Coated Duplex Board offers a smooth, printable surface ideal for high-quality packaging and branding, while Greyboard provides sturdy structural support often used as the backing for boxes and rigid packaging. The coated layer on Duplex Board enhances visual appeal and protects against moisture, whereas Greyboard's uncoated, recycled composition makes it more environmentally friendly and cost-effective. Selecting between the two depends on whether appearance or strength is the priority for the final product.
Table of Comparison
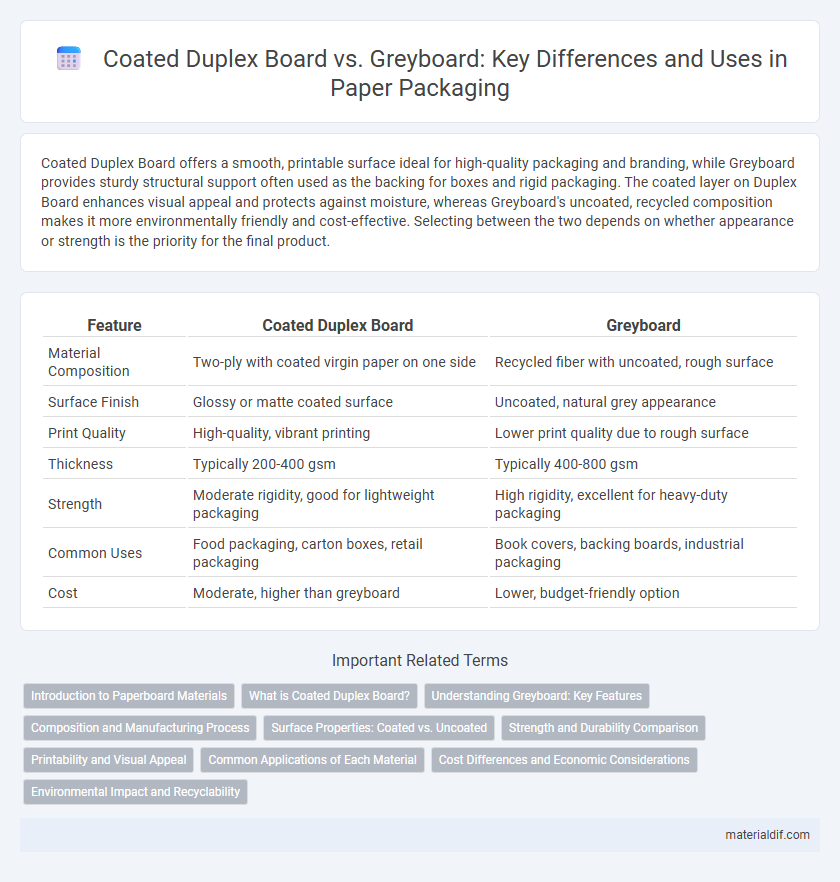
| Feature | Coated Duplex Board | Greyboard |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Two-ply with coated virgin paper on one side | Recycled fiber with uncoated, rough surface |
| Surface Finish | Glossy or matte coated surface | Uncoated, natural grey appearance |
| Print Quality | High-quality, vibrant printing | Lower print quality due to rough surface |
| Thickness | Typically 200-400 gsm | Typically 400-800 gsm |
| Strength | Moderate rigidity, good for lightweight packaging | High rigidity, excellent for heavy-duty packaging |
| Common Uses | Food packaging, carton boxes, retail packaging | Book covers, backing boards, industrial packaging |
| Cost | Moderate, higher than greyboard | Lower, budget-friendly option |
Introduction to Paperboard Materials
Paperboard materials include coated duplex board and greyboard, each serving distinct packaging purposes. Coated duplex board features a smooth, white, printable surface with a multi-layered structure, ideal for high-quality graphic printing and consumer packaging. Greyboard, composed of recycled fibres and often uncoated, provides rigid, economical support commonly used for backing boards, book covers, and rigid boxes.
What is Coated Duplex Board?
