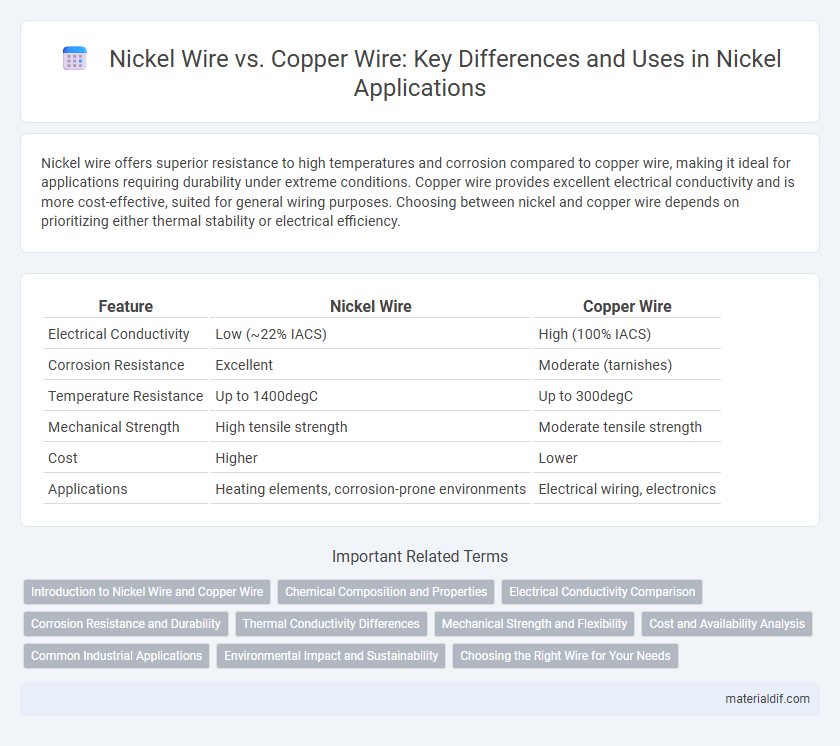
Nickel wire offers superior resistance to high temperatures and corrosion compared to copper wire, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under extreme conditions. Copper wire provides excellent electrical conductivity and is more cost-effective, suited for general wiring purposes. Choosing between nickel and copper wire depends on prioritizing either thermal stability or electrical efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nickel Wire | Copper Wire |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Low (~22% IACS) | High (100% IACS) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Moderate (tarnishes) |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1400degC | Up to 300degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Applications | Heating elements, corrosion-prone environments | Electrical wiring, electronics |
Introduction to Nickel Wire and Copper Wire
Nickel wire exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, high melting point, and strong tensile strength, making it ideal for high-temperature and industrial applications. Copper wire offers superior electrical conductivity and flexibility, widely utilized in electrical wiring and electronics. Both metals serve distinct purposes where nickel prioritizes durability and heat resistance, while copper emphasizes efficient electrical transmission.
Chemical Composition and Properties
Nickel wire consists primarily of nickel with a chemical composition typically exceeding 99% purity, providing excellent corrosion resistance and high melting point around 1455degC, while copper wire is mainly composed of copper with purity levels around 99.9%, known for superior electrical conductivity and a melting point of approximately 1085degC. Nickel wire exhibits superior resistance to oxidation and maintains mechanical strength at elevated temperatures, making it ideal for hostile environments, whereas copper wire's lower resistivity (around 1.68 uO*cm) offers optimal electrical performance in everyday electrical applications. The difference in chemical composition directly influences their physical properties, with nickel's ferromagnetic nature and copper's excellent ductility and thermal conductivity shaping their suitability for specific industrial uses.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Nickel wire exhibits lower electrical conductivity compared to copper wire, with copper having approximately 59.6 million siemens per meter (MS/m) while nickel offers around 14.3 MS/m. Due to copper's superior electrical conductivity, it is the preferred choice for most electrical wiring applications requiring efficient current flow. Nickel wire's conductivity is roughly 24% that of copper, making it more suitable for corrosion-resistant applications rather than primary conductive uses.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Nickel wire exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to copper wire due to its ability to withstand oxidation and chemical exposure, making it ideal for harsh environments. Its durability extends to high temperatures and mechanical stress, maintaining strength and conductivity over time. Copper wire, while highly conductive, is more prone to corrosion and degradation in adverse conditions, limiting its longevity in certain applications.
Thermal Conductivity Differences
Nickel wire exhibits significantly lower thermal conductivity compared to copper wire, with values around 90 W/m*K for nickel and approximately 400 W/m*K for copper, impacting heat dissipation efficiency. This difference makes copper wire more suitable for applications requiring rapid heat transfer and effective cooling, such as electrical wiring and heat exchangers. Nickel wire, despite its lower thermal conductivity, offers superior oxidation resistance and mechanical strength at high temperatures, making it ideal for specialized industrial and high-temperature environments.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Nickel wire exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to copper wire, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under stress. Despite being less flexible than copper, nickel wire maintains excellent resistance to deformation and fatigue over prolonged use. Its combination of strength and moderate flexibility supports its use in high-temperature environments and precision electrical components.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Nickel wire generally has a higher cost than copper wire due to its more complex extraction and processing methods, making it less economically favorable for large-scale applications. Availability of copper wire is significantly greater, as copper is more abundant and widely produced globally, resulting in a more competitive market price. While nickel wire offers superior corrosion resistance and strength, its limited availability and higher price often restrict its use to specialized applications where these properties justify the cost.
Common Industrial Applications
Nickel wire is widely used in high-temperature and corrosion-resistant applications such as heating elements, thermocouples, and aerospace components, where its durability and oxidation resistance outperform copper. Copper wire, favored for its excellent electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness, predominates in electrical wiring, motor windings, and telecommunications. Industrial sectors prioritize nickel wire in environments requiring strength and chemical stability, while copper wire dominates in standard electrical and electronic applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nickel wire demonstrates superior corrosion resistance and longer lifespan compared to copper wire, reducing frequent replacements and electronic waste. The extraction and refining of nickel involve higher energy consumption but advancements in recycling technologies mitigate its environmental footprint. Copper wire, while highly conductive, often requires more intensive mining and processing, posing greater ecological risks and resource depletion.
Choosing the Right Wire for Your Needs
Nickel wire offers superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability compared to copper wire, making it ideal for applications in harsh environments or high-heat conditions. Copper wire excels in electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness, suitable for general electrical wiring and electronics requiring efficient power transmission. Selecting the right wire depends on balancing conductivity needs against environmental durability and budget constraints specific to your project.
Nickel Wire vs Copper Wire Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com