Polyester offers greater durability and resistance to UV rays compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for outdoor applications. Its moisture-wicking properties and ability to retain color better also enhance its appeal over polypropylene. While polypropylene is lightweight and cost-effective, polyester provides superior strength and longevity for various uses.
Table of Comparison
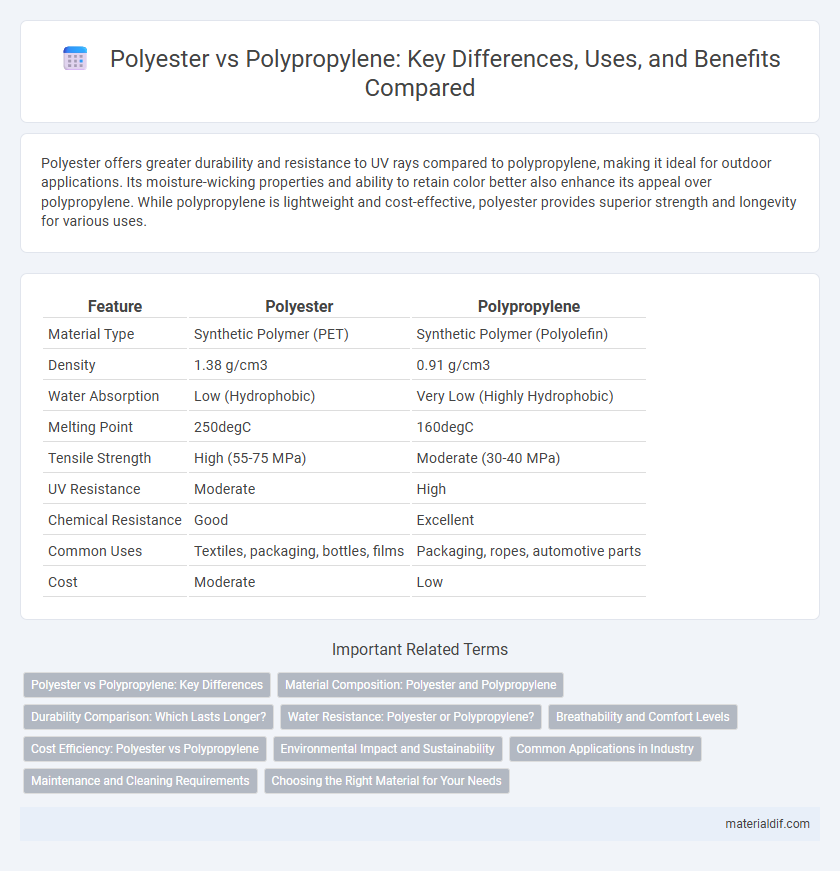
| Feature | Polyester | Polypropylene |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic Polymer (PET) | Synthetic Polymer (Polyolefin) |
| Density | 1.38 g/cm3 | 0.91 g/cm3 |
| Water Absorption | Low (Hydrophobic) | Very Low (Highly Hydrophobic) |
| Melting Point | 250degC | 160degC |
| Tensile Strength | High (55-75 MPa) | Moderate (30-40 MPa) |
| UV Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Common Uses | Textiles, packaging, bottles, films | Packaging, ropes, automotive parts |
| Cost | Moderate | Low |
Polyester vs Polypropylene: Key Differences
Polyester offers superior durability and moisture resistance compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for clothing and upholstery that require long-lasting performance. Polypropylene excels in chemical resistance and lightweight applications, often used in packaging and disposable products. The thermal properties differ significantly, with polyester maintaining stability at higher temperatures than polypropylene, influencing their respective industrial uses.
Material Composition: Polyester and Polypropylene
Polyester is a synthetic polymer derived from petroleum-based products, primarily composed of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) units, known for its durability, moisture resistance, and versatility in fiber and fabric applications. Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer made from propylene monomers, characterized by its lightweight, chemical resistance, and ability to repel water, making it ideal for industrial use and packaging. The difference in material composition results in distinct properties; polyester's aromatic ester groups provide strength and elasticity, whereas polypropylene's hydrocarbon chains contribute to its low density and high chemical inertness.
Durability Comparison: Which Lasts Longer?
Polyester exhibits higher durability compared to polypropylene due to its superior resistance to abrasion, UV exposure, and chemicals, making it ideal for long-term outdoor applications. Polypropylene, while resistant to moisture and chemicals, tends to degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure and mechanical stress. The enhanced tensile strength and resilience of polyester contribute to its longer lifespan in demanding environments.
Water Resistance: Polyester or Polypropylene?
Polypropylene exhibits superior water resistance compared to polyester due to its hydrophobic molecular structure, which prevents water absorption and promotes quick drying. Polyester, while water-resistant, tends to absorb more moisture, making it less effective in consistently wet environments. For applications requiring enhanced water repellency and durability in wet conditions, polypropylene is the preferred choice over polyester.
Breathability and Comfort Levels
Polyester offers moderate breathability and moisture-wicking properties, making it suitable for activewear but sometimes less comfortable in high-heat conditions due to limited airflow. Polypropylene excels in breathability by allowing better moisture vapor transmission, keeping the skin dry and enhancing comfort during intense physical activity or hot weather. Comfort levels often favor polypropylene for prolonged wear because its superior breathability reduces sweat buildup and potential skin irritation compared to polyester.
Cost Efficiency: Polyester vs Polypropylene
Polyester typically offers a lower initial cost compared to polypropylene, making it a cost-effective choice for a wide range of applications. However, polypropylene provides better long-term value due to its higher chemical resistance and durability in harsh environments. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and lifespan, often favors polypropylene despite its higher upfront price.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyester production relies heavily on petroleum, contributing to fossil fuel depletion and microplastic pollution in oceans, whereas polypropylene manufacturing has a slightly lower carbon footprint but still poses challenges due to its non-biodegradability. Both fibers are recyclable, yet polyester recycling infrastructure is more established, facilitating circular economy practices and reducing landfill waste. Innovations in bio-based polyester and polypropylene seek to enhance sustainability by lowering greenhouse gas emissions and using renewable resources.
Common Applications in Industry
Polyester is widely used in the textile industry for clothing, upholstery, and industrial fabrics due to its durability and resistance to shrinking. Polypropylene finds common applications in packaging, automotive parts, and geotextiles thanks to its lightweight, chemical resistance, and moisture-wicking properties. Both materials are essential in manufacturing, with polyester favored for strength and aesthetic qualities, while polypropylene is chosen for cost-efficiency and resistance to environmental factors.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Polyester exhibits superior resistance to shrinking, stretching, and staining compared to polypropylene, making maintenance simpler and less frequent. Its hydrophobic nature allows quick drying and easy removal of water-based stains, while polypropylene may retain oils and require specialized cleaning agents. Both fabrics are machine washable, but polyester's durability withstands higher temperatures and vigorous washing cycles without compromising fabric integrity.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Polyester offers superior durability, moisture resistance, and vibrant color retention compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for applications requiring longevity and aesthetic appeal. Polypropylene excels in chemical resistance and lightweight properties, suitable for environments exposed to harsh chemicals or needing reduced weight. Selecting between polyester and polypropylene depends on factors such as exposure to elements, required strength, and specific end-use performance criteria.
Polyester vs Polypropylene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com