Tissue paper is thin, soft, and highly absorbent, often used for hygiene and packaging delicate items, while kraft paper is thicker, sturdier, and designed for heavy-duty packaging and industrial use. The biodegradable nature of both papers makes them eco-friendly options, but kraft paper's durability makes it more suitable for protective wrapping and shipping. Choosing between tissue and kraft paper depends on the required strength and softness for specific applications.
Table of Comparison
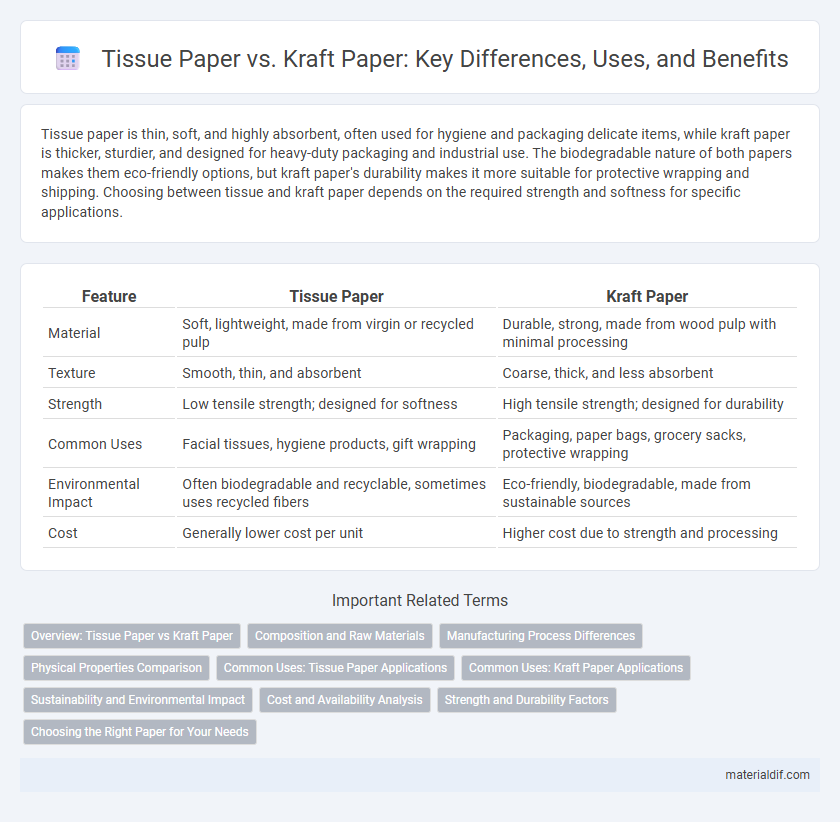
| Feature | Tissue Paper | Kraft Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Soft, lightweight, made from virgin or recycled pulp | Durable, strong, made from wood pulp with minimal processing |
| Texture | Smooth, thin, and absorbent | Coarse, thick, and less absorbent |
| Strength | Low tensile strength; designed for softness | High tensile strength; designed for durability |
| Common Uses | Facial tissues, hygiene products, gift wrapping | Packaging, paper bags, grocery sacks, protective wrapping |
| Environmental Impact | Often biodegradable and recyclable, sometimes uses recycled fibers | Eco-friendly, biodegradable, made from sustainable sources |
| Cost | Generally lower cost per unit | Higher cost due to strength and processing |
Overview: Tissue Paper vs Kraft Paper
Tissue paper is a thin, lightweight material primarily used for hygiene and decorative purposes, characterized by its softness and absorbency. Kraft paper is a durable, coarse paper made from wood pulp, commonly utilized in packaging and industrial applications for its strength and resistance. Both papers serve distinct functions, with tissue paper optimized for comfort and aesthetics, while kraft paper emphasizes robustness and protection.
