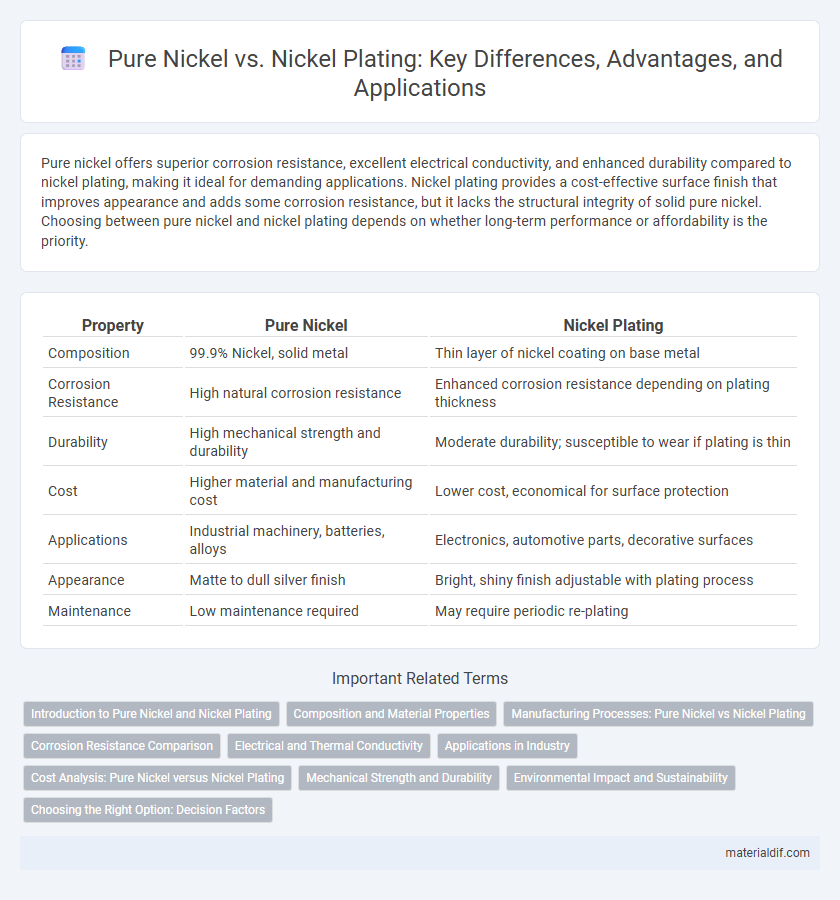
Pure nickel offers superior corrosion resistance, excellent electrical conductivity, and enhanced durability compared to nickel plating, making it ideal for demanding applications. Nickel plating provides a cost-effective surface finish that improves appearance and adds some corrosion resistance, but it lacks the structural integrity of solid pure nickel. Choosing between pure nickel and nickel plating depends on whether long-term performance or affordability is the priority.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Pure Nickel | Nickel Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | 99.9% Nickel, solid metal | Thin layer of nickel coating on base metal |
| Corrosion Resistance | High natural corrosion resistance | Enhanced corrosion resistance depending on plating thickness |
| Durability | High mechanical strength and durability | Moderate durability; susceptible to wear if plating is thin |
| Cost | Higher material and manufacturing cost | Lower cost, economical for surface protection |
| Applications | Industrial machinery, batteries, alloys | Electronics, automotive parts, decorative surfaces |
| Appearance | Matte to dull silver finish | Bright, shiny finish adjustable with plating process |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance required | May require periodic re-plating |
Introduction to Pure Nickel and Nickel Plating
Pure nickel consists of high-purity nickel metal with a minimum nickel content of 99.0%, prized for its excellent corrosion resistance, high melting point, and strong magnetic properties. Nickel plating involves applying a thin layer of nickel onto the surface of another metal to enhance durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal, commonly used in automotive, electronics, and industrial applications. Understanding the differences in composition and function between pure nickel and nickel plating is essential for selecting the appropriate material for specific engineering or manufacturing needs.
