Gypsum board offers superior durability and faster installation compared to Plaster of Paris, making it ideal for modern construction projects. Plaster of Paris provides a smoother finish and is preferred for detailed decorative work and repairs. Both materials are fire-resistant, but gypsum board also offers better sound insulation properties.
Table of Comparison
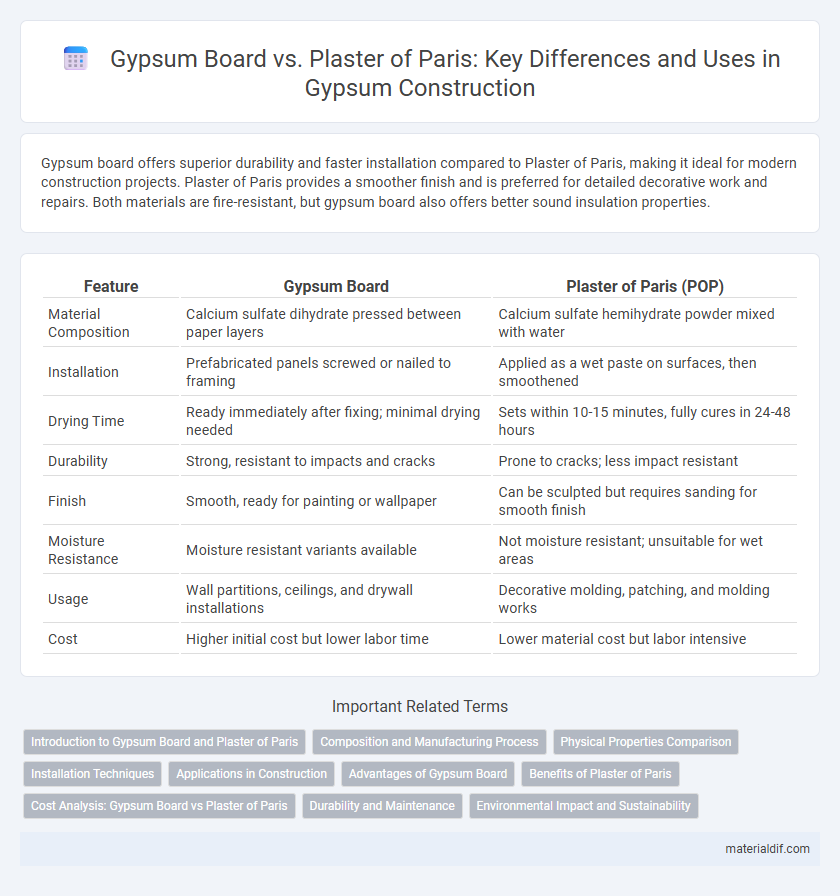
| Feature | Gypsum Board | Plaster of Paris (POP) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Calcium sulfate dihydrate pressed between paper layers | Calcium sulfate hemihydrate powder mixed with water |
| Installation | Prefabricated panels screwed or nailed to framing | Applied as a wet paste on surfaces, then smoothened |
| Drying Time | Ready immediately after fixing; minimal drying needed | Sets within 10-15 minutes, fully cures in 24-48 hours |
| Durability | Strong, resistant to impacts and cracks | Prone to cracks; less impact resistant |
| Finish | Smooth, ready for painting or wallpaper | Can be sculpted but requires sanding for smooth finish |
| Moisture Resistance | Moisture resistant variants available | Not moisture resistant; unsuitable for wet areas |
| Usage | Wall partitions, ceilings, and drywall installations | Decorative molding, patching, and molding works |
| Cost | Higher initial cost but lower labor time | Lower material cost but labor intensive |
Introduction to Gypsum Board and Plaster of Paris
Gypsum board, also known as drywall or gypsum panel, consists of a core of gypsum plaster pressed between two thick sheets of paper, offering a lightweight, fire-resistant, and easy-to-install solution for interior walls and ceilings. Plaster of Paris (POP) is a quick-setting material derived from heated gypsum, primarily used for creating smooth wall finishes, decorative moldings, and casting detailed shapes. While gypsum board provides structural support and speed in construction, POP is favored for fine surface finishing and artistic detailing in interior design.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Gypsum board is primarily composed of a core of natural or synthetic gypsum plaster sandwiched between two layers of paper, manufactured through a continuous process of mixing, forming, and drying on a production line. Plaster of Paris, derived from heating natural gypsum to around 150degC to remove water content, consists mainly of calcium sulfate hemihydrate and is typically mixed with water for manual application. The manufacturing process of gypsum board emphasizes precise control of moisture and curing for uniform panels, whereas Plaster of Paris is produced through calcination and used as a quick-setting powder for molding and casting.