Composition and Raw Materials
Tissue paper is primarily made from virgin wood pulp or recycled fibers, emphasizing softness and absorbency, while kraft paper is produced from chemical pulp through the kraft process, resulting in strong, coarse fibers suited for durability. Tissue paper composition typically involves bleached or unbleached fibers with additives like wet strength resins, whereas kraft paper relies on unbleached cellulose fibers to maintain high tensile strength and resistance. The raw materials for tissue paper often include hardwood and softwood fibers for softness, in contrast to kraft paper's use of primarily softwood fibers for enhanced fiber length and strength.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Tissue paper is produced through a wet pressing process that results in a lightweight, soft, and absorbent material primarily made from virgin wood pulp or recycled fibers. Kraft paper undergoes the kraft pulping process, which uses chemical treatments to break down wood chips into strong cellulose fibers, producing a durable, coarse paper with high tensile strength. The key difference lies in tissue paper's emphasis on softness and absorbency versus kraft paper's focus on strength and resistance, driven by their respective pulp processing and drying methods.
Physical Properties Comparison
Tissue paper and kraft paper differ significantly in physical properties, with tissue paper exhibiting a thin, lightweight, and highly absorbent structure ideal for softness and flexibility. Kraft paper is thicker, stronger, and more durable due to its long kraft fibers, making it suitable for heavy-duty packaging and wrapping. The tensile strength of kraft paper surpasses that of tissue paper, while tissue paper provides better softness and cushioning.
Common Uses: Tissue Paper Applications
Tissue paper is widely used for gift wrapping, cushioning fragile items, and personal hygiene products due to its softness and absorbency. Its lightweight and delicate texture make it ideal for decorative purposes in crafts and floral arrangements. Common applications also include packaging filler and sanitary products, distinguishing it from the sturdier kraft paper used in industrial packaging.
Common Uses: Kraft Paper Applications
Kraft paper is widely used in packaging due to its strength and durability, making it ideal for wrapping heavy items, shipping boxes, and protective cushioning. Its resistance to tearing and moisture allows kraft paper to serve as a reliable material for industrial and agricultural applications, such as pallet wrapping and mulching. Kraft paper also finds common use in arts and crafts, providing a sturdy and eco-friendly option for creating bags, envelopes, and various handmade products.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Tissue paper, typically made from virgin or recycled fibers, offers biodegradability and compostability, making it eco-friendly for short-term use but often demands higher water and energy consumption in production. Kraft paper, derived from the kraft pulping process using wood fibers, exhibits superior strength and durability with a higher recycled content, contributing to reduced deforestation and carbon footprint. Both papers support sustainability, but kraft paper's recyclability and lower processing chemicals position it as a more environmentally responsible choice in packaging and industrial applications.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Tissue paper generally incurs higher costs due to its delicate manufacturing process and limited durability, making it less cost-effective compared to kraft paper, which is produced using less refined fibers and is widely available. Kraft paper benefits from abundant raw materials, notably wood pulp, ensuring consistent supply and competitive pricing, ideal for packaging and industrial use. The cost-efficiency and extensive availability of kraft paper render it preferable for large-scale applications, while tissue paper's premium price aligns with specialized uses demanding softness and absorbency.
Strength and Durability Factors
Tissue paper is thin, soft, and designed for light-duty tasks, resulting in lower tensile strength and less durability compared to kraft paper. Kraft paper is produced from chemical pulp, offering superior tear resistance and long-lasting durability due to its dense fiber composition. The inherent strength of kraft paper makes it ideal for packaging and industrial uses, whereas tissue paper is better suited for hygiene and delicate applications.
Choosing the Right Paper for Your Needs
Tissue paper offers softness and flexibility, making it ideal for gift wrapping, cushioning, and delicate packaging, while kraft paper provides strength and durability, suited for heavy-duty wrapping, shipping, and crafting applications. Consider tissue paper's lightweight and colorful options for decorative purposes, whereas kraft paper's tear resistance and eco-friendly qualities meet industrial and sustainable packaging demands. Selecting the right paper depends on prioritizing softness and appearance versus toughness and environmental impact.
Tissue Paper vs Kraft Paper Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com