Coated Duplex Board is a high-quality paperboard featuring a duplex structure with a white, clay-coated surface on one side and an uncoated gray back. This board is commonly used for packaging applications requiring excellent printability, smoothness, and stiffness, such as food cartons and cosmetic boxes. Its coated surface enhances graphic appeal and moisture resistance compared to Greyboard, which is typically uncoated and used primarily for inner packaging and backing materials.
Understanding Greyboard: Key Features
Greyboard is a dense, recycled paperboard commonly used for packaging and bookbinding due to its rigidity and eco-friendly composition. Its uncoated surface distinguishes it from coated duplex board, offering superior absorbency and suitability for applications requiring adhesive bonding. The high recycled fiber content in greyboard enhances sustainability, making it a preferred choice for environmentally conscious manufacturing.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Coated duplex board consists of a combination of a bleached chemical pulp top layer and recycled greyboard as the base, providing a smooth, printable surface, while greyboard is typically made entirely from recycled fibers and used for rigid packaging. The manufacturing process of coated duplex board involves applying a coated layer over the recycled board to enhance printability and visual appeal, whereas greyboard is produced through a simple pressing and drying of recycled fibers without surface treatment. This distinction in composition and coating results in coated duplex board offering superior brightness, smoother texture, and better print quality compared to the uncoated, rougher greyboard.
Surface Properties: Coated vs. Uncoated
Coated duplex board features a smooth, glossy surface due to its sealed coating, enhancing print quality and resistance to moisture and abrasion. Greyboard, usually uncoated, exhibits a rougher texture with higher porosity, which can absorb ink unevenly and is less resistant to wear and environmental factors. The surface properties of coated duplex board make it ideal for high-end packaging and graphic applications requiring durability and visual appeal.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Coated Duplex Board offers superior strength and durability compared to Greyboard due to its layered clay coating, which enhances resistance to wear and tear while maintaining rigidity. Greyboard, made from recycled fibers, typically exhibits lower tensile strength and is more prone to bending and moisture damage. This makes Coated Duplex Board a preferred choice for packaging that demands robust protection and long-lasting performance.
Printability and Visual Appeal
Coated duplex board offers superior printability due to its smooth, clay-coated surface, which ensures vibrant color reproduction and sharp image clarity, making it ideal for high-quality packaging and promotional materials. In contrast, greyboard has a rougher texture and weaker surface strength, leading to less precise printing results and muted visuals. The enhanced visual appeal of coated duplex board significantly improves brand presentation compared to the utilitarian look of greyboard.
Common Applications of Each Material
Coated duplex board is commonly used in packaging for cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and food products due to its smooth surface and excellent printability. Greyboard is widely applied in bookbinding, carton manufacturing, and backing for notepads because of its sturdy and recycled content properties. Both materials serve distinct purposes, with coated duplex board favored for high-quality visual appeal and greyboard preferred for structural support and durability.
Cost Differences and Economic Considerations
Coated Duplex Board typically incurs higher production costs due to its glossy finish and additional coating layers, making it more expensive than Greyboard, which is uncoated and produced with recycled fibers. Greyboard presents a cost-effective option for packaging and backing applications where aesthetic appeal is less critical, optimizing budget constraints in large-scale manufacturing. Economic considerations favor Coated Duplex Board in premium product markets requiring enhanced durability and visual appeal, whereas Greyboard's affordability benefits bulk and eco-friendly projects.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Coated duplex board offers enhanced recyclability due to its cleaner surface and reduced adhesive use, facilitating more efficient paper recovery compared to greyboard, which often contains higher recycled fiber content but poses challenges in contaminant removal. The environmental impact of coated duplex board is minimized by its lighter weight and lower carbon footprint during production, whereas greyboard's use of recycled materials reduces raw resource extraction but may generate more waste in recycling processes. Choosing coated duplex board supports sustainable packaging goals by balancing renewable content with better end-of-life processing efficiency.
Coated Duplex Board vs Greyboard Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com