesthetic qualities and functional durability.
What Is Low-Iron Porcelain?
Low-iron porcelain is a type of ceramic material characterized by its minimal iron oxide content, typically below 0.1%. This low iron concentration results in a whiter, more translucent appearance compared to high-iron porcelain, which tends to have a creamier or slightly yellowish tint due to higher iron oxide levels. Its purity and clarity make low-iron porcelain ideal for fine china, laboratory ware, and upscale decorative applications where translucency and brightness are crucial.
What Is High-Iron Porcelain?
High-iron porcelain contains a higher concentration of iron oxide, typically above 1%, giving it a darker and more opaque appearance compared to low-iron porcelain. This type of porcelain offers increased strength and durability, making it suitable for industrial applications and cookware. The presence of iron also affects the firing temperature and glaze adhesion, influencing the final texture and finish of the porcelain product.
Color and Appearance Differences
Low-iron porcelain exhibits a bright white and translucent appearance due to minimal iron content, making it ideal for fine, delicate designs and a clean aesthetic. High-iron porcelain contains higher iron levels, resulting in a warmer, creamier color with subtle earthy tones that provide a rustic or antique look. Color intensity and translucency differences between low-iron and high-iron porcelain significantly influence their visual appeal and suitability for various decorative styles.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Low-iron porcelain exhibits higher mechanical strength due to its purer composition, resulting in fewer impurities that can cause structural weaknesses. High-iron porcelain, while more affordable, contains greater iron content that may introduce micro-cracks and reduce overall durability under mechanical stress. Mechanical strength tests consistently show low-iron porcelain's superior resistance to bending and fracture compared to high-iron variants.
Thermal Stability and Durability
Low-iron porcelain exhibits superior thermal stability due to its minimal iron content, reducing heat absorption and enhancing resistance to thermal shock. High-iron porcelain, while generally more durable in terms of mechanical strength, tends to absorb more heat, which can lead to increased vulnerability under rapid temperature changes. The balance between these properties makes low-iron porcelain ideal for applications requiring high thermal resistance, whereas high-iron variants are preferred for their toughness in more mechanically demanding environments.
Suitability for Various Applications
Low-iron porcelain boasts exceptional translucency and brightness, making it ideal for fine tableware and decorative art pieces where aesthetic appeal is paramount. High-iron porcelain offers enhanced strength and durability, suited for industrial uses, architectural tiles, and heavy-duty kitchenware that require resistance to wear and heat. Selecting between low-iron and high-iron porcelain hinges on specific application demands, balancing appearance against functional performance.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Low-iron porcelain offers reduced environmental impact due to lower energy consumption during firing and decreased release of harmful emissions compared to high-iron porcelain. High-iron porcelain contains higher levels of iron oxides, contributing to increased production of greenhouse gases and potential exposure to heavy metals in some industrial processes. Choosing low-iron porcelain supports healthier indoor air quality and minimizes ecological footprint through sustainable manufacturing practices.
Cost Implications of Low-Iron vs High-Iron Porcelain
Low-iron porcelain typically involves higher production costs due to the need for purer raw materials and more refined processing techniques, resulting in a premium price point. High-iron porcelain is generally more affordable, as the higher iron content reduces processing complexity and material expenses. This cost disparity influences the choice of porcelain in applications where budget constraints or aesthetic clarity are critical factors.
Choosing the Right Porcelain for Your Project
Low-iron porcelain offers a bright white appearance and higher translucency, making it ideal for projects requiring a delicate, refined finish such as fine dinnerware or decorative tiles. High-iron porcelain, with its warmer tones and increased durability, suits applications that demand robustness and a rustic aesthetic, like flooring or exterior cladding. Selecting the appropriate porcelain depends on balancing visual appeal against functional requirements, ensuring the material's composition aligns with the project's design intent and performance needs.
Low-Iron Porcelain vs High-Iron Porcelain Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com