Virgin linerboard offers superior strength and stiffness compared to testliner, making it ideal for heavy-duty packaging applications. Testliner primarily consists of recycled fibers, resulting in lower durability but enhanced sustainability and cost-effectiveness. Choosing between virgin linerboard and testliner depends on balancing performance requirements with environmental considerations.
Table of Comparison
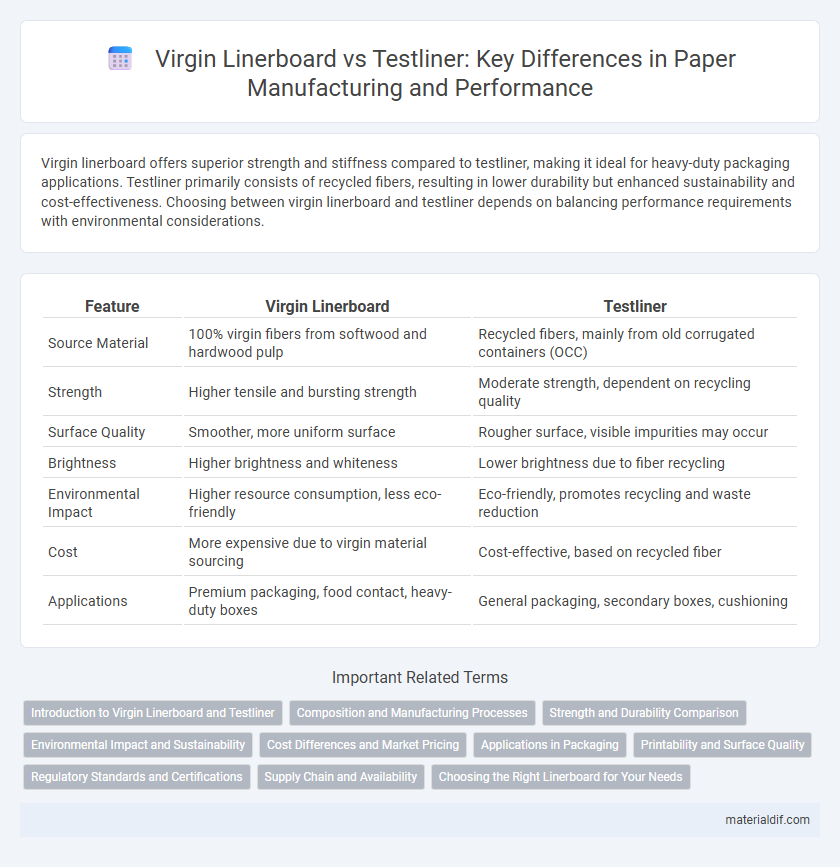
| Feature | Virgin Linerboard | Testliner |
|---|---|---|
| Source Material | 100% virgin fibers from softwood and hardwood pulp | Recycled fibers, mainly from old corrugated containers (OCC) |
| Strength | Higher tensile and bursting strength | Moderate strength, dependent on recycling quality |
| Surface Quality | Smoother, more uniform surface | Rougher surface, visible impurities may occur |
| Brightness | Higher brightness and whiteness | Lower brightness due to fiber recycling |
| Environmental Impact | Higher resource consumption, less eco-friendly | Eco-friendly, promotes recycling and waste reduction |
| Cost | More expensive due to virgin material sourcing | Cost-effective, based on recycled fiber |
| Applications | Premium packaging, food contact, heavy-duty boxes | General packaging, secondary boxes, cushioning |
Introduction to Virgin Linerboard and Testliner
Virgin linerboard, produced from fresh wood fibers, offers superior strength, stiffness, and printability compared to recycled fiber-based materials. Testliner, mainly made from recycled fibers, provides a cost-effective alternative with adequate mechanical properties for less demanding packaging applications. Understanding the differences in fiber composition, manufacturing processes, and environmental impact is key to selecting the appropriate linerboard for specific uses.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Virgin linerboard is made entirely from fresh wood fibers derived from softwood and hardwood trees, providing superior strength and durability due to minimal fiber processing and absence of recycled content. Testliner consists predominantly of recycled fibers sourced from post-consumer paper waste, which undergoes deinking and cleaning to remove contaminants, resulting in a less uniform fiber composition. The manufacturing process of virgin linerboard involves mechanical pulping and chemical treatments to enhance fiber bonding, while testliner production emphasizes the recycling process, including repulping and screening, to optimize fiber reuse and reduce environmental impact.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Virgin linerboard exhibits superior tensile strength and burst resistance compared to testliner due to its use of fresh fibers that maintain longer fiber length and higher fiber bonding capacity. Testliner, primarily made from recycled fibers, often shows reduced durability and lower resistance to moisture-induced weakening, making it less suitable for heavy-duty packaging applications. These strength and durability differences significantly impact performance in high-stress shipping environments, favoring virgin linerboard for premium protection needs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Virgin linerboard is produced primarily from fresh wood fibers, resulting in higher energy consumption and carbon emissions compared to testliner, which is made from recycled fibers. The recycling process used in testliner significantly reduces deforestation and minimizes landfill waste, contributing to a lower environmental footprint. Choosing testliner supports circular economy principles, promoting sustainability through efficient resource utilization and reduced ecological impact.
