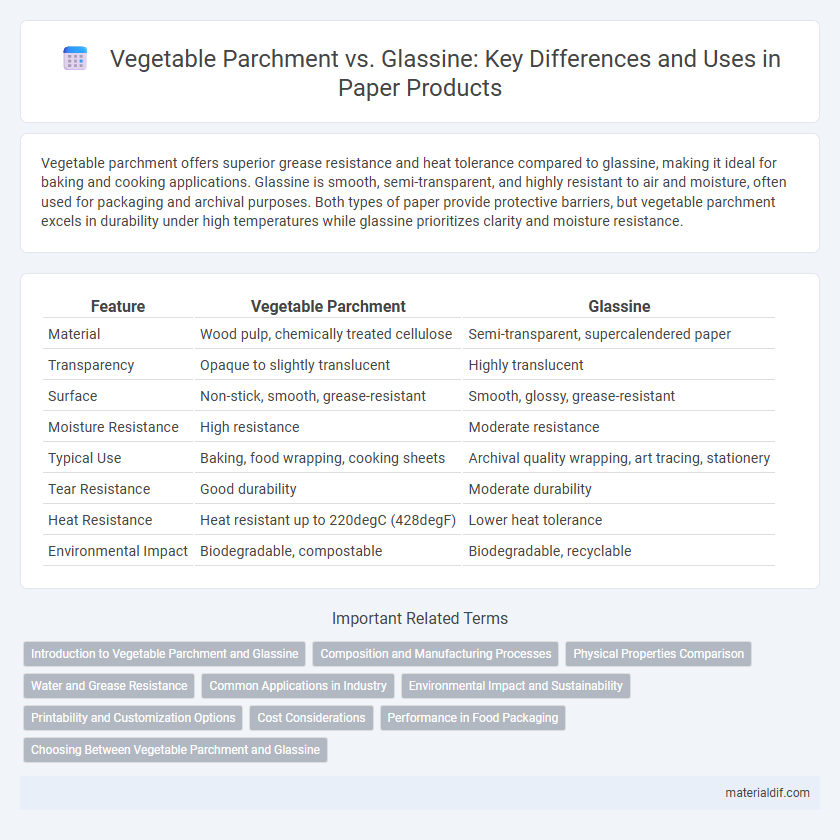
Vegetable parchment offers superior grease resistance and heat tolerance compared to glassine, making it ideal for baking and cooking applications. Glassine is smooth, semi-transparent, and highly resistant to air and moisture, often used for packaging and archival purposes. Both types of paper provide protective barriers, but vegetable parchment excels in durability under high temperatures while glassine prioritizes clarity and moisture resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vegetable Parchment | Glassine |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Wood pulp, chemically treated cellulose | Semi-transparent, supercalendered paper |
| Transparency | Opaque to slightly translucent | Highly translucent |
| Surface | Non-stick, smooth, grease-resistant | Smooth, glossy, grease-resistant |
| Moisture Resistance | High resistance | Moderate resistance |
| Typical Use | Baking, food wrapping, cooking sheets | Archival quality wrapping, art tracing, stationery |
| Tear Resistance | Good durability | Moderate durability |
| Heat Resistance | Heat resistant up to 220degC (428degF) | Lower heat tolerance |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, compostable | Biodegradable, recyclable |
Introduction to Vegetable Parchment and Glassine
Vegetable parchment is a cellulose-based paper treated with acid to create a translucent, grease-resistant, and heat-resistant surface ideal for baking and food wrapping. Glassine, made from highly refined pulp, is smooth, glossy, and resistant to air, water, and grease, making it suitable for archival storage and art applications. Both papers offer distinct advantages in durability and transparency, catering to different packaging and preservation needs.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Vegetable parchment is produced by treating cellulose-based paper with sulfuric acid, resulting in a dense, water-resistant, and grease-resistant material widely used for baking and food packaging. Glassine, on the other hand, is made by supercalendering unsized, uncoated paper to achieve a smooth, glossy, and translucent finish that provides grease resistance but less moisture barrier compared to vegetable parchment. The manufacturing process of vegetable parchment involves chemical modification of fibers for enhanced durability, whereas glassine relies on mechanical pressing to improve surface properties and translucency.
