Paper lamination provides a durable, protective layer that enhances water resistance and adds rigidity to paper products, making them ideal for long-term use. Varnish coating offers a thinner, glossy or matte finish that enhances visual appeal and protects against minor abrasions without significantly increasing thickness. Choosing between lamination and varnish depends on the desired balance between durability, tactile experience, and cost-efficiency in paper pet projects.
Table of Comparison
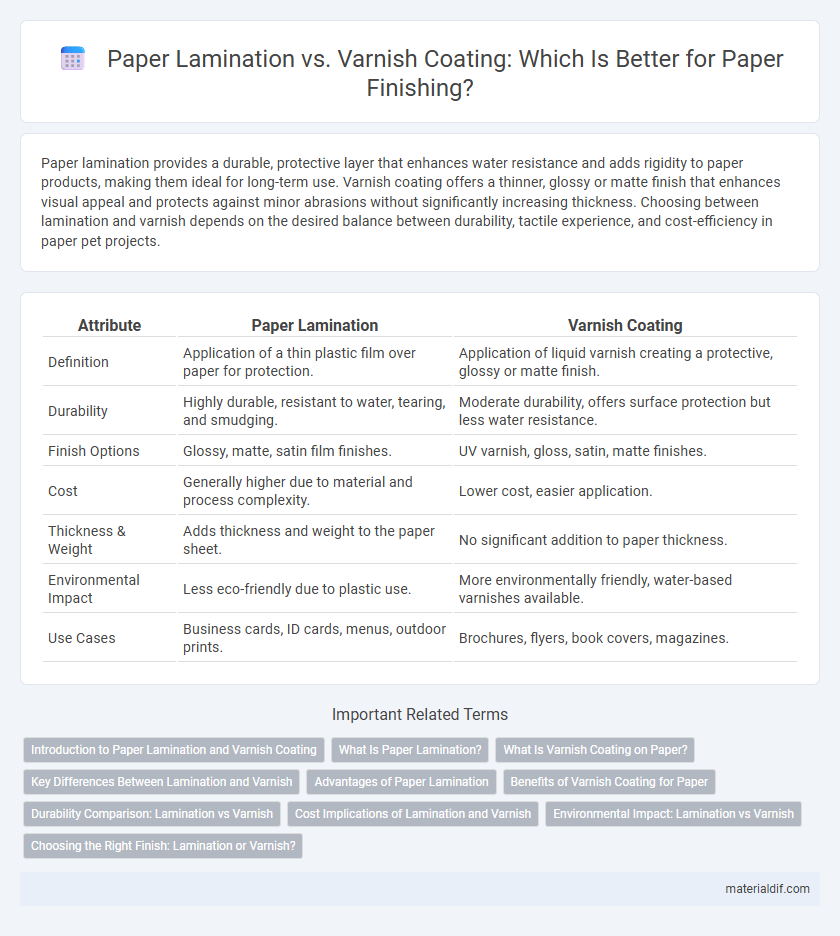
| Attribute | Paper Lamination | Varnish Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Application of a thin plastic film over paper for protection. | Application of liquid varnish creating a protective, glossy or matte finish. |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to water, tearing, and smudging. | Moderate durability, offers surface protection but less water resistance. |
| Finish Options | Glossy, matte, satin film finishes. | UV varnish, gloss, satin, matte finishes. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to material and process complexity. | Lower cost, easier application. |
| Thickness & Weight | Adds thickness and weight to the paper sheet. | No significant addition to paper thickness. |
| Environmental Impact | Less eco-friendly due to plastic use. | More environmentally friendly, water-based varnishes available. |
| Use Cases | Business cards, ID cards, menus, outdoor prints. | Brochures, flyers, book covers, magazines. |
Introduction to Paper Lamination and Varnish Coating
Paper lamination involves bonding a thin plastic film to the paper surface, enhancing durability, water resistance, and visual appeal, commonly used in packaging and book covers. Varnish coating applies a liquid glossy, matte, or satin finish that protects paper from wear and adds aesthetic enhancement without altering texture significantly. Both techniques improve the functional and aesthetic qualities of paper but differ in protective strength and tactile effects.