Cost Differences and Market Pricing
Virgin linerboard typically commands higher market prices compared to testliner due to its superior strength, durability, and brightness, which are crucial for premium packaging applications. The production cost of virgin linerboard is substantially higher because it relies on fresh pulp, requiring intensive energy and raw material inputs, whereas testliner is cost-effective as it incorporates recycled fibers, lowering manufacturing expenses. Market pricing reflects these cost differences, with virgin linerboard priced approximately 15-30% above testliner, influencing buyer decisions in sectors sensitive to price versus quality trade-offs.
Applications in Packaging
Virgin linerboard offers superior strength and stiffness, making it ideal for heavy-duty packaging applications requiring high durability and impact resistance. Testliner, composed primarily of recycled fibers, suits lighter packaging needs where cost-efficiency and environmental sustainability are prioritized. Both materials are widely used in corrugated board production, but virgin linerboard excels in premium packaging for fragile or high-value goods.
Printability and Surface Quality
Virgin linerboard offers superior printability and surface quality compared to testliner due to its higher fiber purity and uniformity, resulting in a smoother surface and better ink absorption. Testliner, made primarily from recycled fibers, typically exhibits more surface roughness and irregularities, which can affect print clarity and color vibrancy. High-quality virgin linerboard is preferred for premium packaging applications where print precision and aesthetic appeal are critical.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Virgin Linerboard typically complies with stringent regulatory standards such as FSC and PEFC certifications, ensuring sustainable forest management and traceability. Testliner, often produced from recycled fibers, must meet recycling and environmental regulations like EN 643 to guarantee quality and safety. Compliance with these certifications plays a crucial role in market acceptance and environmental impact for both paper products.
Supply Chain and Availability
Virgin linerboard offers consistent quality and higher strength, ensuring reliable supply chain performance and reduced variability in production. Testliner, often sourced from recycled fibers, provides a cost-effective alternative but faces availability challenges due to fluctuations in recycled material supply and variable fiber quality. Supply chain resilience for virgin linerboard is enhanced by stable raw material sources, while testliner availability depends heavily on regional recycling rates and market demand for recovered fibers.
Choosing the Right Linerboard for Your Needs
Virgin linerboard offers superior strength, durability, and resistance to moisture compared to testliner, making it ideal for packaging that requires premium protection. Testliner, produced primarily from recycled fibers, provides a cost-effective, environmentally friendly option suitable for less demanding applications. Evaluating product weight, environmental impact, and performance requirements ensures the optimal choice between virgin linerboard and testliner for your packaging needs.
Virgin Linerboard vs Testliner Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com