Composition and Material Properties
Pure nickel consists of approximately 99.9% nickel, offering excellent corrosion resistance, high thermal conductivity, and magnetic properties. Nickel plating involves a thin layer of nickel alloy deposited on substrates, enhancing surface hardness, wear resistance, and providing a protective barrier against oxidation. While pure nickel is used for applications requiring bulk material properties, nickel plating optimizes surface characteristics without altering the core material composition.
Manufacturing Processes: Pure Nickel vs Nickel Plating
Pure nickel manufacturing involves melting and casting high-purity nickel ore followed by hot rolling or extrusion to form solid nickel products with consistent elemental composition and mechanical properties. Nickel plating uses electrochemical deposition to coat a substrate, typically steel or copper, with a thin, uniform layer of nickel, enhancing corrosion resistance and surface hardness. These manufacturing processes differ significantly in scale, cost, and application; pure nickel production requires extensive refining and shaping, whereas nickel plating provides a cost-effective surface modification with controlled nickel thickness.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Pure nickel exhibits excellent intrinsic corrosion resistance due to its uniform metal composition, which prevents rust and oxidation in harsh environments. Nickel plating enhances surface protection on lower-grade metals by creating a thin, corrosion-resistant barrier, though it may wear off over time and lose effectiveness. In contrast to pure nickel, nickel plating is more cost-effective but requires maintenance to ensure long-term durability against corrosion.
Electrical and Thermal Conductivity
Pure nickel exhibits high electrical and thermal conductivity, making it ideal for applications requiring efficient energy transfer and heat dissipation. In contrast, nickel plating offers surface protection and corrosion resistance but typically has lower conductivity due to its thin, layered structure and potential alloy composition. The distinction in conductivity levels between pure nickel and nickel plating affects their performance in electronic components and thermal management systems.
Applications in Industry
Pure nickel is extensively used in industries requiring high corrosion resistance and thermal stability, such as chemical processing, aerospace, and battery manufacturing. Nickel plating enhances surface properties of metals by providing wear resistance, improved conductivity, and aesthetic appeal, making it ideal for automotive parts, electronics, and decorative applications. Selecting pure nickel or nickel plating depends on the application's mechanical and environmental requirements, with pure nickel preferred for structural components and plating favored for surface protection.
Cost Analysis: Pure Nickel versus Nickel Plating
Pure nickel typically incurs higher material and production costs due to its bulk usage and refined metal content, whereas nickel plating offers a cost-effective alternative by providing a thin layer of nickel over base metals, reducing overall nickel consumption. The application of nickel plating significantly lowers expenses in industries requiring corrosion resistance and aesthetic enhancement without compromising structural integrity. Cost analysis reveals nickel plating as a preferred choice for budget-sensitive projects demanding nickel's protective and decorative properties.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Pure nickel exhibits excellent mechanical strength with high tensile strength and good ductility, making it suitable for demanding industrial applications. Nickel plating significantly enhances surface durability by providing corrosion resistance, increased hardness, and wear protection, extending the lifespan of base metals. While pure nickel offers inherent toughness, nickel plating optimizes surface properties without compromising the structural integrity of the substrate.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Pure nickel exhibits superior recyclability and lower environmental toxicity compared to nickel plating, which often involves hazardous chemicals like cyanide and produces toxic waste during application and removal. Nickel plating processes consume significant energy and generate wastewater containing heavy metals, posing challenges for sustainable waste management and environmental protection. Choosing pure nickel reduces environmental footprint by minimizing chemical usage and facilitating closed-loop recycling, advancing sustainability goals in metal industries.
Choosing the Right Option: Decision Factors
Pure nickel offers superior corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and performance in harsh environments. Nickel plating provides a cost-effective surface coating that enhances appearance and protects underlying materials from oxidation and wear. Choosing between pure nickel and nickel plating depends on factors like application requirements, environmental exposure, budget constraints, and desired longevity.
Pure Nickel vs Nickel Plating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com