Physical Properties Comparison
Gypsum board exhibits superior dimensional stability and resistance to cracking compared to Plaster of Paris, making it ideal for long-term wall applications. Its higher tensile strength and flexibility reduce the risk of damage from structural movements, while Plaster of Paris tends to be more brittle and prone to shrinkage. Moreover, gypsum board offers better fire resistance and moisture control, enhancing durability in diverse environmental conditions.
Installation Techniques
Gypsum board installation involves securing large, pre-manufactured panels to wall studs using screws or nails, followed by taping and joint compound application to create smooth surfaces. Plaster of Paris requires a more labor-intensive method, where a wet plaster mixture is applied in layers directly onto lath or existing walls, then carefully smoothed and allowed to set. Gypsum board offers faster, cleaner installation with less drying time, while Plaster of Paris provides greater customization but demands skilled craftsmanship.
Applications in Construction
Gypsum board is widely used in interior wall and ceiling applications for its ease of installation, fire resistance, and soundproofing qualities, making it ideal for residential and commercial buildings. Plaster of Paris is primarily applied as a finishing material for smooth wall surfaces, decorative moldings, and intricate architectural details due to its fast setting time and fine texture. Both materials complement each other by balancing structural efficiency and aesthetic enhancement in modern construction projects.
Advantages of Gypsum Board
Gypsum board offers superior fire resistance and enhanced durability compared to Plaster of Paris, making it ideal for modern construction needs. Its lightweight nature allows for faster installation and reduced labor costs, while also providing better sound insulation properties. The moisture-resistant variants of gypsum board add value by preventing mold and mildew, a significant advantage over traditional plaster.
Benefits of Plaster of Paris
Plaster of Paris offers superior moldability, allowing for intricate decorative finishes and architectural detailing that gypsum boards cannot achieve. Its quick-setting properties enable faster application and curing times, making it ideal for emergency repairs and time-sensitive projects. Plaster of Paris also provides excellent fire resistance and durability, enhancing the longevity and safety of interior surfaces.
Cost Analysis: Gypsum Board vs Plaster of Paris
Gypsum board typically costs more upfront than Plaster of Paris but offers savings through faster installation and reduced labor expenses. Plaster of Paris materials are cheaper, yet drying time and complexity increase overall project costs. Evaluating total expenditure, including labor and time, often favors gypsum board for large-scale or commercial projects.
Durability and Maintenance
Gypsum board offers superior durability compared to Plaster of Paris due to its moisture resistance and impact strength, making it ideal for high-traffic or humid areas. Maintenance of gypsum board is generally easier, as it resists cracking and can be repaired with minimal effort, while Plaster of Paris tends to be more fragile and vulnerable to wear over time. The enhanced longevity and lower upkeep requirements of gypsum board contribute to its cost-effectiveness in both residential and commercial construction.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gypsum board production generates less waste and consumes less water compared to Plaster of Paris, making it a more environmentally sustainable building material. The recyclable nature of gypsum board contributes to reduced landfill accumulation, whereas Plaster of Paris, once set, is less recyclable and more prone to environmental degradation. Gypsum board's lower carbon footprint and energy-efficient manufacturing process further enhance its sustainability credentials in construction projects.
Gypsum board vs Plaster of Paris Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com