Physical Properties Comparison
Vegetable parchment exhibits superior heat resistance and grease repellency due to its silicone or sulfur treatment, making it ideal for baking and food packaging applications. Glassine is distinguished by its smooth, glossy surface and excellent resistance to air, water, and grease, achieved through a high-pressure calendaring process that enhances its density and translucency. While both materials offer moisture barrier properties, vegetable parchment is more durable under heat exposure, whereas glassine provides better strength and protection for archival storage and lightweight wrapping.
Water and Grease Resistance
Vegetable parchment offers superior water resistance due to its cellulose fibers treated with sulfuric acid, creating a dense, waterproof barrier ideal for wrapping moist foods. Glassine provides excellent grease resistance because of its tightly supercalendered structure that repels oils while maintaining translucency. Both papers serve distinct purposes: vegetable parchment excels in preventing water penetration, whereas glassine is preferred for blocking grease and oil stains.
Common Applications in Industry
Vegetable parchment and glassine are widely used in the food packaging industry for their grease-resistant and moisture-resistant properties, making them ideal for wrapping baked goods, candies, and deli items. Vegetable parchment is often preferred in baking applications due to its heat resistance and non-stick surface, while glassine's smooth, glossy finish suits use in archival storage and art supply packaging. Both materials are favored in the pharmaceutical and cosmetics industries for product wrapping because of their protective barrier properties and translucency.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Vegetable parchment and glassine both serve as popular food packaging materials, but vegetable parchment offers superior environmental benefits due to its biodegradable and compostable properties derived from natural cellulose fibers. Glassine undergoes a supercalendering process that reduces its porosity but makes it less biodegradable and more challenging to recycle, increasing its environmental footprint. Choosing vegetable parchment supports sustainability goals by reducing plastic waste and promoting eco-friendly disposal, making it a preferable option for environmentally conscious consumers and businesses.
Printability and Customization Options
Vegetable parchment offers excellent printability with its smooth, non-porous surface that allows for sharp, vibrant images and text, making it ideal for detailed branding applications. Glassine, while also smooth and translucent, tends to be less receptive to ink absorption, which can result in slightly muted print quality but excels in customization with coatings and finishes such as gloss or matte. Both materials support various printing techniques like flexography and digital printing, but vegetable parchment provides more consistent results for high-quality, customized packaging.
Cost Considerations
Vegetable parchment generally costs more than glassine due to its higher manufacturing quality and superior grease resistance. Glassine, being cheaper and easier to produce, is often preferred for bulk packaging where cost efficiency is critical. Choosing between vegetable parchment and glassine involves balancing budget constraints with the need for durability and moisture protection.
Performance in Food Packaging
Vegetable parchment offers superior grease resistance and heat tolerance, making it ideal for wrapping oily or baked goods without compromising freshness. Glassine provides excellent moisture resistance and transparency, enhancing product visibility while maintaining a grease-proof barrier suitable for dry foods. Both materials deliver distinct performance benefits in food packaging, with vegetable parchment excelling in durability and glassine favored for its smooth, glossy finish.
Choosing Between Vegetable Parchment and Glassine
Vegetable parchment offers a grease-resistant, biodegradable option ideal for baking and food wrapping, while glassine provides a smooth, translucent barrier perfect for archival storage and protecting delicate items. Selecting between vegetable parchment and glassine depends on factors such as moisture resistance, transparency needs, and environmental impact. For sustainable packaging, vegetable parchment is preferable, whereas glassine excels in preserving documents and artwork without compromising visibility.
Vegetable parchment vs Glassine Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com