What Is Paper Lamination?
Paper lamination involves bonding a thin layer of plastic film onto paper surfaces to enhance durability, resistance to moisture, and improved visual appeal. This process provides a protective coating that extends the lifespan of printed materials while maintaining flexibility and tactile quality. Lamination is widely used in packaging, business cards, and menus to prevent wear and tear compared to varnish coating, which offers a thinner, less protective surface finish.
What Is Varnish Coating on Paper?
Varnish coating on paper is a clear liquid finish applied to enhance durability, gloss, and visual appeal without altering the paper's texture. This coating protects printed materials from scratches, moisture, and fading while providing a smooth, polished surface. Varnish can be applied in different finishes such as gloss, matte, or satin, making it a versatile choice for various printing projects.
Key Differences Between Lamination and Varnish
Paper lamination involves bonding a thin plastic film onto the surface of the paper for enhanced durability, water resistance, and a glossy or matte finish. Varnish coating applies a liquid varnish layer that provides a shiny or matte surface but offers less protection against physical wear and moisture compared to lamination. Lamination is more effective for long-term preservation, while varnish is often chosen for cost-effective aesthetic enhancement.
Advantages of Paper Lamination
Paper lamination offers superior durability and water resistance compared to varnish coating, extending the lifespan of printed materials significantly. It provides enhanced protection against scratches, tears, and fading while maintaining a smooth, professional finish ideal for high-traffic applications. The ability to choose from matte, gloss, or satin lamination enhances visual appeal and tactile experience, making it a versatile choice for packaging, book covers, and marketing materials.
Benefits of Varnish Coating for Paper
Varnish coating enhances paper durability by providing a protective layer that resists scratches, moisture, and dirt, ensuring longer-lasting print quality. This coating improves the visual appeal with a glossy or matte finish that intensifies colors and sharpens image details. Varnish also allows for targeted application, enabling designers to highlight specific areas while maintaining cost efficiency compared to full lamination.
Durability Comparison: Lamination vs Varnish
Lamination provides superior durability compared to varnish coating, offering enhanced resistance to water, tearing, and abrasion, which significantly extends the lifespan of printed materials. Varnish coating, while also protecting paper, is more susceptible to scratches and wear under heavy use due to its thinner protective layer. For applications requiring long-term preservation and frequent handling, lamination is generally the preferred choice for maintaining structural integrity and appearance.
Cost Implications of Lamination and Varnish
Lamination generally incurs higher upfront costs than varnish coating due to the use of plastic films and more complex machinery, increasing production expenses. Varnish coating offers a cost-effective alternative, providing a protective layer with lower material and application costs, ideal for budget-conscious projects. Choosing between the two depends on the desired durability, finish quality, and budget constraints within printing and packaging industries.
Environmental Impact: Lamination vs Varnish
Paper lamination typically involves plastics like polyethylene, which contribute to non-biodegradable waste and complicate recycling processes, increasing environmental impact. Varnish coating, often water- or UV-based, generally offers a thinner, solvent-free option that enhances recyclability and reduces landfill burden. Choosing varnish over lamination significantly lowers ecological footprint by promoting better recyclability and minimizing plastic pollution.
Choosing the Right Finish: Lamination or Varnish?
Choosing the right finish between paper lamination and varnish coating depends on durability and appearance requirements. Lamination offers superior protection against moisture, scratches, and wear, making it ideal for frequently handled materials, while varnish coating enhances gloss and texture with a wide range of finishes from matte to high-gloss. Selecting the finish involves balancing cost, tactile feel, and intended usage to ensure longevity and visual impact of printed materials.
Paper Lamination vs Varnish Coating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com